Diagnostics
Vascular obstruction is a condition that requires prompt medical attention, as there is a risk of death.
To prevent the development of complications, a very precise research method is used: Dopplerography and duplex scanning. Using an ultrasound device, the doctor assesses the state of blood flow and determines the affected area. The method is used to examine the vessels in the legs and arteries supplying the brain. An additional way to make a diagnosis is radiography using a contrast agent. Most often used to determine obstruction of the heart vessels. In case of acute blockage of cerebral vessels, MRI and CT are used to visualize a developing stroke.
The traditional technique boils down to dissolving the resulting blood clot. For this purpose, anticoagulants or thrombolytics are prescribed. For coronary artery stenosis, Nitroglycerin is prescribed, which can expand the lumen of the vessel, as well as medications that contain acetylsalicylic acid, which can prevent the formation of blood clots:
Causes and symptoms of vascular blockage
Often, the cause of blockage of blood vessels is also a genetic predisposition .
Depending on what mechanisms were involved, exogenous blockage , when it occurs due to the entry of bacteria and parasites, air, gas or foreign bodies. There is also endogenous blockage , when fat accumulates in the vessels, a blood clot forms, decompression sickness develops, and amniotic fluid spills.
Blockage of many blood vessels in the brain occurs most often due to the formation of cholesterol plaques, which gradually increase and block the lumen in the vessels. This disrupts the flow of blood to the brain, harms the vessels themselves, which lose their elasticity and strength, and a blood clot develops. As a result of such phenomena, a stroke or hemorrhage may develop.
IMPORTANT! The main reason that provokes the appearance of blood clots and other problems with the blood vessels of the brain is an unhealthy diet, with a lot of fatty foods, alcohol and cigarettes.
The presence of fatty, low-quality foods provokes the formation of excess bad cholesterol in the body, which in turn causes the appearance of atherosclerosis . The latter is the cause of frequent strokes and cerebral hemorrhages. A cholesterol plaque disrupts the wall of a vessel, an artery, and leads to a narrowing of the vein. In the future, other diseases may develop that will require surgery.
Symptoms of blockage of blood vessels in the brain may include:
- loss of speech or unclear speech of the patient,
- severe headache and dizziness.
When the brain tissues do not receive the required amount of oxygen-enriched blood, this leads to the death of its cells and tissues, the entire structure of the brain and its functionality changes. Depending on which part of the brain the vascular damage is localized, loss of sensitivity of tissues and limbs develops, vision and hearing decrease.
Treatment of cerebral embolism involves urgent surgical intervention.
Blockage of the heart vessels can occur regardless of a person’s age. Modern medicine can explain some of the mechanisms of development of this pathology, although it is not yet possible to name all the causes of the disease.
When the brain tissues do not receive the required amount of oxygen-enriched blood, this leads to the death of its cells and tissues, the entire structure of the brain and its functionality changes. Depending on which part of the brain the vascular damage is localized, loss of sensitivity of tissues and limbs develops, vision and hearing decrease.
Consequences of the disease
A decrease in patency can have the most unpleasant consequences for the patient. The consequences of a developing disease can be very diverse and, again, will depend on the location of the damaged vessel.
So, at the initial stage * blockage of blood vessels in the extremities * is fraught only with the appearance of pain and pulling sensations in the legs. Prolonged obstruction entails the formation of trophic ulcers and complete tissue necrosis. With such a diagnosis, the patient is indicated for limb amputation. Otherwise, he may develop gangrene.
Prolonged ischemia of the heart vessels often causes the development of myocardial infarction. The extent of tissue damage in this case will depend on the volume of the area affected by the obstruction.
Long-term blockage of blood vessels in the brain is no less dangerous. Increased blood pressure and headaches caused by ischemia of brain tissue often indicate the onset of an ischemic attack, the final stage of which may be a stroke.
MRI of the brain vessels will allow the doctor to get a complete picture of the state of the brain tissue and take timely measures to exclude death or permanent disability.
