Professor Zvi Ram Leading surgeon of the Department of Neurosurgery
Brain lymphoma in Israel at the Top Assuta clinic has been successfully treated for quite a long time, so the clinic’s doctors are guided not only by theoretical knowledge, but also by impressive practical experience. Every decision made regarding the treatment of a patient is carefully considered and discussed with specialists in various fields. This is done to achieve maximum objectivity and select the most correct method of therapy.
The diagnostic center of the Top Assuta clinic uses all licensed developments of medical equipment, which makes it possible to obtain the most accurate research results. Top Assuta Clinic provides a full range of medical services, creating for its patients the most comfortable conditions for recovery.
82%
successful cases of treatment with conservative methods
5000
foreign patients are treated annually at the Top Assuta clinic
88%
patients returned to their usual lives after treatment for brain lymphoma
Types of brain lymphoma
There are non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and Hodgkin's disease. In the first case, a tumor develops in the event of a mutation in one lymphocyte cell. When the entire lymphatic system is affected, Hodgkin's disease begins.
Non-Hodgkin's lymphomas of the brain can be primary or secondary. Mainly men are susceptible to this disease. The primary tumor rarely appears in the brain. More often it is formed as a result of metastases, and is secondary.
Lymphocytes contain B cells and T cells, which is taken into account when classifying pathology. Mutations in 85% of cases occur in B cells.
The following types of tumors in B cells are distinguished:
- Diffuse large cell lymphoma. It is diagnosed in 30% of cases, mainly among older people. It is easily treatable, and most patients live longer than 5 years after diagnosis of the disease.
- Small cell lymphocytic lymphoma. The tumor grows slowly, but is highly malignant. This type of lymphoma occurs in 7% of patients. This tumor can develop into a tumor with rapid growth.
- Follicular lymphoma. A fairly common tumor, diagnosed in 22% of cases. It grows slowly and has low malignancy. People over 60 years of age are at risk. The disease is easy to treat, 60% of patients live longer than 5 years.
- Mantle cell lymphoma. This tumor grows slowly, but the prognosis for its treatment is unfavorable, since only 20% of patients survive. This lymphoma occurs in 6% of cases.
- Burkitt's lymphoma. The disease is diagnosed in people over 30 years of age, mainly among men. It occurs very rarely, only in 2% of cases. The success of treatment depends on the stage at which the pathology is detected. Timely chemotherapy increases the chances of recovery.
T tumors are classified as follows:
- T-lymphoblastic malignant lymphoma. It affects young people in their 20s. It is diagnosed in 75% of cases. Chances of survival increase if the disease is diagnosed in the early stages. If the tumor has affected the spinal cord, recovery is unlikely and is observed only in 20% of patients.
- Anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Pathology occurs in young people. Recovery is possible if treatment is started in the early stages.
- Extranodal T-cell lymphoma. The pathology affects people of any age and can occur at different ages; the outcome depends on the stage of the disease.
Reticulosarcoma
Reticulosarcoma is a malignant proliferation of cells of reticular lymphoid tissue. She doesn't show herself for a long time. Only in later stages, when metastases appear, the patient’s liver and spleen become enlarged, and jaundice may begin.
Primary reticulosarcoma is localized in the lymph nodes. At this stage, the lymph nodes are very dense and do not hurt. Over time, the tumor grows into nearby tissues, resulting in impaired blood circulation and lymphatic drainage. When spreading to the lymph nodes of the mediastinum, the neoplasm compresses the esophagus and trachea. Metastases into the abdominal cavity lead to excessive accumulation of fluid in the lower abdomen, and when the vessels passing through the chest cavity are damaged, compression syndrome occurs. Growth in the intestines leads to obstruction.
Microglioma
Refers to primary malignant lymphomas. The neoplasm consists of atypical microglial cells.
Diffuse histiocytic lymphoma
A malignant form of the disease, characterized by the proliferation of large lymphoma cells with abundant cytoplasm and polymorphic nuclei. such cells are capable of phagocytosis, consuming mainly red blood cells. Diagnosed extremely rarely.
Bone marrow lymphoma
The bone marrow stores stem cells of red blood cells, platelets, and leukocytes. Increased division of lymphocytes leads to the displacement of blood cells. Thus, hematopoiesis is disrupted. This pathology is called bone marrow lymphoma. It does not show any signs for a long time, and is detected only at stages 3-4.
