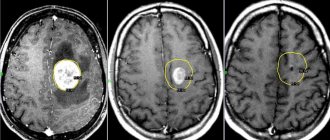
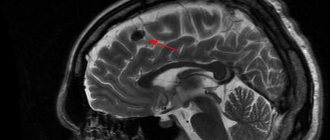
The body of any living creature must work smoothly, like a clockwork. Any disruptions will certainly affect your overall well-being. In the last century, scientists determined that the brain emits electrical signals that are produced by many neurons. They pass through bone and muscle tissue and skin.
They can be detected by special sensors attached to different parts of the head. The amplified signals are transmitted to an electroencephalograph. After deciphering the resulting electroencephalogram (EEG), neurologists often make a frightening diagnosis, which may sound like “mild diffuse changes in the bioelectrical activity of the brain.”
Recorded bioelectrical activity is an indicator of the functioning of brain cells. Neurons must be connected to each other to exchange data on the functioning of all organs. Any deviations in the BEA indicate malfunctions in the brain. If finding the lesion is problematic, then the term “diffuse changes” is used - uniform changes in the functioning of the brain.
What is EEG
“Communication” of neurons occurs through impulses. Diffuse changes in the BEA of the brain indicate improper organization of communication or its absence. The difference in biopotentials between brain structures is recorded by electrodes that are attached to all main areas of the head.
The resulting data is printed on graph paper in the form of multiple electroencephalogram (EEG) curves. A small difference between the measurement results and the normal value is called mild diffuse changes.
There are factors that may distort the results of the study. Doctors should definitely take them into account:
- general health of the patient;
- age group;
- the examination is done in motion or at rest;
- tremor;
- taking medications;
- vision problems;
- consumption of certain foods;
- last meal;
- cleanliness of hair, application of styling products;
- other factors.
EEG provides a unique opportunity to evaluate the functioning of individual parts of the brain. Low vascular conductivity, neuroinfections, and physical injuries cause diffuse changes in the brain. Electric sensors are capable of recording the following rhythms:
- Alpha rhythm. It is registered in the area of the crown and back of the head in a calm state. Its frequency is 8-15 Hz, the highest amplitude is 110 μV. Biorhythm rarely appears during sleep, mental stress, or nervous excitement. During menstruation, the levels increase slightly.
- The beta rhythm is the most common rhythm in adults. It has a higher frequency than the previous type (15-35 Hz) and a minimum amplitude of up to 5 µV. However, during physical and mental stress, as well as when the sensory organs are irritated, it intensifies. Most pronounced in the frontal lobes. By deviations of this biorhythm one can judge neuroses, depression, and taking a number of substances.
- Delta rhythm. In adult patients it is recorded during sleep, but in some people during wakefulness it can occupy up to 15% of the total impulse volume. In children under one year of age, this is the main type of activity; it can be recorded already from the second week of life. Frequency – 1-4 Hz, amplitude – up to 40 µV. These indicators allow you to determine the depth of the coma, suspect the effects of drug use, the presence of a tumor and the death of brain cells.
- Theta rhythm. Dominant rhythm for children under 6 years old. Sometimes it occurs later in life, but only in dreams. Frequency 0 4-8 Hz.
Interpretation of results
Diffuse changes in the EEG indicate the absence of obvious lesions and foci of pathology. In other words, the potentials are different from the norm, but there are no critical deviations yet. The manifestation will be expressed as follows:
- conductivity is heterogeneous;
- asymmetry appears periodically;
- fluctuations beyond the normal limits;
- polymorphic polyrhythmic activity.
The EEG may show signs of increased ascending activating influences of nonspecific medium structures, which indicates physiological reactions. Most often, the range of certain types of waves is exceeded. However, to make a diagnosis of “diffuse lesion,” deviations must be present on all counts.
The waves will differ in shape, amplitude and periodicity. Rhythm is the main evaluation parameter. Uniformity allows us to talk about the coordinated work of all components of the nervous system and is the norm.
