All tumor formations that affect certain organs and tissues of the human body are divided into malignant and benign. The main signs characterizing benign neoplasms:
- the tumor consists of mature cells;
- grows slowly;
- has clear boundaries;
- does not grow into surrounding tissues.
The benign nature of the tumor does not mean that it is harmless, especially if it is located in a limited intracranial space. All tumor processes in the brain, including benign ones, due to compression of vital cerebral structures, pose a serious threat to human health and life. Using the CyberKnife stereotactic unit, doctors at the Radiation Therapy Center of the OncoStop project remove tumors of any location.
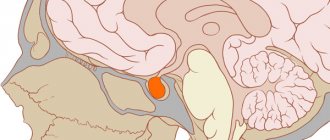
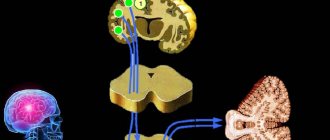
Pituitary adenomas
They make up about 10% of primary brain tumors and are most often found in the anterior third of the gland. They can appear at any age, but usually occur in older people. Women of childbearing age develop more often than men of the same age group. There are hormonally active (secreting) and hormonally inactive pituitary adenomas.
Pituitary adenoma
Most formations are hormonally active. In turn, they are classified according to the type of hormone produced, an excess of which in the body leads to the appearance of characteristic symptoms.
Causes
The exact cause of brain cancer has not been identified. It is known that the disease occurs under the influence of several factors. These include head injuries and previous brain surgery.
Work in chemical production and frequent examination of the head with X-rays can lead to cancer. The influence of electromagnetic fields emitted by a telephone is being studied.
Factors that increase the likelihood of developing the disease include age over 50-55 years, the presence of tumors and close relatives. The disease is affected by sudden hormonal changes - pregnancy, menopause.
Meningiomas
They grow not from brain tissue, but from the soft membranes covering it (meninx), which is why they got their name. They make up about a third of all primary neoplasms. Most often observed in women, starting from middle age (2 times more often than in men). The incidence rate increases after 60 years. They are rare in children. The typical location is in the upper regions, but can also form at the base of the skull. They usually grow inward, causing compression of adjacent parts of the brain. Sometimes they grow outward, which is accompanied by thickening of the cranial bones in the problem area. May contain calcifications, fluid-filled cavities (cysts), and vascular nodes.
Why does it appear
There are no clear reasons for the formation of tumor formations. There are certain factors that can have a catalyzing effect on tumor development. But in one case it will work, in another - the person will live his whole life without developing pathology.
To prevent brain tumors, it is very important to avoid prolonged overheating and exposure to direct sunlight.
In hot weather, be sure to wear a hat and drink enough clean water.If a brain tumor is detected, visiting the bathhouse, sauna, taking vitamin supplements and medications that improve cerebral circulation are strictly prohibited.
Neurologist, reflexologist, hirudotherapist
Kislitsyna Ekaterina Nikolaevna
10 years of experience
Hereditary predisposition
This fact is due to the fact that under the influence of unfavorable factors, genes that are passed on to descendants can be modified (improved or degraded). Such an oncogene can appear even after several generations if a certain impact occurs on it. Therefore, if there was a negative impact on the body now, then the consequences may appear in the future in descendants.
Radiation or chemical effects on the body
This may be an unfavorable region of residence with increased radiation levels or professional activities related to working with lead, mercury, or oil
Consequences of past viral and bacteriological diseases
Exposure to the body of bacteria and viruses, especially the brain and central nervous system, can trigger the formation of tumor formation.
Schwannomas
Develop from Schwann cells of the auditory nerve, also called the 8th cranial, acoustic or vestibulocochlear nerve.
Places of formation of schwannomas
Usually located between the cerebellum and the pons, in the region of the posterior fossa. They grow very slowly, are quite rare (no more than 8%), and develop in middle age. The risk of the disease is twice as high in women.
Choroid plexus papillomas
They arise from mutated cells of the choroid plexuses, which are part of the structure of the membranes lining the ventricles of the brain and producing cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Typically diagnosed in children and young people.
Traditional sites of formation of choroid plexus papillomas
In children with brain tumors under the age of one year, choroid plexus papillomas range from 10 to 20%, from 1 year to 1 year – 2-4%. At the same time, depending on age, the localization of the lesion also differs: the older the patient, the lower the tumor is located.
