Many smokers feel that cigarettes help them calm down and relax in difficult situations. However, in reality this is just an illusion. Nicotine has a negative effect on the functioning of the central nervous system. People who have this bad habit fall into a state of panic more easily, they have increased nervousness and irritability. Therefore, it is important to understand exactly how smoking affects the nervous system.
Harm of smoking to the respiratory system
First of all, the harm of smoking affects the upper respiratory tract, as well as the lungs. Poisons inhaled when smoking with tobacco smoke irritate the mucous membranes of the larynx, bronchi, trachea and pulmonary alveoli.
During smoking, smoke and tar inhaled by a person dry out the upper respiratory tract, which leads to the death of epithelial villi. As a result, the villi can no longer trap dust and small particles that come with the air. For this reason, the lungs become contaminated with dirt particles and various resins. These processes cause a cough that constantly increases. Over time, this cough becomes chronic, chronic bronchitis develops, which makes itself felt with any hypothermia. When a smoker coughs, a lot of gray mucus is coughed up.
The most common smoker's disease is chronic bronchitis. This disease affects 88% of smokers. This cough is most intense in the morning. With constant coughing, irritation of the vocal cords occurs, which leads to a change in the timbre of the voice. Also, long-term smoking causes tracheitis and laryngitis, which makes the smoker more susceptible to respiratory diseases. Smoking reduces the elasticity of lung tissue, which leads to poor lung function. This makes itself felt when walking or running quickly, when shortness of breath occurs. At this time, the lungs cannot stretch to the required size and the person has to breathe more often. Thus, the ventilation function of the lungs is impaired. Research conducted by scientists on this matter showed that among smokers with an experience of 3 to 5 years, insufficiency of the ventilation function of the lungs was observed in 30.3% of cases, and among smokers with a smoking experience of 6 to 9 years, such insufficiency was observed in 34.3% .
Studies have shown that smoking causes all types of cancer of all human respiratory organs. The risk of developing lung, stomach and larynx cancer increases most. The incidence of this type of cancer depends on smoking history.
A person who smokes more than 10 cigarettes a day has a 10 times greater chance of developing lung cancer than a non-smoker. Scientists say smoking is the main cause of lung cancer. On average, there are 30 times more cases of lung cancer in people who smoke than in people who do not smoke.
It has been established that smoking directly affects the possibility of developing a disease such as tuberculosis. Studies conducted on this matter have shown that 90% of people with tuberculosis are smokers or were smokers before. Smoking also reduces the effectiveness of tuberculosis treatment.
Studies based on a number of autopsies have shown that the lungs of a 40-year-old person exposed to long-term tobacco smoke look like the lungs of a 70-year-old person.
Smoking has such a harmful effect on the respiratory system mainly due to the tar and tar contained in tobacco smoke. About 800 g of tar passes through a smoker's lungs per year.
Getting rid of a bad habit
Why do smokers love cigarettes so much, being well aware of the harm that nicotine causes to their health? The short-term alkaloid produced still helps to relax the body, improve mood and boost energy levels. A person psychophysiologically gets used to smoking, and quitting this harmful activity is not so easy.
It is very important to find an activity that would distract you from thinking about a cigarette. Every time you feel like picking it up, pick up something else. There are many pleasant things to do: reading, watching movies, walking, chatting with friends.
You yourself will understand how great it is when your mood does not depend on the dose of nicotine.
Today, many special devices have been developed for those who want to break a bad habit. Experienced smokers will experience nervous stress at first and may lash out at others. An unhealthy craving for food is likely: a person will need something to occupy his hands. Medicines will help: chewing gum, lollipops, nicotine patch. The financial side will be a good psychological incentive. Calculate how much money you save by not buying more cigarettes.
If you are wondering whether smoking affects the human nervous system, the answer is yes. It causes real addiction and inhibits the natural processes in the central nervous system. Take care of your health and don't let bad habits enslave you.
The brain is one of the largest and most complex organs in the human body. It contains more than one hundred billion nerves that interact through trillions of synapses.
The brain is divided into several lobes:
Frontal. Responsible for problem solving, judgment and motor functions.
Parietal. They control sensations, handwriting, and body position in space.
Temporal. Associated with memory, smell and hearing.
Occipital . Contains a visual information processing system.
The brain is surrounded by a layer of tissue called the meninges. The skull helps protect its contents from damage.