Changes in the EEG for a number of indicators can be observed in most people - caffeine, nicotine, alcohol, sedatives affect the data obtained as a result of the study, causing minor diffuse changes. A few days before the examination, it is advisable to stop using them.
Paroxysmal activity
This is a recorded indicator indicating a sharp increase in the amplitude of the EEG wave, with a designated source of occurrence. This phenomenon is believed to be associated only with epilepsy. In fact, paroxysm is characteristic of various pathologies, including acquired dementia, neurosis, etc.
In children, paroxysms can be a variant of the norm if there are no pathological changes in the structures of the brain.
During paroxysmal activity, the alpha rhythm is mainly disrupted. Bilaterally synchronous flashes and oscillations are manifested in the length and frequency of each wave in a state of rest, sleep, wakefulness, anxiety, and mental activity.
Paroxysms look like this: pointed flashes predominate, which alternate with slow waves, and with increased activity, so-called sharp waves (spikes) appear - many peaks coming one after another.
Paroxysm with EEG requires additional examination by a therapist, neurologist, psychotherapist, a myogram and other diagnostic procedures. Treatment consists of eliminating causes and consequences.
In case of head injuries, the damage is eliminated, blood circulation is restored and symptomatic therapy is carried out. For epilepsy, they look for what caused it (tumor, etc.). If the disease is congenital, the number of seizures, pain and negative effects on the psyche are minimized.
If paroxysms are a consequence of problems with blood pressure, treatment of the cardiovascular system is carried out.
Diffuse changes in biopotentials
Deviations in brain function are associated with localized or diffuse damage. In the second case, it is problematic to accurately determine the source of violations.
Such changes are called diffuse.
With focal lesions, their location is usually easy to determine. For example, problems with balance and severe nystagmus are symptoms of cerebellar damage.
Diffuse mutations can be diagnosed using two methods:
- Neuroimaging – MRI, CT. Tomograms make it possible to examine the thinnest sections of the brain in all planes. This method is good for diagnosing the consequences of atherosclerosis and vascular dementia. Such abnormalities with high blood cholesterol levels can be detected even when memory problems have not yet manifested themselves.
- Functional – EEG. Electroencephalography allows you to obtain indicators that are a quantitative characteristic of brain function. It helps diagnose epilepsy before seizures occur. Epilepsy is always accompanied by diffuse changes in BEA of a specific nature, causing seizures. The diagnosis must indicate their degree: mild, severe, moderate. Even completely healthy people are diagnosed with a mild degree.
There is no need to worry about this - the word “healthy” is not in any EEG report. The entire cortex undergoes diffuse changes, but this does not indicate the presence of local damage.
The main symptom of epileptic activity will be an anomaly of the delta rhythm, periodic tracing of peak-wave complexes. Only a neurophysiologist can issue a correctly deciphered EEG conclusion, since extensive changes in brain activity may not be accompanied by other signs of epilepsy.
Then the doctor talks about “the interest of the middle structures” or uses other similar vague formulation. This does not mean anything, since the EEG only makes it possible to confirm or exclude epilepsy. The absence of epileptic activity is indicated by “vague” diagnoses.
Significant diffuse changes are the result of the appearance of scar tissue, inflammatory processes, swelling, and death of brain structures.
Connections are disrupted in different ways across the surface of the brain.
Functional version of changes
Functional changes appear when the functioning of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland is disrupted. They pose a great threat in the short term, but prolonged exposure leads to irreversible consequences. The irritative nature of changes is often associated with cancer. Lack of proper treatment leads to a deterioration in the general condition.
The reasons that caused the change in biopotentials can also manifest themselves in a number of symptoms. At the initial stage of the disease, minor dizziness appears, but later seizures are likely.
Increased bioelectrical activity of the brain leads to:
- decreased performance;
- slowness;
- memory disorders;
- mental disorders: low self-esteem, indifference to previously interesting things.
Neurological signs develop:
- muscle spasms;
- headache, dizziness;
- deterioration of vision and hearing.
Deep diffuse changes in the brain indicate a tendency to seizures.