Complications
When using surgery, the risk of complications cannot be excluded. The most common consequences are:
- Significant decrease in visual acuity.
- Decreased performance.
- Difficulty speaking.
- Convulsive syndrome.
In the postoperative period, patients need to lead a healthy, calm lifestyle, follow doctors’ recommendations, undergo regular examinations, and avoid physical and mental fatigue, stress, and anxiety. The duration of the recovery period depends on the volume of intervention. The larger the tumor and the closer it is to vital brain centers, the longer it will take for a person to recover.
Patients with a tumor should not self-medicate. Traditional methods, medications prescribed to yourself without consulting a doctor can aggravate the course of the disease, push it to further development and develop into oncology. The prognosis for most patients with a benign tumor is favorable. The main thing is to seek medical help in a timely manner.
Cysts
Although they are considered benign, they can cause serious problems when located in structures that control vital body functions.
Cysts can appear in a variety of areas of the brain
They are varied, the most common are arachnoid (filled with fluid), colloid (filled with a thick iron-like substance), dermoid and epidermoid (filled with soft tissue) cysts.
Reviews
Sergey, 38 years old, Penza
I went to the doctor with complaints of constant dizziness, migraines and general weakness. I was sent for a comprehensive examination to a neurologist, and even had an MRI. Meningioma was discovered. It was small in size and located very well. Therefore, doctors decided to remove it. The operation went well, although the recovery period was long. I feel good now.
Marina, 41 years old, Orsk
I noticed constant disruptions in the sexual cycle, so I decided to go to the gynecologist. The doctor examined me and recommended blood tests and an ultrasound. Based on the results, an MRI was required because a tumor of the pituitary gland was suspected. The study confirmed the doctors’ fears – prolactinoma was found. The doctor prescribed medications that helped the tumor shrink in size. The problem is no longer a concern.
Symptoms of a benign brain tumor
It is necessary to immediately make a reservation: it is impossible to determine by any external signs that a benign and not a malignant neoplasm has appeared in the brain. Moreover, certain disturbances in well-being can only cause the doctor to suspect a tumor process. Only diagnostics can confirm or refute these suspicions. At the same time, based on the patient’s complaints, the neurologist makes preliminary conclusions and draws up an examination plan.
“Even a benign tumor that grows in the head is potentially dangerous,” says Robert Fenstermaker, MD, chairman of the department of neurosurgery at Roswell Park Cancer Center (USA). “The space inside the skull is not unlimited, and even if a brain tumor is benign and grows slowly, it will eventually begin to compress the brain, symptoms will develop and this can be life-threatening.”
Benign brain tumors manifest themselves in a variety of symptoms, the nature of which is primarily determined depending on the location of the lesion and its size.
- An extremely slowly growing chondroma may not show itself in any way for a long time. When the tumor grows in size, it begins to compress nearby structures, which most often leads to headaches, hearing impairment, and visual hallucinations.
- With choroid plexus papillomas, general cerebral symptoms are observed, including characteristic headaches and other signs of increased intracranial pressure.
- It is impossible to identify any general symptoms for cysts due to the wide variety of neoplasms of this type and the possibility of their appearance in a variety of places.
- Ependiomas are characterized by irritability, vomiting, insomnia, and headache. In children under one year of age, one of the first symptoms is often an abnormal increase in head size.
- The symptoms of benign adenoma and malignant adenocarcinoma of the pituitary gland are identical, therefore, when making a diagnosis, other features are taken into account, including the absence of metastases and growth into neighboring sections, scan data, etc. Among the most common manifestations are headache, behavioral disturbances and visual disturbances. Signs of this type of hormone-producing tumors depend on the type of hormone produced.
- Meningiomas grow slowly and can become large before they begin to interfere with normal brain function. Symptoms depend on the location of the tumor. Most often, patients complain of headache, weakness in the arm or leg. Seizures, personality changes, and vision problems may also occur.
- In the vast majority of cases, lipomas do not cause any health problems.
- Schwannomas are characterized by unilateral hearing loss and noise or ringing in the ear. Less often, patients complain of dizziness. If the process affects the 7th cranial nerve, its paralysis may develop. Sometimes there is difficulty swallowing, changes in taste, unsteady gait, and disturbances in eye movements.
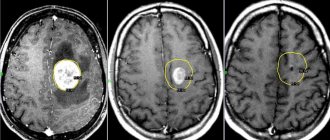
Diagnostics
If a benign tumor in the head is suspected, the neurologist will prescribe a series of diagnostic procedures and examinations. It will be necessary to evaluate visual functions, the condition of the fundus, vestibular apparatus, sense of smell, taste and hearing, and measure intracranial pressure.