The disease is difficult to treat, and the effectiveness of therapy is influenced by internal and external factors.
Forms
The morphological substrate of the tumor is Berezovsky-Stenberg-Reed cells, however, their number in the tumor tissue rarely exceeds 10%. The second variant of cells is Hodgkin cells, which are a provariant of the Berezovsky-Stenberg-Reed cell. Depending on how the tumor tissue looks under a microscope, there are five forms of Hodgkin lymphoma.
- The variant of Hodgkin's disease with lymphocytic predominance accounts for 5-6% of all cases of HL. There are very few Berezovsky-Stenberg-Reed cells.
- The mixed cell variant is diagnosed in three quarters of patients. Berezovsky-Stenberg-Reed cells and Hodgkin cells are found in sufficient numbers.
- Lymphocytic depletion is the most rare morphological variant of the tumor (less than 1%).
- The most common variant of Hodgkin's lymphoma is nodular sclerosis.
- With nodular lymphoid predominance, the lymph node tissue is completely or partially replaced by an infiltrate of a nodular structure, often combined with zones of diffuse growth.
Causes
The exact causes of brain lymphoma are unknown. Medical research has found that brain lymphoma develops when the immune system is weakened. Pathologies favor:
- HIV infection;
- radiation exposure;
- genetic predisposition;
- systematic influence of carcinogens, which include heavy metals and various chemicals;
- Epstein-Barr virus;
- Infectious mononucleosis;
- environmental conditions;
- organ transplantation;
- blood transfusion;
- age after 60 years.
The described factors, under certain conditions, provoke the development of the disease, especially with a complex effect.
External factors
There are external factors that can cause brain lymphoma. Among them:
- radiation exposure;
- vinyl chloride gas, which is used in the production of plastics;
- aspartame is a sugar substitute.
The reasons for the development of the disease have not been precisely established. Most doctors believe that the appearance of lymphoma is promoted by the electromagnetic field and high-voltage transmission lines.
Weak immune system
People with impaired immune system function are at risk of developing primary brain lymphoma. The causes of lymphoma in immunodeficiency are:
- Organ transplantation.
- HIV.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Contact with a carcinogen.
When lymphoma occurs in a healthy person, it usually develops in the lymph nodes. In patients with immunodeficiency virus, the disease progresses in the spinal cord or brain.
Genetic predisposition
The cause of the development of cancer is genetic predisposition. Members of the same family are faced with the occurrence of benign tumors, but if treatment is ignored, they can develop into cancer. Children of HIV patients are often born with brain lymphoma.
Neurofibromatous diseases cause the development of spinal cord tumors. The disease is inherited by relatives of the first order.
Forecast
Survival statistics, as for many cancers, are not very optimistic. With normal therapy, 75% of patients are able to overcome the five-year mark. In old age, the threshold drops to 40%.
Relapses after treatment. The return of any disease is dangerous for the patient, and recurrence of lymphoma is doubly dangerous. Despite the severity of cancer, it is necessary and worth fighting it. And the result can be quite optimistic.
To localize it, the method of radical therapy is used (and very successfully). The side effects from it are no stronger than from the original treatment regimen, and the effect can be noticeable. Its task is to suppress the disease as soon as possible and prevent the tumor from starting to grow again.
Symptoms
People with lymphoma in the brain experience varying degrees of the following symptoms:
- speech disorder;
- dropsy;
- visual impairment;
- nerve damage without inflammation;
- numbness of the hands;
- hallucinations;
- mental disorders;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- fever;
- headache;
- dizziness;
- sudden weight loss.
The symptoms of lymphoma are aggravated by the fact that the pathology can lead to ischemic stroke and hemorrhage. The resulting hematomas disrupt brain activity and provoke the development of encephalopathy.
Diagnostics
A number of laboratory methods are used to accurately diagnose lymphoma. Among them:
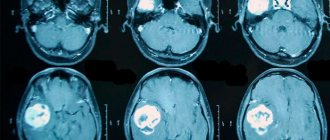
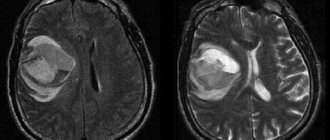
- CT scan.