A slight change is pronounced when:
- softening and thickening of tissues;
- tissue inflammation.
General cerebral changes in the bioelectrical activity of the brain are noted when:
- encephalitis;
- meningitis;
- atherosclerosis.
With diffuse glioma, a number of changes can be seen on the EEG. It takes 6-12 months to restore the natural functioning of neurons.
What is disorganization of bioelectrical activity of the brain
The term "irritation" means irritation. This word can be applied to all organs, but is more often used in the neurological field of medicine to name an irritation of the brain. Superficial structures (bark) and deeper components (trunk) can be involved in the process of this pathology.
It is also interesting to know that children, elderly people, and adults are equally susceptible to the manifestation of this symptom. In addition, the frequency of occurrence is in no way affected by a person’s gender. The reasons for the development of irritation can be very diverse, but there are several main ones:
- penetration of infectious agents for rheumatism, influenza, rubella, malaria, measles;
- the presence of diseases associated with metabolic disorders;
- pathological blood circulation due to atherosclerosis, ischemia, trauma or excessive intracranial pressure;
- neoplasms that compress the structures, they can be both benign and malignant;
- genetic predisposition to the occurrence of irritative changes;
- drug or alcohol use;
- psycho-emotional instability;
- insufficiently good ecology;
- hazardous at work.
What symptoms indicate damage to the cerebellum: congenital and acquired pathologies.
How glial changes in the brain manifest themselves: causes and mechanisms of development.
In addition, girls and women who previously had brain damage and are now planning a pregnancy should be extremely attentive to their condition. Since hormonal surges during gestation and the period of breastfeeding can trigger a relapse of the disease.
The word "irritation" is a loanword whose roots come from the Latin word irritare, meaning "to embitter" or "to irritate." Irritation of the cerebral cortex is irritation of parts of the brain, which entails many dangerous and unpleasant consequences for health.
Irritation of diencephalic structures of the brain is a neurological term that characterizes a number of disorders caused by irritation of parts of the brain. Depending on which part of the brain is affected, different symptoms may occur.
Slight diffuse changes in the bioelectrical activity of the brain often accompany injuries and concussions. With proper treatment, the patency of the impulses is restored after several months or even years.
Slight diffuse changes in the BEA of the brain are a consequence of traumatic and infectious factors, as well as vascular diseases.
- Concussions and injuries - the severity of the manifestation depends on the severity of the injury. Moderate diffuse changes in the bioelectrical activity of the brain lead to mild discomfort and usually do not require long-term treatment. The consequence of severe injuries are volumetric lesions of impulse conduction.
Desynchronization of bioelectrical activity immediately affects the patient’s well-being and discomfort. Initial signs of disturbances appear already in the initial stages.
Timely detection of moderately severe disorganization of the BEA is not critical for the health of the human body. It is enough to pay attention to deviations in time and prescribe restorative therapy.
Disorganization of the bioelectrical activity of the brain can be detected using several methods.
- History - a picture of diffuse disorders of BEA is visible in clinical manifestations identical to other diseases of the central nervous system. The doctor diagnosing pathological changes will conduct a full examination of the patient and pay attention to concomitant diseases and injuries.
Decoding the EEG does not make it possible to see the cause of the anomalies caused. EEG is useful in diagnosing advanced rates of BEA formation. In this case, it is possible to prevent the development of epileptic seizures.
Treatment of changes in the BEA of the brain is prescribed only after a complete examination of the patient, since to improve well-being, it is critical to eliminate the causes of the disorder.
Rough diffuse changes are a consequence of scar formation, necrotic transformations, swelling and inflammatory processes. Conduction disturbances are heterogeneous. Functional instability of the BEA in this case is necessarily accompanied by pathological disorders of the pituitary gland or hypothalamus.
The biopotential of the neural network, numbering 11-51 billion cells, is damaged for a number of reasons. BEA of the brain manifests itself based on the deviation, frequency (in μV, Hertz, boundary values, respectively):
- alpha - 5-100 and 8-13;
- beta waves - up to 20 and 14-40;
- gamma – 15 and 30-100;
- delta – 20-200 and 1-4.
