Causes of medulloblastoma
Most cases of the disease are considered sporadic. However, scientists have been able to identify several hereditary diseases that significantly increase the risk of medulloblastoma. Such diseases include Gorlin syndrome, Turcot syndrome, Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome, and blue nevus syndrome. The exact causes of the appearance of a tumor in the central nervous system are still being studied by scientists. Today, doctors can speak with confidence only about risk factors for the occurrence of pathology:
- effects on the body of varnishes, carcinogens, household chemicals, paints;
- age (the disease is often diagnosed in children under 10 years of age);
- genome-damaged cells;
- viral infections (HPV, cytomegalovirus, herpes infections, infectious mononucleosis);
- burdened heredity.
Classification of medulloblastomas
According to histological structure, the following types of medulloblastoma are distinguished:
- a tumor containing muscle fibers;
- a tumor that forms from neuroepithelial cells containing melanin;
- the most benign tumor containing fat cells.
To determine the clinical prognosis for each patient in neurology, the modified Chang classification is used. It is based on criteria such as the degree of infiltration, metastasis, and the size of medulloblastoma. As for the size of the tumor, it is almost always about 3 centimeters.
- T1 - neoplasm, which is localized within the roof of the IV ventricle and the cerebellar vermis;
- T2 - a tumor that can grow deep into neighboring structures and also partially fill the fourth ventricle of the brain;
- T3A is a neoplasm that grows into the area of the cerebral aqueduct or into the foramina of Luschka and Magendie, which provokes the appearance of hydrocephalus;
- T3B - tumor growing into the brain stem;
- T4 - a tumor that provokes hydrocephalus due to blocking the outflow pathways of cerebrospinal fluid, can grow into the brain stem;
- M0 - neoplasm that is not accompanied by metastasis;
- M1 - during laboratory tests, tumor cells are detected in the cerebrospinal fluid;
- M2 - metastases appear in the subarachnoid space;
- M3 - the appearance of metastases in the subarachnoid space;
- M4 - metastases that have spread beyond the central nervous system.
Causes and provoking factors
Basically, such neoplasms are irregular in nature. An exception to this rule are people suffering from hereditary diseases, which significantly increase the risk of developing malignant processes in the body. This is possible if the patient has Turcot, Gorbin and others syndrome.
The exact cause of the development of the pathological condition could not be determined. Scientists identify only certain factors that increase the risk of tumor formation. The disease can occur under the influence of:
- early age of the patient and the associated immaturity of the body;
- ionizing radiation;
- viral diseases that contribute to damage to the genome of cells. These are herpes, cytomegalovirus, human papillomavirus and others;
- hereditary predisposition;
- carcinogenic substances found in food and household chemicals.
The tumor gradually grows into the brain stem and affects the cranial nerves. This condition is typical for advanced stages of development of the pathological process.
Symptoms of medulloblastoma
The symptoms of the disease are determined by several factors: the localization of the tumor, the severity of the cerebral syndrome, the location of metastases and their extent. In 80% of cases, medulloblastoma is localized in the cerebellum, which provokes the development of cerebellar ataxia. This pathology is characterized by the formation of a cerebellar gait - the patient is forced to walk with his legs apart and balancing with his hands so as not to accidentally fall.
Since the patient's coordination of movements is impaired, he falls very often, especially when making turns. If the tumor begins to deepen into the brain stem, the patient’s well-being deteriorates sharply, as geodynamic and respiratory disorders begin to appear. The results of assessing the patient’s neurological status show gaze paresis, suppression of the pharyngeal reflex, convergence disorder, and spontaneous nystagmus. If the spinal cord joins the pathological process, paralysis of the limbs and sensory impairment may occur.
Patients with medulloblastoma also experience general cerebral symptoms: increased irritability, psychomotor agitation, disorientation in time, place and self. The patient complains of severe headache, vomiting, nausea. In pediatric patients, the symptoms of the disease may not appear immediately, since in children the size of the skull is enlarged, the blood vessels are elastic, and the brain is plastic. Therefore, the diagnosis is usually made very late - only after medulloblastoma has occupied the fourth ventricle of the brain, the worm, and has grown into the bulbar structures.
If medulloblastoma grows and metastases appear, the patient's condition begins to rapidly deteriorate. Unlike other types of brain tumors, medulloblastoma is capable of metastasizing beyond the central nervous system. Namely, patients are found to have metastases in the lungs, bones and liver. The most common and dangerous complication of the disease is hydrocephalus. It appears due to blockage of the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid by a neoplasm, which rapidly increases in size. Clinical manifestations of this pathology will be:
- headache;
- downward displacement of the eyeballs;
- strabismus;
- nystagmus;
- nausea.
What's happened
Medulloblastoma is a neuroectodermal tumor located in the cerebellar vermis. Its growth into the 4th ventricle of the brain is also noted.
Against the background of the pathological process, the cerebrospinal fluid outflow is blocked, and the cerebrospinal fluid circulation pathways are blocked. With this condition, various complications can arise, which significantly worsens the prognosis for life.
During histological examination, it is possible to establish the presence of a large accumulation of cellular structures that are round in shape and poorly differentiated.
According to statistics, medulloblastoma in children is diagnosed in 30 percent of all cases of malignant lesions. Boys are more susceptible to the disease. In girls, the disease is detected half as often. The peak incidence usually occurs between the ages of 5 and 10 years.
Diagnosis of medulloblastoma
To make a diagnosis, the doctor uses the results of comprehensive ophthalmological, neurological and liquorological examinations. Additionally, laboratory tests may also be required: general analysis and biochemical blood tests, general urine analysis.