How to treat pathology
Regardless of the severity and nature of the disease, it requires proper and timely treatment. In general, the tactics involve two directions.
Symptoms of blockage of the veins of the lower extremities located close to the surface are most specific. The clinical picture looks like this:
1.General information
Obviously, there is no need to describe in detail the key role and countless functions of the brain in the human body. Let us only note that the central nervous system, i.e. The brain and spinal cord are an incredibly complex organ that controls absolutely all processes, including the activity of the endocrine glands (which, in turn, regulate the functioning of internal organs through hormones). For the most part, this control by the central nervous system is carried out automatically, without the participation of consciousness. However, the neural tissue of the brain, like any other living tissue, can perform its functions productively only if there is a constant supply of nutrients and energy, i.e. oxygen necessary for redox biochemical reactions. The brain receives all this through the bloodstream. And if for some reason the flow of arterial blood enriched in the lungs is sharply reduced or completely blocked, a catastrophe will very soon occur in this area, in the literal sense of the word.
Ischemia (lack of blood supply) triggers dystrophic and degenerative changes (structural and functional degradation of tissue, which, against the background of constant starvation, copes with its tasks increasingly poorly); then atrophy occurs - gradual death and reduction in volume. In the event of a sudden interruption (ischemic attack), if the blood supply is not restored quickly enough, necrosis begins - mass death of specialized cells. In general, this terrible phenomenon is called “infarction” (of the myocardium, kidney, spleen, etc., including the brain), however, in relation to the central nervous system, the term “stroke” (literally “stroke”, more accurate modern) is more often used term – stroke, i.e. acute cerebrovascular accident). Strokes are divided into two unequal groups: rarer hemorrhagic strokes (hemorrhages), caused, for example, by the rupture of a congenital arterial aneurysm, and ischemic strokes (over 80% of all strokes), associated with restriction or blocking of blood flow through the vessels supplying the brain.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
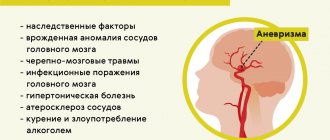
Factors affecting blockage
- an unbalanced diet with a predominance of fatty foods, fast food is dangerous for the formation of cholesterol plaques,
- a sedentary lifestyle contributes to blood stagnation,
- excessive consumption of alcohol and cigarettes affects the elasticity of tissues,
- excess weight leads to additional stress on the circulatory system,
- stress,
- genetic predisposition,
- diabetes,
- taking contraceptives,
- lipid metabolism disorders.
What information is missing from the article?
- Detailed review of medications
- More practical treatments
- Innovative developments in this area
- Qualified expert opinion
2. Reasons
Considering the critical, priority importance of the brain, evolution took care of its maximum protection: powerful skull bones, upper location, as well as “reserve circuits” of cerebrovascularization (blood supply to the brain). The brain receives nutrition from several main vessels - the carotid and vertebral arteries; the latter, merging, form the unpaired basilar artery, or vertebrobasilar arterial system. If there are disturbances in any of the blood supply channels, other channels compensate for the deficiency in order to preserve the functioning of the brain at any cost. The compensatory capabilities of the brain in this sense are very great (and have not yet been sufficiently studied), however, unfortunately, they also have their limits. With intense sudden ischemia, the cerebrovascular system simply does not have time to react and prevent irreversible necrotic changes.
Spasm of the main cerebrovascular vessels can occur for various reasons: massive bleeding, sudden blow, rapid hypothermia, poisoning with certain substances, etc. However, all these factors occupy only a small proportion compared to the leading cause of ischemic stroke: embolism, i.e. blockage of the arteries by a detached atherosclerotic plaque, a clot of coagulated blood, etc. In general, arterial hypertension and atherosclerosis, lipid metabolism disorders with the accumulation of mushy deposits on the walls of blood vessels, are typical “diseases of civilization”, since they are largely caused by the very lifestyle and destructive habits of modern man: physical inactivity, extremely unhealthy diet and overeating, smoking etc. It is no coincidence that circulatory disorders in various systems of the body (primarily the coronary and cerebral arterial systems) consistently occupy first place in the lists of causes of non-violent mortality.