According to physiology, the bioelectrical activity of brain processes is expressed by certain moderate and not very signs, if they occur, you should seek medical help.
Diffuse sclerosis
This type of pathology occurs most often.
The main culprit is tissue compaction as a result of oxygen deprivation. It occurs due to circulatory disorders and disorders that impair the transport of oxygen to cells. Older people are at greater risk. In the absence of effective treatment, complications develop. Liver failure and improper functioning of the kidneys cause general toxic damage to the body.
In addition to the above reasons, moderate diffuse changes in the bioelectrical activity of the brain develop due to disturbances in the functioning of the immune system. It affects the myelin sheath, destroying the protective layer. Multiple sclerosis begins to develop. Among patients with this disease, the majority are young people.
Prevention
The most common cause of diffuse changes is circulatory disorders due to vascular atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis develops against the background of poor nutrition. Some drugs can strengthen vascular walls, one of them is Ginkgo Biloba. And drugs of the statin class are now capable of lowering cholesterol levels. Fibrates reduce the ability to synthesize fats, thereby preventing the development of atherosclerosis.
And, of course, you need to take care of your head, since diffuse disorders after blows and head injuries take a long and difficult time to treat. But if you take care of the harmonious system of synaptic connections, monitor your diet and give yourself time for proper rest, your brain will function flawlessly and accurately for a long time.
Softening tissue
Softening of tissue appears after severe trauma, heart attack, resuscitation encephalopathy, acute neuroinfections with dislocation and cerebral edema.
Factors influencing the speed of the process:
- size, location of the outbreak;
- features and rate of development of concomitant pathologies.
Moderate changes in the bioelectrical activity of the brain occur due to various factors, but an indispensable condition will be damage to all brain tissue.
The following reasons are identified:
- cerebral edema;
- neuroinfections;
- suffered clinical death.
Inflammation in the brain occurs due to exposure to neuroinfections. In most cases, patients die.
What do EEG results show?
An electroencephalogram shows the functional state of brain structures during mental and physical stress, during sleep and wakefulness. This is an absolutely safe and simple method, painless, and does not require serious intervention.
Today, EEG is widely used in the practice of neurologists in the diagnosis of vascular, degenerative, inflammatory brain lesions, and epilepsy. The method also allows you to determine the location of tumors, traumatic injuries, and cysts.
EEG with the impact of sound or light on the patient helps to express true visual and hearing impairments from hysterical ones. The method is used for dynamic monitoring of patients in intensive care units in a coma state.
- EEG for children under 1 year of age is performed in the presence of the mother. The child is left in a sound- and light-proof room, where he is placed on a couch. Diagnostics takes about 20 minutes.
- The baby's head is wetted with water or gel, and then a cap is put on, under which the electrodes are placed. Two inactive electrodes are placed on the ears.
- Using special clamps, the elements are connected to wires suitable for the encephalograph. Due to the low current, the procedure is completely safe even for infants.
- Before monitoring begins, the child's head is positioned level so that there is no forward bending. This may cause artifacts and skew the results.
- EEGs are done on infants during sleep after feeding. It is important to let the boy or girl get enough immediately before the procedure so that he falls asleep. The mixture is given directly in the hospital after a general medical examination.
- For children under 3 years old, an encephalogram is taken only in a state of sleep. Older children may remain awake. To keep the child calm, they give him a toy or a book.
An important part of the diagnosis are tests with opening and closing the eyes, hyperventilation (deep and rare breathing) with EEG, squeezing and unclenching of the fingers, which allows disorganization of the rhythm. All tests are conducted in the form of a game.
After receiving the EEG atlas, doctors diagnose inflammation of the membranes and structures of the brain, latent epilepsy, tumors, dysfunction, stress, and fatigue.
The degree of delay in physical, mental, mental, speech development is carried out using photostimulation (blinking a light bulb with eyes closed).
For adults, the procedure is carried out subject to the following conditions:
- keep your head motionless during manipulation, eliminate any irritating factors;
- Before diagnosis, do not take sedatives or other drugs that affect the functioning of the hemispheres (Nerviplex-N).
