Medical certificate
Encephalopathy is a pathology accompanied by damage to brain cells. Its development is caused by the action of damaging factors, which always leads to disruption of the functions of brain structures. Encephalopathy is not an independent disease, but a syndrome that can be caused by many reasons. It helps to reduce the number of nerve cells, the appearance of minor hemorrhages and swelling of the meninges.
Depending on the time of occurrence and underlying causes, the pathology is:
- Congenital (develops as a result of genetic abnormalities, intracranial injuries during childbirth).
- Acquired. This form, in turn, is divided into:
- Toxic. Occurs due to constant exposure to toxic substances (poisons, chemicals, alcohol).
- Post-traumatic. It is a consequence of traumatic brain injury.
- Metabolic. It is based on serious metabolic disorders with simultaneous pathological changes in internal organs.
- Radial. Develops due to exposure to ionizing radiation on the brain.
- Vascular or discirculatory (angioencephalopathy) of the brain. Associated with constant disruption of the blood supply.
The latter form of the disorder is the most common. We will dwell on this in more detail in today’s article.
Definition of pathology
Microangiopathy is a disease that occurs due to persistent, irreversible damage to small vessels located in the brain, which often indicates a direct dependence on the presence of arterial hypertension. According to statistics, more than 60% of patients over the age of 55 years, and more than 80% of patients over the age of 85 suffer from arterial hypertension and the consequences of this pathology.
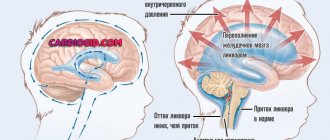
First of all, regularly high blood pressure negatively affects small-diameter vessels. As a result, the white medulla is damaged, the perivascular space expands, and lacunar infarctions develop - an acute circulatory disorder in a limited area fed by a small penetrating artery.
Microangiopathy provokes degenerative changes in brain tissue, leading to the development of vascular dementia, deterioration of cognitive functions, and stroke. There is a proven close relationship between angiopathy and comorbid conditions - diabetes mellitus and metabolic disorders occurring against the background of cumulative damage to the vascular system of the brain.
Arterial hypertension correlates with pathologies such as obesity, hyperuricemia (increased concentration of uric acid in the blood plasma), insulin resistance, glucose intolerance, and lipid metabolism disorders. Hyalinosis (a type of protein degeneration with the formation of compactions in the walls of blood vessels), which occurs against the background of atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension, worsens the structure of the vascular wall.
The tissue of the walls becomes dense, loses elasticity and flexibility, and the lumen narrows significantly. Endothelial dysfunction plays an important role in the pathogenesis of circulatory disorders and stroke. The endothelium controls vascular tone, influencing the functioning of the blood supply system. Endothelial cells, which make up the tissue of the walls of blood vessels and capillaries, are normally capable of producing anti-atherosclerotic substances, including nitric oxide.
The angioprotective effect of nitric oxide consists of vasodilation (relaxation of the smooth muscles of the vascular wall), inhibition of adhesion (adhesion, adhesion) of leukocytes, suppression of adhesion and aggregation (attachment) of platelets, proliferation of muscle tissue cells of the walls. Microangiopathy syndrome is a brain pathology that affects the rheological properties of blood and hemostasis, which is expressed in an increase in platelet aggregation activity.
The pathological process provokes the development of thrombosis, atherogenesis, and inflammatory processes. Platelets play a key role in clinical events in atherothrombosis. Atherosclerotic disease in its chronic form may not manifest itself with severe symptoms, but if complicated by thrombosis, it leads to transient ischemic attacks, stroke, acute myocardial infarction, and angina.
Angioencephalopathy of the brain - what is it?
This is a pathological disorder accompanied by impaired brain function due to circulatory problems. Compared to a stroke, this condition is not acute. Its development is based on chronic hypoxia of brain tissue. Neurons are particularly sensitive to oxygen deficiency. For example, when it is lacking, cognitive functions are the first to suffer, movements become difficult, and the emotional background changes.
Angioencephalopathy is a pathology of neurological etiology. Its prevalence is about 5% of the entire world population. Among other vascular disorders, it occupies a leading position. Moreover, it is mainly people over 40 who suffer from the manifestations of the disease. The older a person is, the higher the likelihood of developing this disorder. The risk group also includes people whose work involves severe intellectual stress.
Causes
The causes of the disease are often associated with age-related destructive processes in the tissues of the vascular wall. Factors influencing the development of pathology:
- Vascular atherosclerosis.
- Arterial hypertension.
- Diabetes.
- Malfunctions of the cardiovascular system.
- Injuries in the head area.