Visit our Neurology page
Relief of the disease
Treatment of vein blockage is carried out using modern methods that eliminate pathology both in the initial and late stages of development. Options for relieving the disease are selected depending on the degree of damage to the vessel. Blocked veins in the legs, for which there are no symptoms, can be treated with medication at home.
Drug therapy
Conservative therapy is prescribed in the initial stages of the disease and is carried out at home. It is a drug treatment combined with compression and physical therapy. To eliminate blockage of veins, certain groups of drugs are used:
- Direct anticoagulants: Fraxiparin, Heparin, Fragmin, Clexane. Allows you to reduce blood density and clotting. The drug requires constant monitoring of the blood flow, as it can cause bleeding.
- Indirect anticoagulants: Coumadin, Warfarin. Designed to suppress the production of prothrombin, which increases blood clotting.
- Enzymatic drug. Indicated for dissolving blood clots: Urokinase.
- Hemorheoletics: Reosorbilact, Refortan. The therapeutic effect is to regulate the composition, structure and circulation of blood flow.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Diclofenac. Prescribed in case of severe pain due to blockage of the veins of the leg.
Drugs for drug treatment are prescribed only by the attending physician, who determines the exact dosage and treatment regimen for each patient, based on his diagnostic data. The patient can take medications at home in the form of tablets or visit a day hospital for injections.
In case of illness, enzymatic preparations are prescribed to dissolve blood clots.
Surgical intervention
Blocked veins in the legs, which cannot be treated with drug therapy at home or in a hospital, require surgical intervention. Basically, surgical methods are indicated for the formation of a volumetric thrombus, which has a high risk of detachment from the vessel wall. Proven and effective means are used as operational methods.
Troyanov-Trendellenburg method. It involves suturing the lumen of the trunk of the main saphenous vein with metal clips or clamps, which allow blood flow to circulate freely, but will not allow a blood clot to penetrate into the femoral vein.
Kava filter. The essence of this option is to install a symmetrical trap, reminiscent of an umbrella frame, into the inferior vena cava. It prevents the blood clot from moving towards the heart, lungs and brain, capturing it with its spokes.
Thrombectomy. Designed to remove a blood clot from the arteries of the lower extremities using a surgical catheter. The procedure is performed through a micro-incision in the groin area, into which a thin, hollow tube is inserted for surgical manipulation.
The listed procedures do not require long-term hospitalization. As a rule, after 3-10 days the patient is discharged home.
3. Symptoms and diagnosis
The clinical picture of blockage of the blood vessels supplying the brain can vary over a very wide range.
Symptoms depend, first of all, on the location and extent of the ischemic area. Early warning signs may include frequent dizziness and headaches, decreased memory and intellectual productivity, presyncope and sudden short-term fainting (syncope), false tactile sensations (paresthesia).
With more pronounced pathology, numbness, partial paralysis, certain speech disorders (articulation disorders, inability to quickly update the necessary words, impoverishment of vocabulary), various dysfunctions in the field of recognition, coordination of movements and spatial orientation, fine motor skills (in particular, writing) are added. , emotional response, behavior, physiological processes and many others.
With stroke, the same focal symptoms develop, by definition, acutely, catastrophically; Unlike disorders of brain activity during transient attacks or crises, such symptoms are persistent.
Diagnosis of suspected thromboembolism includes a mandatory consultation with a neurologist, as well as, if indicated, a number of related specialists (cardiologist, neurosurgeon, etc.). The most informative instrumental research methods are X-ray contrast multislice computed tomography (MSCT in angiographic mode), Dopplerography (ultrasound assessment of the patency of the great vessels), and MRI angiography.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
How to distinguish phlebothrombosis from thrombophlebitis
The two processes that occur in the vessels of the legs have a number of important differences:
- Phlebothrombosis is a blockage in the deep veins, and thrombophlebitis is a blockage in the superficial veins.
- With phlebothrombosis, the risk of developing thromboembolism (a fatal complication of occlusion) is much higher than with the second pathology.