The structure of a smoker's brain is no different from a similar organ in a person without bad habits. However, over time, the electrical activity of the cells in the head of a smoker decreases. As a result, intellectual abilities suffer, memory deteriorates, and a smoker spends, on average, 20% more time solving complex problems than a healthy person. However, the worst possible consequence of smoking is a stroke - an acute disorder of cerebral circulation.
Is nicotine dangerous for human health?
Smoking kills half of all smokers, plus 600,000 people a year due to secondhand smoke. This makes it the world's worst preventable killer. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the death toll due to this bad habit will reach a billion people by the end of the century.
Smoking is harmful to the heart
Smoking has serious harm to the cardiovascular system. Vascular and heart diseases are observed several times more often in smokers than in non-smokers. Long-term smoking causes chronic hypoxemia, when the level of oxygen in the blood decreases, as well as the appearance of atherosclerotic plaques.
The main negative impact on the heart is caused by nicotine, as well as products contained in tobacco smoke. These substances disrupt metabolism, increase blood pressure, and also increase the content of catecholamines and bad cholesterol in the blood.
Under the influence of tars that enter the body during smoking, vascular spasms occur in the heart and their structure is disrupted. Carbon monoxide released from smoking greatly reduces the amount of oxygen reaching the heart. The resulting oxygen starvation reduces the lifespan of a smoker’s heart.
Smoking increases blood clotting, which leads to the formation of blood clots in the heart cavity and blood vessels. In cases where such blood clots break off, a stroke, myocardial infarction, or pulmonary infarction occurs. Thus, the risk of sudden death in a smoker is 5 times higher than in a non-smoker.
Another harm of smoking for the cardiovascular system is that high concentrations of nicotine reduce the content of the hormone prostacyclin, which causes damage to cell membranes. A decrease in prostacyclin levels provokes the development of diseases that affect the heart and cardiovascular system. Constant oxygen deprivation and high blood pressure caused by smoking negatively affects the blood vessels and heart of a person. The heart is also affected by carbon monoxide, which reduces the rate of oxidation in mitochondria. When smoking, the level of lipids in the blood increases, as well as the content of cholesterol and betalipoprotein. These processes cause plaque to form on the coronary vessels supplying the heart. Atherosclerosis, in turn, is the main cause of the development of coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction and sudden death. Studies conducted after post-mortem autopsies showed that the area affected by atherosclerosis of the arteries in a smoker is 2 times larger than in a non-smoker.
It has been established that in a smoker the number of red blood cells glued together in pairs is 10%, while in a non-smoker it is 3%. Nicotine increases the ability of platelets in the blood to stick together, which causes blood clots to form in the blood. All these processes increase blood viscosity, slowing blood flow. As a result, the level of oxygen in the blood decreases, increasing the likelihood of myocardial infarction.
Heart-related death in a smoker occurs 20 years earlier than in a non-smoker.
How does smoking affect growth?
It is difficult to calculate how many centimeters of height and kilograms of muscle mass a teenager who starts smoking loses. But the fact that they lag behind non-smoking peers in physical development is a proven fact.
Causes of slow growth due to smoking in adolescents include:
- Inhibition of the production of somatotropic hormone - growth hormone.
- Deficiency of testosterone hormone production.
- Insufficient oxygen supply to muscle tissue (hypoxia).
- Impaired absorption and assimilation of proteins, vitamins and minerals necessary for normal growth and development of bone and muscle tissue.
Testosterone, being a natural anabolic, stimulates the construction of new tissue. With testosterone deficiency, the growth and development of muscle tissue is inhibited. During hypoxia, tissues experience oxygen starvation, which delays all metabolic processes. Hypovitaminosis of vitamins A, B, C, E slows down the processes of nutrient assimilation, which leads to slower growth. With a lack of vitamin D, phosphorus and calcium are absorbed more slowly, and bone cells (osteoblasts) do not have enough starting material for synthesis.
Harm of smoking to the brain
The human nervous system is one of the most vulnerable and fragile systems of the body. The physical and psychological state of a person directly depends on the brain. That is why smoking has serious harm on the human brain.
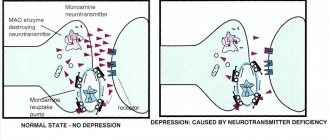
When nicotine enters the bloodstream through the lungs, it reaches the brain in about 8 seconds. The effect of nicotine extends to all parts of the nervous system, including the pleasure center in the brain. This is the main reason for addiction to nicotine. Brain cells are the most sensitive to nicotine. When smoking, nicotine causes vasoconstriction in the brain, which greatly reduces blood flow to brain cells. This provokes headaches and memory problems. Nicotine causes disruption of nerve impulse transmission. Nerve cells generate biocurrents that are well recorded by an electroencephalograph. Studies have shown that smoking causes a noticeable weakening of the bioelectrical activity of the brain. Moreover, this weakening is proportional to the number of cigarettes smoked.
