Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain has become widespread due to its safety and accuracy. In the article you will learn everything about how MRI of the brain is done, features and contraindications to the procedure and the results of its implementation.
The study is carried out using a special device - a magnetic tomograph, which is a huge magnet. The procedure is absolutely painless and fairly quick. The patient is placed in the tube of the device, which takes a series of photographs of the organ being examined in three projections. Next, the images are sent to a computer screen, where they are deciphered by a doctor.
In what cases is an MRI of the brain done?
Tomography can be either the main diagnostic method or an additional one. Indications for the procedure are the following conditions and diseases:
- neoplasms;
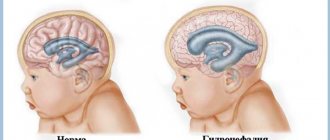
- developmental anomalies;
- injury;
- stroke;
- intense headache of unknown origin;
- pathology of the pituitary gland;
- vascular abnormalities;
- multiple sclerosis and other diseases of the nervous system;
- dementia;
- epilepsy;
For frequent or persistent headaches, MRI is used if:
- the attacks became more frequent and more severe;
- coordination of movements is impaired;
- there is a connection between headaches and coughing and sneezing;
- there is an oncological disease of another localization;
- attacks occur at night, interrupting sleep.
Tomographic scan of the brain
Magnetic resonance imaging is also successfully used to diagnose the following pathologies:
- Acute cerebrovascular accident. This can be an ischemic attack, ischemic stroke, hemorrhagic stroke, post-traumatic hemorrhage.
- Intracranial space-occupying formations. Tomography is the main method for:
- primary diagnosis of extra- and intracerebral tumors;
- differential diagnosis of tumors, abscesses and other pathologies;
- assessing the success of tumor removal, postoperative complications, and continued tumor growth.
- Metastatic lesions of the central nervous system. For tumors with a high frequency of metastatic brain damage (lung cancer, breast cancer, melanoma and others), magnetic resonance scanning is included in the mandatory examination protocol.
- Multiple sclerosis and other diseases of the white matter of the brain. MRI is the most accurate diagnostic method in this case. The use of intravenous contrast allows one to visualize lesions, determine their size, and monitor the progress of treatment.
- Dementia and memory disorders. Tomography is necessary for:
- exclusion of possible tumors, hemorrhages;
- determining the duration and nature of the process;
- assessing the success of treatment.
- Epilepsy. MRI of the brain is a mandatory examination procedure for patients suffering from epilepsy. It helps to exclude tumors, pathologies of the brain and blood vessels, the consequences of injuries, and inflammatory processes. To visualize minor structural changes, images of thin sections (1–3 mm) are taken using additional signal amplification modes (according to the epileptic protocol). The second most common possible cause of epilepsy is benign tumors. Detecting them on MRI gives the patient a chance for recovery with surgery.
- Pathology of the pituitary gland. The main examination method is tomography with intravenous contrast.
Harm and danger of MRI procedure
Important ! Experts in the field of radiography have now come to the conclusion that magnetic resonance imaging is absolutely safe. According to current practice, there have not been a single case of side effects occurring after MRI.
This examination using a tomograph can be prescribed for both young children and adults. The only exceptions can be patients with installed prosthetic implants containing paramagnetic elements, and pregnant women in the early stages.
There are only a few potential risks with an MRI examination:
- in the presence of paramagnetic implants - if you do not warn before tomography, unpleasant consequences may occur. Since the method is based on magnetic waves, it is possible to shift metal fillings, implants or prostheses. It is not recommended to perform tomography with installed hearing aids and pacemakers;
− in case of claustrophobia - a psychological moment that stops many patients who have a fear of closed spaces;
− early stage of pregnancy - many experts are of the opinion that examination is not recommended for pregnant women and exposure to magnetic waves can harm the fetus.
Separately, it is worth noting that the use of a contrast agent can cause an allergic reaction and some discomfort. But before using contrast, testing is carried out in advance, which immediately shows the manifestation of such reactions.
Note! The harm from tomography does not exceed the values that come from a mobile phone and computers, as well as other devices that are used constantly. Patient reviews also confirm the absence of any complications after magnetic resonance imaging.