- Blood diseases with bleeding disorders.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Age over 50 years.
Fibrinoid necrosis, accompanied by atrophy of loose connective tissue cells, is one of the causes of vascular pathology. The connective tissue loses its normal structure with a characteristic fibrillar relief. It becomes homogenized, homogeneous. The pathological process occurs due to deposits of fibrinogen (blood plasma protein), which turns into fibrin.
Main reasons
Angioencephalopathy develops in the presence of concomitant pathologies of the vascular system. The disease occurs in people suffering from:
- vascular atherosclerosis;
- hypertension;
- low pressure;
- hormonal imbalances;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- thrombosis;
- increased blood viscosity;
- systemic vasculitis;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- diabetes mellitus;
- kidney pathologies;
- malformations of the cervical spine.
Among all the causes of cerebral angioencephalopathy, atherosclerosis and hypertension are especially worth noting. It is these disorders that in most cases lead to circulatory problems.
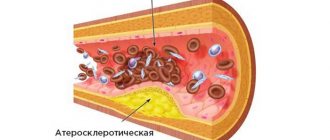
With atherosclerosis, plaques form on the inner walls of blood vessels throughout the body. They reduce the lumen of the bloodstream, and in some cases even completely block it. As a result, the area supplied by this vessel begins to experience a deficiency of useful microelements and oxygen. The medulla shows extreme sensitivity to the lack of these components. Just a few minutes of oxygen deprivation can trigger the death of neurons.
The vessels of the brain have the property of independent regulation of tone. Thanks to it, an increase in blood pressure in the body does not affect the increase in these parameters in the structures of the head. The blood flow remains virtually unchanged. However, long-term progressive hypertension leads to depletion of the compensatory capabilities of blood vessels. As a result, they become sclerotic and lose their tone and elasticity.
Symptoms
Identifying symptoms of cerebral microangiopathy at an early stage and subsequent correct treatment can prevent the development or slow down the progression of dementia. Often the pathology is asymptomatic, especially in the initial stages of its course. First of all, the doctor pays attention to the deterioration of mental activity and nonspecific cerebral symptoms.
A clinical marker at an early stage is anxiety and depressive disorders. At the same time, patients practically do not complain of sadness, a feeling of melancholy, or a sad mood. They are more concerned about somatic symptoms - asthenia (muscle weakness, impotence), loss of appetite, increased fatigue, sleep disturbance. Signs of microangiopathy are complemented by psycho-emotional disorders.
Often irritability and grumpiness are attributed to age-related personality changes. In the first stages, mild disturbances in motor activity may be observed - slower steps, changes in gait, instability of body position, often associated with dizziness. The progression of the pathology leads to an increase in cognitive deficit. Manifestations of severe, progressive microangiopathy of brain tissue:
- Deterioration of cognitive abilities - memory, mental activity, attention.
- Dementia.
- Mental disorders characterized by disturbances in the emotional state.
- Motor dysfunction (pyramidal insufficiency - spasticity, paresis, paralysis).
- Extrapyramidal disorders (hypokinesia - limitation of motor activity with a decrease in the tempo and range of movements, parkinsonism).
- Cerebellar disorders (impaired motor coordination, stability, balance, fine motor skills).
- Malfunctions of the autonomic system (nausea, increased sweating, tachycardia, heart rhythm disturbances, changes in blood pressure).
The progression of the disease provokes sphincter dysfunction - from episodes of urinary incontinence to complete urinary incontinence and episodes of fecal incontinence. Pseudobulbar disorders appear - dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), dysarthria (unclear pronunciation of words).
Risk factors
Doctors have been actively studying angioencephalopathy of the brain for several decades, what it is, and the features of its course. Thanks to numerous studies, they were able to identify the so-called risk group, being in which increases the likelihood of developing pathology. It includes people:
- those suffering from addictions (smoking, alcohol abuse);
- experiencing chronic fatigue;
- exposed to daily stress;
- not watching their diet.
In addition, the presence of hypertension among close relatives significantly increases the risk of angioencephalopathy.
Clinical picture
Until a person realizes that he has serious health problems, he will not go to the doctor. It is necessary to understand the symptoms of cerebral angioencephalopathy so as not to miss the initial stage of the disorder.
The primary symptom of this disease is a decrease in memory. A person does not remember some important dates, even forgets serious events in life. Performance gradually decreases. The ability to work is lost literally a few minutes after it begins. The patient himself may experience tinnitus. His mood is constantly changing: sometimes he is positive, sometimes he slips into a depressed state.
Stages of development of the disorder
In its pathogenesis, angioencephalopathy goes through three stages. Each of them is characterized by certain manifestations.