To identify intracranial hypertension in a patient, the doctor prescribes an ophthalmoscopy. Diagnosis of the disease in children involves the use of neurosonography. To assess the process of metastasis, PET (positron emission tomography) is prescribed. Additionally, a biopsy, determination of tumor markers in the blood, and consultation with a neurosurgeon may be prescribed.
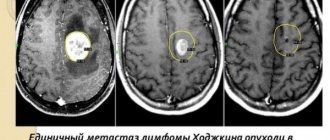
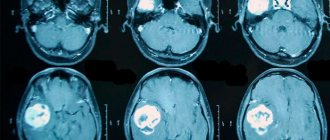
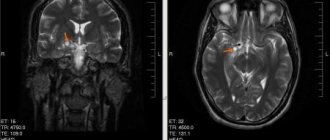
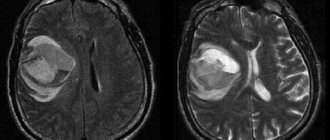
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are rightfully considered the most reliable methods for diagnosing neoplasms. Both of these diagnostic techniques can detect even the most minor changes in the structure of the patient’s brain.
- CT scan. The results of this study make it possible to identify a tumor that looks like oval or round voluminous neoplasms that heterogeneously accumulate a contrast agent. The doctor also notices that the tumors have displaced the fourth ventricle ventrally. During the examination, it is possible to identify microcalcifications and cysts.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. If the patient has medulloblastoma, this technique is performed in order to identify metastases. During the study, the patient is injected with a contrast agent, which accumulates heterogeneously in different parts of the medulloblastoma. Thanks to the introduction of a contrast agent, it is possible to accurately detect tumor metastasis in the soft meninges of the brain and spinal cord.
Treatment of medulloblastoma
Medulloblastoma is a life-threatening disease for the patient, the treatment of which must be undertaken in a timely manner. To remove the tumor and its consequences, a whole range of techniques is used: surgical treatment, radiation therapy, chemotherapy.
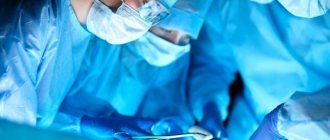
- Surgery. To remove a midline tumor, the doctor will need to open the posterior cranial fossa. During this operation, the semi-arches of the first and second cervical vertebrae are also removed. However, if the tumor has managed to penetrate the brain stem or is well attached to the fourth ventricle, it is almost impossible to completely remove it. In most cases, after elimination of medulloblastoma, a ventriculo-peritoneal shunt will be required. The risk of metastases after the procedure is about 10-20%.
- Radiation therapy. After eliminating the tumor, doctors prescribe radiation therapy. The most optimal doses are 10-15 Gy to the area of the spinal cord with metastases and 35-40 Gy to the entire craniospinal region. The duration of radiation therapy is 6-7 weeks. This treatment method can cause side effects: inhibition of hematopoiesis, damage to the skin and mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Chemotherapy. Prescribed after surgery. The most effective drugs are: nitrosourea, vincristine, procarbazine. The drugs used in chemotherapy have a toxic effect not only on the tumor, but also on healthy organs. As a result, complications such as allergic reactions and toxic damage to the liver, gastrointestinal tract, urinary system, and heart arise.
- Measles virus. An innovative method of treating medulloblastoma, which is currently being studied by scientists, is the use of a blood virus that has been subjected to genetic modification. Experiments by scientists have confirmed that this virus kills malignant cells in 72 hours.
- Diets and regimen. Complex treatment of the disease necessarily involves normalization of the regimen and a special diet. Patients are advised to eat frequently and in small portions, and eat more citrus fruits. It must be remembered that during illness, the taste preferences of patients can change greatly, but they should definitely be taken into account when preparing food.
- Rehabilitation. After completion of treatment, patients must undergo rehabilitation, the program of which is selected individually in all cases. The patient is also recommended to be regularly monitored by a doctor in order to promptly detect tumor recurrence.
Forecast and prevention of medulloblastoma
The prognosis for patients with medulloblastoma is unfavorable due to the high risk of death and disability. Timely detection, accurate diagnosis and selection of an appropriate method of surgical treatment will increase the chances of a favorable outcome of the disease.
In neurology, it is customary to distinguish two prognostic groups of patients with medulloblastoma - low and high risk. Patients are included in the low-risk group based on the following indicators: tumors of type T1 and T2, absence of metastasis, age over three years, total tumor removal. The high-risk group is formed on the basis of such indicators as age under three years, metastasis, tumors of type T3 and T4, subtotal removal of medulloblastoma.
About 75% of low-risk patients can survive five years after surgery. Only 35% of high-risk patients can do this. Doctors give the worst prognosis to patients whose tumor relapses after surgery. Their average life expectancy after the appearance of a new tumor is about 13-18 months. There is no specific prevention for medulloblastoma.
Rehabilitation after surgery
The first part of the postoperative period takes place in the intensive care unit. There, patients undergoing medulloblastoma surgery undergo hourly neurological testing, vital sign monitoring, and laboratory tests as needed. Within 48-72 hours, doctors perform an MRI. The procedure is necessary to assess the extent of tumor removal. After the operation, an oncologist is also consulted. It is necessary for planning postoperative chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy.
In addition, in the postoperative period, patients may experience neck pain and symptoms of ataxia. The patient may also experience headache, nausea, or vomiting, which is a consequence of anesthesia and/or irritation of the area located in the floor of the fourth ventricle. Otherwise, recovery measures after surgery to remove medulloblastoma are the same as for other neurosurgical interventions. Rehabilitation is aimed at improving coordination, cognitive skills, normalizing blood pressure, as well as preventing complications in the cardiovascular and immune systems.