If your doctor prescribes magnetic resonance imaging, you can safely undergo the examination without fear for your own health or the health of your children and loved ones, since preventing diseases at the earliest stages increases the chances of positive treatment.
You can learn more about the brain tomography procedure by watching this video:
MRI of the brain, how the procedure works
No preliminary preparation is required before the study. You must come to the procedure in loose clothing without metal accessories. Considering that magnetic fields damage credit cards, flash cards and mechanical watches, they need to be laid out in advance. It is advisable not to use cosmetics, as they may contain metal particles.
The patient is placed on a special movable table that slides inside a magnet. It is very important that the person lies still when the image is taken. The clicks that the magnet makes help you understand that shooting has begun.
The computer on which the images are received is located in the next office.
For greater comfort, the patient is offered headphones with pleasant music. The scanner is air conditioned and well lit.
How to prepare for an MRI with contrast?
Proper preparation for MRI reduces the risk of discomfort during the administration of a contrast agent. It is recommended to refrain from eating and drinking at least 3-4 hours before the scan. This will relieve the feeling of nausea and vomiting. Read more about preparing for an MRI.
Patients with chronic kidney disease or a tendency to allergies should warn their doctor - it may be necessary to select a safe contrast agent.
Complete information regarding MRI of the brain (addresses of clinics, cost, preparation, etc.) is available around the clock on our website.
Modern tomographs: types and characteristics
The level of magnetic field voltage is the main indicator for magnetic resonance imaging scanners. According to this parameter they are divided into:
- low-field – up to 0.5 Tesla;
- mid-field – from 0.5 to 0.9 T;
- high-field – from 1.0 to 1.5 T;
- ultra-high field – 3 Tesla.
To obtain high-quality images, the device must have a power of at least 1.0 Tesla.
Low-field devices are cheaper, they have fewer restrictions on metal in the body, and for some studies their power will be sufficient. But for brain diseases, particularly accurate diagnostics are needed, so it is recommended to undergo examination using high-field devices.
High-field tomograph Philips Intera 1.5 Tesla
The DiMagnit clinic has a high-field tomograph generating a magnetic field of 1.5 Tesla. It has all the latest options built into it, allowing the radiologist to adjust the contrast of the image during the examination, while immediately seeing the final result.
Philips Intera 1.5 T tomograph is the gold standard and a very high-quality device.
There are scanners with a power higher than 1.5 Tesla, but their use is more justified for research purposes. These devices require very strict technical safety regulations. The price of the procedure increases accordingly.
However, the diagnostic benefit does not correlate with the increased cost.
What is MRI?
MRI is the latest research method that is capable of recognizing the slightest changes in the structure of the organs being studied, identifying not only pathology in the structure, but also identifying any disease at the very beginning of its development.
The MRI procedure is carried out based on the operation of a magnet, which is the main part of the tomograph apparatus. The operation of the device is based on a physical phenomenon called magnetic resonance. Any substance under study is distinguished by its characteristic structure, which ensures the receipt of signals as a result of magnetic resonance.
The amplitude of the transmitted signals is a quantitative characteristic of the analysis of information that is obtained as a result of scanning. Each area of the organ being examined has its own value, which indicates the frequency of nuclear magnetic resonance. It is converted into a computer tomogram, which records layer-by-layer sections of the structure of the organ being studied.
The operation of the device is based on the action of magnetic fields that do not pose a threat to human health. The innovative method allows you to obtain several images in different projections by scanning. All high-resolution images are necessarily recorded on electronic media. After carefully studying them, the doctor gives a conclusion.
Possible limitations for MRI
The procedure is contraindicated in the following cases:
- the patient’s weight is more than 130 kg, the abdominal circumference at the maximum protruding points is more than 150 cm;
- the presence of ferromagnetic implants, foreign bodies, hemostatic clips;
- installed non-removable electronic devices (insulin pump, pacemaker, hearing aid and others);
- severe claustrophobia, unstable mental state;
- first trimester of pregnancy;
- less than 5 years of age.
It is safe to perform tomography in the presence of non-magnetic (for example, titanium) medical implants.
Metal teeth, prosthetic hip joints and spinal fixation devices do not pose a danger, but they can create pronounced local artifacts, which interferes with the correct interpretation of the results. Therefore, they should not be in the diagnostic area.