- At the initial stage, the lumen of the vessels narrows, and the lack of blood supply is not yet clearly expressed. Typically, patients attribute all symptoms to banal overwork. They are worried about weakness, fatigue, and sleep disturbances. Headaches and the appearance of spots before the eyes are possible.
- At the second stage, the signs of cerebral angioencephalopathy remain the same, but now they are more pronounced. This period is accompanied by massive destruction of cells and the connections between them. The gait becomes shaky and unstable. Sometimes there is trembling in the limbs. The emotional sphere also suffers. There is increased irritability and resentment increases.
- The third stage is characterized by severe disturbances of the psyche and mental functions against the background of irreversible damage to brain tissue. It becomes difficult for a person to navigate in space. He loses the ability to independently carry out work activities. Symptoms may vary depending on which part of the brain is involved in the pathological process. Impaired vision, hearing, and sensitivity are not excluded.
The last stage of angioencephalopathy is the most difficult. In this case, the pathology can cause dementia (dementia).
Symptoms and stages of development
During the development of encephalopathy, the patient is concerned about:
- headache;
- hearing impairment in the form of congestion and tinnitus;
- low performance and constant fatigue;
- decreased concentration and absent-mindedness;
- memory impairment;
- sudden mood changes. The patient becomes irritable, aggressive, his life rhythm is disrupted;
- drowsiness during the day and insomnia at night.
How pronounced these symptoms will be depends on how severely the brain tissue is affected.
The pathological process can develop in several stages:
- Initially, the disease affects a small number of brain cells, so violations of their functions are quite difficult to identify without special diagnostic tests. The ability to concentrate attention and memory is slightly impaired, so the person does not pay attention to the changes. But at the same time, changes occur in the psycho-emotional state of a person. At this stage of development, the patient suffers from loss of strength, impaired attentiveness, depression, depression, and suicidal thoughts. If the problem is not detected and corrected in time, then the next stage begins.
- The second stage of development of the pathology is accompanied by massive destruction of brain cells, destruction of the connection between them, which is accompanied by pronounced cognitive disorders. The patient in this case suffers from partial amnesia, a sharp deterioration of memory, absent-mindedness, decreased concentration, convulsions, numbness of the limbs, and impaired coordination of movements.
- The third stage is characterized by focal and irreversible damage to brain tissue. In such cases, the disease manifests itself as dementia and other symptoms depending on which part of the brain is affected the most. The last stage of angioencephalopathy may be accompanied by tinnitus, weakness, mood instability, insomnia, decreased level of thinking, visual disturbances, amnesia, voice changes and impaired swallowing reflex, involuntary twitching of the lips.
WE RECOMMEND SEEING: Cerebral angiodystonia of cerebral vessels
At the last stage, the pathological process leads to disability of the patient. A person completely loses the ability to fully navigate everyday life and society.
Diagnostic methods
The presence of vascular disorders can be confirmed only after a comprehensive examination and consultation with specialized specialists. A therapist treats cerebral angioencephalopathy in adults. If there are concomitant pathologies, you will need to contact a cardiologist, neurologist and endocrinologist.
Diagnosis of the disorder begins with an external examination of the patient and examination of his complaints. If angioencephalopathy is suspected, instrumental and laboratory tests are required. The standard course of such events includes:
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the head to assess blood circulation.
- Angiography.
- Doppler examination of blood vessels.
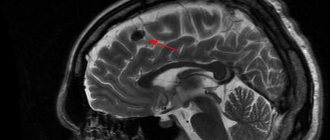
- MRI. This is the most informative diagnostic method that can show MRI signs of cerebral angioencephalopathy.
The patient must also take a blood biochemistry test and undergo a blood clotting test, as well as an analysis for cholesterol and glucose levels. Based on the examination results, the doctor can make a conclusion about how damaged the brain is and select therapy.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of vascular microangiopathy of the brain is made based on medical history. The doctor determines the risk factors that are associated with the pathology - excess weight, abnormal glycemic index, long-term arterial hypertension, diseases of the cardiovascular system. A biochemical blood test shows the level of glucose and lipids, and features of renal function. To confirm the diagnosis, an instrumental examination is performed with visualization of the elements of the blood flow system.
An MRI study shows destructive changes in the tissues of the vascular wall of small arteries. Disturbances are manifested by leukoencephalopathy (diffuse damage to the white medulla), lacunar infarction, the presence of foci of microhemorrhages, and atrophic tissue changes. Additional instrumental methods: Dopplerography, electrocardiogram, electroencephalogram.
