Agenesis of the corpus callosum is a congenital brain abnormality that occurs in a newborn in the early prenatal period. Develops between 12 and 16 weeks of gestation because fetal brain development is at its peak during this period.
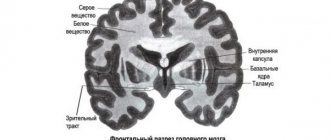
The corpus callosum (CC) is a large, white, C-shaped plexus of fibers that divides the cerebral cortex into the right and left hemispheres. It is an integral both structural and functional part of the human brain. It forms the bottom of the longitudinal fissure separating the left and right hemispheres.
Although the corpus callosum is thought of as one large white bundle of fibers, it is made up of individual fibers known as commissural fibers.
The main purpose of the corpus callosum is to integrate information by combining both hemispheres of the brain to process motor, sensory and cognitive signals. The MT connects similar areas of the brain and transmits information through the left and right hemispheres.
It is the most extensive connecting pathway in the brain, with 200 million axonal projections in the middle of the two hemispheres. It occupies the center of the brain and is more than 10 cm long.
Children born with this diagnosis have varying outcomes, ranging from normal function in the mildest cases to a range of potential health problems.
Agnesia of the corpus callosum in a newborn can cause delays in the development of the child’s motor and speech skills. But for many, emerging cognitive impairments do not prevent them from having normal intelligence.
A disorder of the corpus callosum is not a disease in itself. Many people with AMT lead healthy lifestyles. Mild cases include minor motor problems, while more severe cases include low IQ, blindness, seizures, spastic movements and more that require medical attention.
Kinds
Structural disorders of the corpus callosum take on different types due to various reasons:
- AMT – complete absence of body. If nerve fibers do not cross between the hemispheres during the critical prenatal time, then this will not happen in the future. The absence of the corpus callosum becomes a permanent feature of the human brain.
- Hypogenesis is the partial absence of the corpus callosum. At the same time, MT begins to develop, but something stops it. As the body develops from front to back, part of it is directed to the front of the brain, and the back part does not form.
- Hypoplasia of the corpus callosum. In this case, the MT is formed, but its volume is incomplete, since during its formation the number of commissural fibers was less than that necessary for the formation of the MT.
- Dysgenesis. A condition in which the corpus callosum has an unusual shape. Dysgenesis means that the MT has developed but is not fully formed or is not formed correctly. Dysgenesis is a broad term for any abnormality of the corpus callosum that is not completely absent (agenesis).
Failures in brain development are possible at any stage of the formation of the central nervous system. In the first and second trimesters, there may be a decrease in the number of neurons, incomplete formation of various parts of the brain, and then this will lead to damage or death of the corpus callosum.
AMT-related brain abnormalities:
- hydrocephalus;
- Arnold-Chiari defect;
- schizencephaly (deep clefts in the brain tissue);
- holoprosencephaly (inability of the forebrain to divide into lobes);
- migration disorders;
- Aarsky-Scott syndrome;
- Aicardi syndrome.
The types of abnormalities that occur depend on the timing and cause of the disorder in prenatal brain development. If the corpus callosum does not form during the prenatal period, it will not develop later.
Anatomy and functions
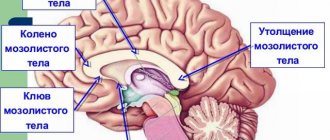
The corpus callosum is covered on top by a small layer of cerebral gray matter, which explains, accordingly, the gray covering on it. Upon visual examination, 3 main sections can be distinguished:
- trunk (or midbrain);
- knee (part of the brain located in the front);
- beak or splenium of the corpus callosum (posterior section).
The brightness of the large commissure (when viewed on photographs or in section) is provided by fibers that are located radially and are located in each of the hemispheres.
The middle section, when viewed, looks like a bulge, which is also the longest part of the entire brain. The posterior section is visually visible as a thickening relative to other sections and zones, which is freely located above neighboring areas of the brain. The gray matter is represented by stripes and is located on top.
Functions provided by the corpus callosum:
- transfer of information (impulses) important for the functioning of the body from one hemisphere to the other;
- formation of the main characteristics that define personality and its characteristics;
- basic (basic, defining) skills and the possibility of their application throughout a person’s life;
- work on the formation of the emotional and personal sphere.
Stages and degrees
There are two stages of AMT:
- Primary, genetic. The defect develops as an isolated condition until the fetus is 12 weeks of age.