Symptoms of the disease
Complete blockage of the vessels of the lower extremities has clear, clearly defined symptoms. In particular, patients note:
- the so-called “whiplash” - intense pain that occurs unexpectedly;
- feeling of coldness in the extremities;
- decrease in the brightness of the color of the skin of the legs, in the vessels of which there is a blockage;
- feeling of weakness in the legs;
- lameness;
- in the arteries located below the site of occlusion, pulsation is not palpable.
In cases where there is only partial blockage of the veins of the lower extremities, the clinical picture is not pronounced. It is for this reason that the patient may not suspect that he has a pathology. As the lumen decreases, the following clinical manifestations may appear:
- painful sensations in the limb that suffers from pathology;
- pronounced swelling of the leg at one point;
- staining the skin red or blue;
- muscle tightening;
- the affected limb becomes larger.
Symptoms of blockage of the veins of the lower extremities located close to the surface are most specific. The clinical picture looks like this:
- pain in the area of the vessel with occlusion;
- change in the color intensity of the skin just above the affected vessels of the legs (pallor);
- dense formations felt when touched;
- swelling near the damaged vessel.
4.Treatment
For partial, chronic, gradually progressive disorders of cerebral circulation, it is prescribed strictly according to indications and taking into account a number of individual factors, i.e. self-medication is strictly contraindicated and deadly! – various effective therapeutic regimens, including stimulants of cerebral hemodynamics and neurometabolism (nootropics), protectors of cognitive functions, thrombolytics, antiplatelet agents, vitamin complexes.
It is mandatory to normalize your lifestyle, exercise and sleep patterns, and give up bad habits.
However, in the most acute and severe cases of embolism, the only choice is neurosurgical intervention to restore the patency of the cerebrovascular vessels and eliminate the consequences of ischemia. At the same time, timely seeking specialized help and strictly following the recommendations of a neurologist in most cases allows one to avoid such an outcome. The brain is not an organ that can be risked by waiting for natural or non-medical healing.
Dyspnea
This symptom is observed when the coronary arteries are damaged. People experience shortness of breath because their hearts are unable to transport the required level of blood to meet the body's needs.
People often think that shortness of breath is not a serious problem. But sometimes it can be the main sign of coronary heart disease that requires treatment.
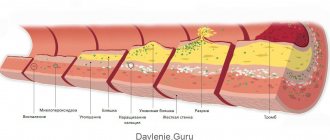
Mechanism of blood clot formation
The process of blood clot formation is called thrombosis.
The point of this process is to block the damaged area by denaturing protein and other blood elements. The structure of the thrombus is designed to maintain normal blood flow, and its reliable adhesion to the vessel under normal conditions does not provide for separation.
Blood clots form in this way:
- From the damaged area on the vessel, substances begin to be released that inhibit processes that reduce blood clotting.
- Platelets begin to change their structure, and components (thrombin and thromboblastin) are released into the blood, promoting its clotting.
- Fibrinogen (a protein that promotes rapid platelet sedimentation) under the influence of thrombin is converted into a substance that is the basis of a blood clot and forms it in the form of a mesh of threads.
- Blood elements (erythrocytes, platelets, leukocytes) begin to accumulate in the cells of the thrombus mesh.
- The formation becomes denser over time.
- The process of thrombus formation is completed, and the damaged vessel is occluded.
Classification of vascular pathologies
• Atherosclerosis• Endarteritis• Varicose veins• Vascular obstruction• Blockage of deep veins• Thrombophlebitis
In the first case, there is a complete narrowing of the distance between the walls of the veins of the lower extremities. Acute vascular insufficiency can also be diagnosed.
As for chronic occlusions, they are characterized by not complete, but only partial narrowing of the lumen. Chronic forms of venous insufficiency are also observed.
This group includes a number of diseases that can be divided into two types:
- Arterial lesions: atherosclerosis, obliterating endarteritis and others.
- Vein diseases: varicose veins, phlebitis, thrombophlebitis, thrombosis.