Smoking can cause disruption in the activity of the central and peripheral nervous systems. Inflammation of the nerve trunks is noted, characterized by polyneuritis, neuritis and radiculitis.
Smoking causes a disruption in the flow of nervous processes, which leads to irritability, conflict and the manifestation of the so-called complex character.
Israeli scientists conducted studies that showed that the IQ of a smoker noticeably decreases after smoking a pack of cigarettes a day. The data was as follows: a non-smoking person had an IQ of 101, a regular smoker had an IQ of 94, and a person who smoked more than 20 cigarettes had an IQ of no more than 90. It is believed that the decrease in the level of intelligence is associated with insufficient oxygen supply to the brain caused by smoking. With tobacco smoke, a person inhales more than 4,000 harmful substances, of which about 30 are toxic. When nicotine enters the brain, in the first 7 seconds it activates nerve cells, but then they are depressed.
Indian scientists have found that smoking can encourage white blood cells to attack healthy cells, which can lead to damage to brain cells. This is why smoking is one of the causes of the development of multiple sclerosis.
Protecting the nervous system from the harmful effects of nicotine
It is clear that you need to quit smoking, but this path may not be as simple as it seems at first glance. How to protect the nervous system from the influence of nicotine? Move as much as possible. When moving, the brain is activated, muscle activity affects conductivity in nerve fibers - this will have a positive effect on the functioning of the central nervous system.
Develop your intellectual activity:
- solve crossword puzzles;
- read;
- engage in literary creativity.
Eat right so that your body does not suffer from a lack of important microelements and vitamins.
Spray to the rescue
When a smoker gives up a cigarette, at some point the hand itself reaches out for another portion of nicotine. Associated withdrawal symptoms may make the situation worse. Special sprays will come to the rescue.
It only takes a few minutes for the strong desire to smoke to disappear.
Smoking has a detrimental effect on the entire body, and the biggest impact falls on the nervous system. There are four stages in the formation of persistent nicotine addiction, which leads to changes in the functioning of the human nervous system. To restore your health, you need to make an effort and get rid of a bad habit.
Harm of smoking to the digestive system
When cigarette smoke enters the oral cavity, it irritates the tongue, gums, pharynx and palate. Tobacco smoke also causes cracking of tooth enamel. As a result, the teeth become infected with various bacteria, which lead to decay, causing bad breath. When smoking, the salivary glands are irritated by tobacco smoke, which leads to intense salivation.
It has been established that the mortality rate from cancer of the oral cavity and esophagus among smokers is 4 times higher than that of non-smokers. These diseases are associated with both chemical and thermal effects of smoking.
Many stomach diseases are directly related to smoking. Components of tobacco smoke affect the stomach both through the nervous system and when swallowing salivary fluid saturated with chemicals from tobacco smoke. This effect causes irritation of the gastric mucosa, leading to increased secretion of gastric juice with high acidity. Constriction of the stomach vessels can lead to decreased blood circulation in its parts with subsequent formation of ulcers. Constant irritation of the mucous membrane when smoking causes chronic inflammation, which leads to gastritis.
There is a clear connection between smoking and the spread of gastric and duodenal ulcers. The number of deaths from this disease among smokers is 4 times higher than the number of deaths from such diseases among non-smokers.
It has been established that nicotine has a harmful effect on the functions of the stomach and intestines, reducing their peristalsis. This leads to decreased appetite and poor digestion. Semi-digested food stagnates in the digestive organs. In some cases, nicotine causes involuntary spasms in the rectum. This can lead to the formation of hemorrhoids and sometimes hemorrhoidal bleeding.
Smoking does a lot of damage to the liver. Scientists conducted studies in which rabbits were exposed to tobacco smoke. As a result of exposure to tobacco smoke, changes occurred in the liver cells of rabbits, even to the point of degeneration. A person who smokes experiences an enlarged liver, which goes away after completely stopping smoking.
The harm of smoking also extends to the pancreas, causing serious diseases of this organ. A smoker's risk of developing pancreatic cancer is twice the risk of a non-smoker.