- Secondary, complicated. It occurs against the background of an already formed corpus callosum. It appears in combination with other cerebral disorders, including various malformations: cleft brain, lack of separation between the hemispheres, midline facial defects. The consequences of the disorder range from mild to severe.
Children with the most severe brain defects may have:
- intellectual disabilities;
- convulsions;
- hydrocephalus, the accumulation of excess fluid in the brain system;
- spasticity or increased muscle tone;
- dysgenesis, in which the corpus callosum develops incorrectly or defectively;
- hypoplasia, in which the corpus callosum is thinner than normal.
Agenesis and hypoplasia of the corpus callosum
The plexus of nerve fibers in the brain connecting the right and left hemispheres is the corpus callosum, consisting of more than two hundred million nerve fibers. The corpus callosum is the largest structure that connects the hemispheres. Once formed, the corpus callosum grows further in length and width. The intersection of fibers and their penetration from one hemisphere to the other begins at twelve weeks.
With congenital partial or complete absence, they speak of agenesis of the corpus callosum .
In the case of aplasia (agenesis) and hypoplasia of the corpus callosum , the main commissure formed by the commissural fibers is either partially or completely absent and the third ventricle remains open. With agenesis, there are columns of the fornix and transparent septa, and in the case of hypoplasia, only the posterior commissure is absent, and the corpus callosum is shortened. Defects in the corpus callosum generally accompany other disorders in the brain, although they can also occur in isolation.
These types of defects begin to appear approximately in the second week after conception.
The frequency of their occurrence is one in two to three thousand.
Neurological defects
Associated neurological defects may include:
- microgyria,
- porencephaly,
- optic nerve atrophy,
- lipomas (corpus callosum and interhemispheric),
- hypoplasia of the limbic system,
- interruption of the beginning of the corpus callosum,
- schizencephaly,
- cysts in the area of the corpus callosum,
- spina bifida,
- colobomas (defect of the lens, eyelid tissue or iris, choroid or retina of the eye),
- absence of a transparent partition and a number of others.
Possible manifestations of the disease include microcephaly, HCF, seizures (rare), early puberty, and cleft syndrome, which is more common in acquired defects of the corpus callosum than in congenital defects.
In particular, the disease can also manifest itself as Aicardi syndrome, which is considered a rare genetic disease, which is characterized by agenesis of the corpus callosum, epileptic seizures in the form of infantile spasms, peculiar lacunar transformations in the fundus, and special changes in electroencephalography of the brain, known as the “split brain” pattern. , inhibition of psychomotor development, and also facial dysmorphism.
All about agenesis of the corpus callosum
Agenesis of the corpus callosum is a congenital structural disorder of neuroontogenesis. Clinically, agenesis of the corpus callosum manifests itself in mental retardation of various levels. movement disorders, epileptic seizures, as well as abnormal development of internal organs. Agenesis of the corpus callosum can be inherited or may occur as a result of spontaneous mutations. Among the variants of agenesis of the corpus callosum, the most common is Aicardi syndrome .
There have been approximately five hundred cases of Aicardi syndrome worldwide, most of all in Japan.
A wide variety of eye development abnormalities have been observed in Aicardi syndrome. These are, for example, retinitis pigmentosa, with varying degrees of deterioration in visual acuity, microphthalmia, optic nerve atrophy, cataracts.
Skeletal abnormalities in developmental disorders of the corpus callosum
There are also skeletal anomalies - hemivertebrae and missing ribs.
Maxillofacial anomalies were also observed, the most common of which were protruding incisors, a reduced angle of the nasal septum, an upturned tip of the nose, and sparse eyebrows. In addition, 22.5% of patients had skin lesions, and 7.5% had malformations of the limbs. Abnormalities in the gastrointestinal tract and a high incidence of tumor formation were also noted.
Therapy for Aicardi syndrome has not yet been developed, so symptomatic treatment is used. Basically, it all comes down to eliminating infantile spasms, but this treatment is complex and its effectiveness is too low. A variety of drugs are used in the highest possible doses.
For example, at the beginning of treatment, vigabatrin (Sabril) is prescribed - up to one hundred milligrams per kilogram of the patient’s body weight per day.
An alternative treatment is the use of corticosteroid hormones.
MOST INTERESTING NEWS
Hello. I have a very pressing question. Because Doctors only reassure and don’t really say anything. There is little information about this on the Internet. I really need your help. We were examined today. A diagnosis was made. hypoplasia of the corpus callosum, deformation of the choroid plexuses of the 2nd degree, the pattern of convolutions is underlined, the brain parenchyma is not homogeneous.