The main methods for detecting tumors in the brain include electroencephalography, radiography, CT, MRI, laboratory analysis of cerebrospinal fluid and blood. An integrated approach helps to most accurately determine the type, location and condition of the tumor.
Treatment of benign brain tumor: basic principles and choice of method
In some cases, the doctor may choose active surveillance. This applies to patients with arachnoid cysts and meningiomas, as well as lipomas, which do not cause significant health problems and, as a rule, are detected by chance or during preventive cancer screening.
If a patient is diagnosed with a benign brain tumor that is “unfortunately” located, interferes with the quality of life for other reasons, or has a high risk of malignancy, treatment is aimed at removing the tumor (surgery) or destroying it using modern radiosurgical methods.
For example, some meningiomas can be removed by traditional surgery, while others are inoperable. In the latter case, the tumor can be destroyed using CyberKnife, Gamma Knife, TrueBeam installations. Depending on the characteristics of the tumor, tomotherapy or proton therapy may also be the optimal treatment method.
Operable colloid, epidermoid and dermoid cysts are most often removed in the traditional way or using endoscopic or microsurgical technologies. If indicated, additional antibacterial drug therapy may be prescribed. Sometimes cyst removal is complicated, impossible, or only partially possible.
Radical removal of chondroma, choroidal papilloma, ependyoma, pituitary adenoma can be carried out surgically or radiosurgically.
When treating patients with schwannomas, microsurgical methods or stereotactic radiosurgery are usually used. According to indications, medication, hormonal and radiation therapy are additionally prescribed.
Leading neurosurgeons have high hopes for intraoperative fluorescent control for the purpose of total resection of tumors, in particular pituitary adenomas, since incomplete removal of neoplasm leads to relapses in 20% of patients. But although pituitary adenomas are rarely malignant, they can cause serious problems by compressing nearby areas of the brain, which can lead to Cushing's disease, gigantism, blindness and death.
At the medical school. Perelman University of Pennsylvania developed the first organ-specific marker OTL38, which consists of two parts: folate and an infrared-luminescent dye. Since folic acid is actively used for the development and growth of neoplasms, they are characterized by a high content of folate receptors on the cell surface (which is sometimes more than 20 times higher than the normal level). By binding to receptors, OTL38 causes luminescence of the affected tissues, making it possible to accurately identify the boundaries of the tumor and completely remove it.
As noted by Yu.K. Lee, MD, PhD, professor in the Department of Neurosurgery at the University of Pennsylvania, said, “This study heralds a new era in personalized tumor surgery. Surgeons can now see the molecular characteristics of a patient’s tumors, not just light absorption or reflectivity.”
If you need a second opinion to clarify your diagnosis or treatment plan, send us an application and documents for consultation, or schedule an in-person consultation by phone.
+7 499 490-24-13
Expert opinion
Stages of tumor growth
- Visiting a doctor if the initial symptoms of the disease occur: pain in the head, nausea and vomiting, change in gait, etc. This will allow you to perform a surgical operation and remove the tumor partially or completely.
- Monitoring when visiting a doctor is less positive. The affected cell structure begins to actively divide and put pressure on nearby tissues. At this stage, surgery may no longer be appropriate. The patient's age and personal characteristics of his body also matter. After 65 years of age, a patient who has undergone surgery, chemotherapy and radiation treatment has a greatly reduced chance of survival.
- A neoplasm at the third stage of development is very often inoperable. The patient can live with a tumor at this stage for no more than 2 years. The development of education proceeds quickly, the patient loses vitality in a short time and is rarely able to fight the disease.
- The likelihood of recovery at this stage is very low. Here, much depends on the support of relatives and friends, and the patient’s desire to live. On average, at this stage, with metastases that have already affected other organs in the body, life is calculated in several months, very rarely in years. Only every fifth person out of a hundred can overcome this line.
With timely detection, timely treatment and competently performed surgery, the patient can live for many more decades. However, unfortunately, even the use of modern treatment methods does not guarantee a 100% cure.
Despite this, the patient should not despair. The terrible diagnosis, of course, will turn his life 180°, but this is not a reason to stop fighting for life. In the history of medicine there are many examples of how illness receded before a person’s powerful will to live.