The cardiovascular system
Nicotine activates the vasomotor center, stimulates the release of adrenaline, which causes spasm and increased vascular tone. This is an additional load on the heart muscle, since it is much more difficult to move blood through narrowed vessels. Compensatory heart enlarges due to the growth of muscle fibers, myocardial hypertrophy is formed. The increased load leads to rapid wear and tear of the heart muscle, disturbances in the myocardial conduction system, and arterial hypertension. In addition, smoking contributes to disruption of the function of the endothelium lining the arteries from the inside, which contributes to the early development of atherosclerosis, and subsequently its complications: myocardial infarction, stroke, damage to the arteries of the lower extremities.
Harm of smoking to the genitourinary system
Considering the effect smoking has on the vascular and nervous system, one cannot fail to note in this regard the serious harm it causes to the genitourinary system, since the genitals have an abundant blood supply and innervation. The reproductive system is not isolated, and therefore, when problems with the cardiovascular system arise in the body, the same problems affect the reproductive system, causing, for example, a decrease in erection. There is a decrease in the frequency of sexual intercourse, and erectile dysfunction develops.
In both women and men, substances entering the body along with tobacco smoke cause hypoxia and hypoxemia of organs, including the genitals. This process is due to the fact that nicotine negatively affects both the cerebral cortex and the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. Due to vasospasm caused by nicotine, less blood flows into these organs, which leads to a decrease in their production of gonadotropic hormones, which command the human gonads to produce hormones. Accordingly, the production of male and female sex hormones decreases.
The harmful effects of smoking cause many diseases of the genitourinary system, including malignant changes in the cervix caused by hypoxia, prostate adenoma, carcinomatosis of the genital organs, as well as impotence.
How does smoking affect your voice?
Smoke, spreading through the respiratory tract, damages the vocal cords located in the larynx. The mucous membrane of the larynx swells, and with slight tension (loud speech), hemorrhages occur in the thickness of the muscles that form the ligaments. Toxic smoke components are deposited on the ligaments themselves, causing the development of erosions, ulcers and other damage. All these pathological processes lead to the fact that the smoker's voice becomes dull and hoarse. When chronic laryngitis develops, the voice may forever lose its previous timbre and sonority.
CNS addiction to nicotine
In the process of smoking, an unhealthy craving for nicotine consumption arises, which manifests itself daily. Smokers experience obsessive and compulsive addiction at the same time. Psychophysical dependence appears directly from smoking and the participation of alkaloids in the metabolic processes of the body. Psychological addiction is manifested by a person’s need to smoke, when the addict thinks about a cigarette and enjoys the process of inhaling tobacco smoke. Physical dependence involves the constant presence of nicotinic acid in the blood. In both cases, the addict experiences an urgent need to smoke.
The chemical mechanism of action of the alkaloid is a broad effect on the adrenal glands and the hormone adrenaline they secrete. The release of adrenaline improves mood and gives an imaginary feeling of relaxation and tranquility. At first, the smoker achieves a state of relaxation and calm with the help of one cigarette, but soon such a dose of nicotine will not help achieve the desired effect. A person has to smoke several cigarettes in a row. There are several stages in the addiction of the central nervous system to smoking:
- A person engages in “indulgence” - smokes one or several cigarettes a day, a pack can last for a week or two. At this stage, there is no alkaloid dependence yet, but problems with digestion and blood vessels arise. They are reversible - they disappear after a person stops smoking.
- An established addiction in which a person smokes up to 10 cigarettes a day and feels discomfort without nicotine.
- Smoking a pack of cigarettes per day. Such people have a pronounced psychophysical dependence.
- Heavy smokers who smoke about two packs per day have severe withdrawal symptoms.
How dangerous is nicotine for humans?
According to statistics, smoking causes the death of exactly 50% of all smokers. The World Health Organization has predicted that by the end of this century the total number of people who have died due to this addiction will reach 1 billion.
Most believe that nicotine is the only problem for all smokers. Experts in the field say that this component is certainly addictive, but at the same time, its daily dose can be completely safe. That is why many doctors and psychologists propose to draw a clear line between nicotine and smoking.
Numerous studies confirm that it is not nicotine that kills a person, but smoking in general. The fact is that in the production of cigarettes more than 40 types of carcinogens and 12 cocarcinogens that contribute to the development of oncology are used.
It sounds strange, but nicotine also has positive properties. Acting as a stimulant, it increases heart rate and speeds up the filtering of afferent signals (perception of the outside world). American clinical studies conducted in 2000 found that in people with Parkinson's disease, nicotine stimulation improved both mental and motor functions.