Most currently used intrauterine contraceptive devices do not shift under the influence of a magnetic field, do not heat up, and do not form artifacts.
But the main safety rule is that the doctor must know about the existence of these items, have documentary evidence of their properties and be confident that there is no harm to health.
Contraindications for the study
MRI of the brain, like most complex types of diagnostic studies, has its indications and contraindications. Before performing an MRI of the brain, the doctor should ask the patient the following factors:
- presence of allergies to medications;
- diseases suffered immediately before the study;
- intolerance to confined spaces;
- increased excitability.
Categorical contraindications to MRI are the first trimester of pregnancy, the presence of metal objects in the patient’s body (pacemaker, bone plates, implants), chronic renal failure, mental illness with increased nervous excitability.
Conducting a contrast study
Before the procedure, it is necessary to administer a trial drug to determine whether there is an allergic reaction to the drug or how the person reacts to the drug. Then a special substance should be administered in the required dosage. The contrast agent helps to thoroughly examine the desired tissue areas, which can be examined in detail. When a special drug is administered, the patient experiences a feeling of cold, he feels blood rushing to the head, and sometimes a metallic taste is felt in the mouth. The patient may feel nauseous or have pain in the area where the injection was given.
Sometimes a spectroscopic study is carried out, which allows us to fully assess the state of biochemical reactions in the cellular area.
Useful to know: What does an encephalogram provide for studying the brain?
The procedure is not capable of causing any discomfort. The only difficulty is that you need to lie motionless for forty minutes to forty-five minutes. As a result, the examination is difficult to carry out for children. Such studies are carried out in an open hardware device, and if at all small, then the procedure is carried out under anesthesia.
If sedatives were not administered before the study, there is no need to recover afterward. A person can lead a normal life, he can eat and drink after he has left the office. During the day, a woman who is feeding her baby with breast milk should not put her baby to her breast.
to contents ^
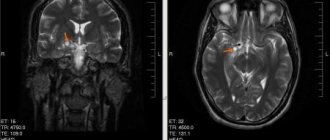
What the study shows
Thanks to the effect of magnetic resonance waves on the brain and a three-dimensional image on a computer screen, the doctor will be able to identify the presence or absence of the disease. To make the MRI procedure more effective and carry as much information as possible, a contrast agent is used.
Such a substance can help determine the presence of changes in brain tissue. Most of the injected substance collects in areas that may be pathological. For example, if a person has even a small cyst, the substance will accumulate in it. Thanks to this substance, the doctor will be able not only to identify the presence of a deviation in the patient’s health, but also to determine how serious the disorder is.
Contrast is administered intravenously to the patient before the procedure, and all parameters of the person must be taken into account. In order to understand what the device shows, you will need to decrypt the data by a specialist.
This procedure will not bring any changes to brain activity.
What does MRI help detect?
An MRI is prescribed if the development of dangerous diseases is suspected:
- benign and malignant neoplasms;
- abnormalities in the vascular region, including aneurysm;
- stroke manifestations;
- pathological changes in the inner ear and visual functionality;
- injury to any part of the brain;
- various ailments in the pituitary region;
- in case of dysfunction of the nervous system, as well as multiple sclerosis and others.
to contents ^
How to prepare for the procedure
Before being sent for diagnostic resonance imaging studies using a computer, the patient must undergo a complete examination. The doctor identifies contraindications and can also give detailed recommendations.
It is worth excluding clothing models with details made of metal materials, including buttons, zippers, rivets and others. Clothes should be loose so that there is no discomfort during the examination, since lying down should be motionless for several minutes. You should not be wearing watches, jewelry, hearing aids, or other metal products. Remove all foreign objects from your pockets, as their presence often distorts the test result.
Before undergoing a CT scan, you can eat and drink whatever you like. You should only exclude the consumption of alcoholic beverages, which is a categorical prohibition. With a contrast type of procedure, you should not eat for a 3-hour period. If you have a heavy lunch, you may feel uncomfortable.
Sometimes the doctor may prescribe the administration of a special solution before the tomography. This will help make a better diagnosis. But you need to make sure there are no allergic reactions to the drug.
If you follow all these recommendations, the procedure will be carried out without pain, and the result will be reliable.
to contents ^