Taking medications
It is not possible to completely restore brain function with angioencephalopathy. Therefore, the therapeutic methods used for treatment should be aimed at slowing down destructive changes in cerebral circulation and eliminating the microsomatic processes that provoked them.
The chronic form of the pathology does not require hospitalization. The patient can be admitted to the hospital only if there is a somatic defect and a high probability of stroke.
Depending on the stage of cerebral angioencephalopathy, treatment is carried out using the following drugs:
- Nootropics (“Nootropil”, “Actovegin”). Helps improve metabolic processes between cells.
- Antihypertensive drugs (“Lisinopril”, “Nimodipine”). Stabilizes blood pressure and improves its performance.
- Anticoagulants (“Curantil”). With their help, they achieve a decrease in blood viscosity.
- Statins (“Lovastatin”, “Simvastatin”). Drugs from this group are recommended for atherosclerosis, since in this case it is necessary to reduce cholesterol levels.
- Chondroprotectors. Used in the presence of severe problems with the spinal column.
If a patient suffers from diabetes, he is given a special diet and appropriate medications.
Types of microangiopathy
Peripheral microangiopathy can affect small arteries, veins, and capillaries located in the brain. If large vessels are affected, we are talking about a form of the disease called macroangiopathy. Depending on the causes, nature of changes and characteristics of the course of the disease, types are distinguished: cerebral, hypertensive, lenticulostriate, diabetic microangiopathy.
Cerebral
Cerebral microangiopathy of brain tissue is a form of the disease that is characterized by endothelial dysfunction, which negatively affects the structure and tone of the vascular wall. Cerebral angiopathy is accompanied by a decrease in the bioavailability of nitric oxide, which leads to a decrease in protective functions and damage to small vessels and capillaries of the brain. The situation worsens against the background of oxidative stress (the action of free radicals) - the accumulation of free oxygen, which inactivates nitric oxide.
Hypertensive
Pathology occurs due to arterial hypertension. During an ophthalmological examination, foci of microhemorrhage and a tortuous, corkscrew-shaped bed of arteries and veins are revealed (Gwist's symptom).
Lenticulostriate
This form of pathology is diagnosed in every 6th newborn during a routine examination using neurosonography. It is considered a variant of the norm. The child is under the supervision of a neurologist. Often, after a course of treatment with drugs that stimulate trophism of brain tissue and cellular metabolism, regression of destructive changes and restoration of normal blood supply are observed.
Diabetic
Destructive changes in the vascular wall with subsequent disruption of blood flow occur against the background of progression of diabetes mellitus. It is characterized by thickening of the basement membranes, proliferation of connective tissue, followed by narrowing of the lumen.
The need for surgery
When the lumen of the vessels is significantly narrowed, angioencephalopathy of the brain continues to progress, surgery is recommended. There are two ways to improve blood circulation with this diagnosis: stenting or bypass surgery. In the first case, the walls of the vessels are expanded and strengthened, and in the second, the diseased vessel is replaced with an artificial one. The decision about which type of surgery to use is made by the doctor. At the same time, it takes into account the severity of the disease and the presence of concomitant health problems.
Prognosis for recovery
The sooner treatment is started, the higher the likelihood of a favorable outcome. Doctors find it difficult to give any prognosis for cerebral angioencephalopathy, since its course depends on several factors:
- location of the lesion;
- timeliness of diagnosis and therapy;
- general state of human health;
- severity of the primary disease.
According to medical statistics, vascular encephalopathy is the cause of dementia in older people in 15% of cases.
Possible complications
Patients with angioencephalopathy must be prescribed background therapy with antiplatelet medications to stabilize blood pressure. Untimely treatment of vascular pathologies of the brain can lead to complications such as oxygen starvation, disruption of the integrity of blood vessels and hemorrhage. Over time, such patients develop fits of laughter, followed by hysteria. There is a coordination disorder and manifestations of oral automatism. Against the background of damage to the occipital zone of the brain, a decrease in vision and even its complete loss cannot be ruled out.
Prevention methods
Now you know the main causes and symptoms of cerebral angioencephalopathy, what it is. Is it possible to prevent the development of the disease?
First of all, doctors advise undergoing a medical examination once a year to identify pathology at the initial stage. In this case, no specific therapy is prescribed, but constant monitoring by specialized specialists is required.
If you are at risk, you should pay special attention to your own health. You need to establish a sports regime and regularly do exercises for the collar area. The therapist should tell you more about them. Some people benefit from physical therapy sessions. At the same time, one should not forget about proper nutrition. You will need to exclude excessively salty and peppery foods from your diet.