However, nicotine in its pure form is deadly. It has been proven that its increased doses destroy brain activity, especially in children. The greatest impact falls on the areas responsible for memory, speech and intelligence.
Withdrawal and recovery
Over a long period of smoking, the nervous system gets used to nicotine and, without the required dose, stops working fully. Therefore, a person experiences withdrawal syndrome, accompanied by the following symptoms:
- sudden mood swings;
- anxiety and panic attacks;
- irritability;
- nervousness;
- increased sweating;
- hot and cold flashes;
- migraine;
- apathy;
- depression;
- pulse disturbances.
These symptoms appear especially clearly in the first few weeks after refusal and recede after a month and a half. For the nervous system to recover at least half, it requires at least 30 days. Gradually, neural processes will improve and begin to work without deviations.
As a result, positive changes will occur in the body of a former smoker:
- sleep will improve;
- a state of calm will come;
- aggressiveness and irritability will disappear;
- the functioning of the sense organs will be restored;
- Brain activity will increase.
To fully recover, the nervous system of a heavy smoker needs about six months. The uniqueness of the central nervous system is that it has the ability to regenerate, so quitting smoking is a 100% guarantee of recovery.
It is possible that drug intervention will be required to normalize the functioning of the central nervous system. It is important to understand that drugs are prescribed only as prescribed by a doctor. You should not self-medicate without first consulting a specialist.
The nervous system is the most unique and least studied in the body. Being the brain center, it is responsible for all physiological processes. Although it has the ability to recover, you should not poison it with nicotine and neglect the work of other vital systems.
Every heavy smoker will say that smoking helps him calm down, concentrate in a critical situation, and relax after a working day. This is an illusion: smoking and the nervous system do not have such a connection. On the contrary, smoking a cigarette harms the functioning of the central nervous system.
Reproductive system
In girls, the menstrual cycle is disrupted, which subsequently negatively affects the ability to conceive. According to statistics, if a girl does not quit smoking even when pregnant, she often gives birth to children with developmental defects, and premature birth is observed 6 times more often than among non-smoking women.
In young men, toxic combustion products of tobacco slow down the synthesis of testosterone, the main male hormone that plays a key role in the onset of puberty. Suppression of sperm activity often leads to male infertility.
Smoking and potency in men - a strong relationship
It has been proven that cigarettes have a pathological effect on potency. By deliberately poisoning the body with toxic compounds, a man sooner or later comes to the understanding that smoking and impotence are cause and effect. The inhabitants of the planet suffer from male impotence, regardless of their country of residence, level and status of life. Nicotine addiction contributes to a complete or partial lack of sexual desire in men and problems with ejaculation. Delving into the mechanism of how smoking affects potency, it can be noted that after smoking a cigarette, sexual activity and sperm quality decrease.
Heavy smokers can test the effects of cigarettes by abstaining from smoking for 8 hours, after which they can compare their orgasm and the duration of sexual intercourse. Whereas after smoking several cigarettes in a row, problems with erection are guaranteed.
Scientists and doctors note that smoking and impotence are connected, which is why the first point for successful treatment of erectile dysfunction is quitting cigarettes.
The impact of smoking on the psyche and can it be avoided?
Smoking is a drug addiction that deprives a person of freedom. This applies not only to cigarettes, but also to hookahs, vapes and other electronic devices. Fortunately, it is possible to get rid of this addiction, since nicotine, compared to other drugs, is quite mild.
The most important thing in quitting smoking is a sincere and personal desire to recover, and qualified help from specialists will significantly speed up the process. If we talk about the nervous system, its functions are restored, although this will take a very long time.
National Teen Smoking Prevention Program
Smoking is perceived by society as a bad habit, which is associated with possible health risks in the distant future, but does not cause much harm to the smoker at a given time. This is a misconception. WHO regulatory documents define tobacco smoking as a chronic relapsing disease with the formation of addiction.
It is necessary to develop a national program to combat smoking, which would include legislative, administrative, and educational measures:
- Increase in prices for tobacco products.
- Introducing bans on all tobacco advertising.
- Implementation of the law restricting smoking at work, in educational, medical, cultural and other public places.
- Conducting various educational and awareness-raising events aimed at explaining the harmful effects of smoking on the health of the nation.
But parents play the main role in shaping a teenager’s strong motivation to avoid smoking and other bad habits. It is in the family that the foundations of morality and behavior in society and commitment to a healthy lifestyle to maintain health are laid in the process of education.