- Spinal tap to examine cerebrospinal fluid.
- X-ray examination of the chest to examine the condition of the lymphatic system.
- Trephine biopsy is an examination of brain tissue for the presence of lymphoma by opening the skull.
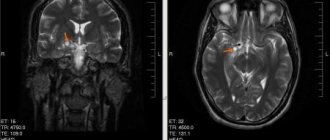
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain.
- Stereotactic biopsy for histological examination.
- General blood analysis.
If there is a lack of information to study the material, it is possible to use an ultrasound examination or perform a bone marrow biopsy, which can detect the disease at the initial stage of development.
Therapy
Whether it is possible to cure brain lymphoma with chemotherapy, there is no consensus among doctors. In most cases, complex treatment of brain lymphoma is practiced. During chemotherapy, the patient's condition improves if large dosages of drugs are used in treatment. Medicines are selected individually, taking into account the sensitivity of lymphoma to certain substances. It is advisable to use chemotherapy in conjunction with a course of radiation therapy, which increases the patient's life span. This is especially true for HIV-infected patients.
To eliminate the symptoms of the disease, narcotic medications are used that can reduce pain. Surgery is not recommended due to the risk of neurological damage due to accidental damage to the tissue surrounding the lymphoma. The operation is also difficult due to the difficulty of establishing clear boundaries of the tumor.
Dehydration begins with a group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (non-narcotic analgesics), such as ketans, nise or airtal. These are weak painkillers and the effect may not be enough even at the initial stage. Of the drugs that can be sold in pharmacies without a prescription, it is better to ask for Celebrex. To purchase narcotic drugs you will need a prescription form 107-1/u-NP. The pink form is obtained from your GP.
The disease in its advanced form is treated with the help of palliative medicine, the essence of which is to provide emotional support to the patient and improve overall well-being. Headaches at this stage are so severe that they cannot be relieved with narcotic analgesics.
Treatment methods
For a long time, radiotherapy has had no equal in the fight against lymphomas; it consistently provides high efficiency, but, unfortunately, with a temporary nature, which is associated with radiation exposure. A more stable and sustainable result with a tandem of radioactive and chemical exposure.
Despite all the effectiveness of chemotherapy, its implementation means the destruction of not only diseased cells, but also healthy ones. Side effects depend on the drug chosen and its dosage. Usually this:
- anemia and severe weakness due to it;
- gagging and nausea;
- partial or complete hair loss;
- a feeling of dry mouth, which is accompanied by ulcers and wounds;
- failure of the gastrointestinal tract;
- decreased immune capacity, which creates a high risk of infection;
- weight loss due to lack of appetite.
If the patient has an adequate immune status, then they can easily tolerate such aggressive therapy, receiving remission for several years. Oncologists call immunocompetent patients this way. Some clinics are conducting experimental treatments based on immune and targeted therapies. Unfortunately, long-acting drugs for lymphoma have not yet been created.
WE RECOMMEND SEEING: What is a cerebrospinal fluid cyst?
Therapy begins with the administration of corticosteroids to correct brain swelling and normalize the patient’s well-being. For chemotherapy, Methotrexate is used in large dosages, which are administered through a vein or through a spinal puncture.
Rarely, only one medication is used in treatment, usually several drugs are used at once. Most often, combination therapy is based on Etoposide, Tamozolomide, Cytarabine and Rituximab.
Symptomatic treatment removes the accompanying negative clinical picture, such as:
- hypertension;
- severe pain;
- neuropathy;
- hypercalcemia.
Palliative therapy for the final stages of this type of brain cancer is based on blocking pain, often with narcotic-based analgesics. There is nothing more doctors can do for the patient.
Important! Surgery is not used to treat brain lymphoma, since this is a high risk of disrupting the patient’s nervous and mental activity. Doctors have repeatedly tried to remove such tumors neurosurgically, but this invariably led to injury to the brain structures at a deep level, since the lymph does not have clear boundaries.
Oncologists recommend that young patients undergo a stem cell transplant, but this expensive procedure does not always give the expected result. It is difficult to find a donor who fully matches all markers. Most often these are direct relatives, but if they are not there, the patient is put on a waiting list. The search for a donor can take years, which the patient does not have.