Before the manipulation, the doctor conducts a conversation with the patient, putting him in a positive mood, calming him down and instilling optimism. Next, special electrodes connected to the device are attached to the head, and they read the readings.
The examination lasts only a few minutes and is completely painless.
Provided that the rules described above are observed, even minor changes in the bioelectrical activity of the brain are determined using EEG, indicating the presence of tumors or the onset of pathologies.
Reasons for violation of BEA
Disturbances in brain activity can result from:
- infections;
- vascular changes;
- physical damage.
Main reasons:
- Injuries, concussion. They determine the degree of pathology. Moderate cerebral changes do not require long-term medication and cause mild discomfort. More severe injuries cause more serious impairments.
- Irritative inflammation spreads to the medulla and cerebrospinal fluid. Changes develop gradually after meningitis and encephalitis.
- The early stage of vascular atherosclerosis becomes a source of minor diffuse changes. But later, due to poor blood supply, neuronal conduction begins to degrade.
- Irradiation, chemical toxemia. Tissue irradiation causes general diffuse changes. The results of intoxication affect the ability to lead a normal life.
- Accompanying diffuse disorders. They are explained by dysfunctions of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland (a special case is the empty sella syndrome of the brain).
The severity of the injury and the duration of the disease affect the number of lost connections between neurons.
Often in the EEG results one can see the diagnosis “signs of increased ascending activating influences of nonspecific medium structures.” It does not have a specific genesis. Moderate irritation of cerebral formations leads to primary changes.
Serious physical damage currently occupies the leading place among the root causes. Diffuse swelling provokes brain contusion, which appears during car accidents during sudden braking. Doctors do not guarantee a complete recovery even in the absence of fractures and hemorrhages.
This group of diffuse injuries is called axonal, and they are classified as very severe. With a sharp decrease in speed, axonal rupture occurs, since the stretching of cellular structures cannot compensate for the impact of sudden braking. Treatment takes time, but it is often ineffective: a vegetative state develops as brain cells stop functioning normally.
Causes of cerebral disorganization
Diffuse changes in BEA do not appear out of nowhere and are not genetically determined. These anomalies are formed due to disruption of certain processes and damage to neural connections. In particular, many diseases lead to disruption of the central nervous system.
Head injury
The intensity of diffuse changes in BEA completely depends on the severity of the injury. Moderate injuries cause discomfort in the patient and do not require long-term therapy.
Severe injuries can cause serious changes in the BEA, leading to severe dysfunction in the central nervous system.
Brain injuries include:
- concussion – occurs after a minor head injury;
- compression - occurs due to hematomas and reduction of intracerebral space in the cranial cavity;
- bruise - damage to the brain due to a blow to the head, often accompanied by hemorrhage;
- intracranial hemorrhage - destruction due to an impact on one of the blood vessels, which leads to local hemorrhage into the cranial cavity.
Inflammations affecting GM substance
Mild changes in BEA can occur due to inflammatory diseases affecting the brain substance.
Meningitis
This is an inflammatory process localized in the meningeal membranes. The main symptom of the pathology is intense headache, accompanied by nausea and repeated vomiting.
The disease is infectious or bacterial in nature, is very dangerous and can be fatal, especially if a child gets sick.
Arachnoiditis
The second name of the pathology is serous meningitis, since it involves serous inflammation of the arachnoid membrane of the brain. Its causes are injuries, intoxication of the body, acute and chronic infections. The disease can develop with slowly growing tumors and encephalitis.
With arachnoiditis, constant headache, nausea, and vomiting occur. Neurological disorders depend on the lesion.
Encephalitis
Encephalitis is a group of pathologies characterized by inflammation of the brain. They arise due to the action of pathogenic bacteria and viruses.
The most common is tick-borne encephalitis, carried by ticks. In addition to it, influenza, rheumatic, epidemic, and Japanese encephalitis are also distinguished.
The disease manifests itself with headaches, high fever and general weakness.
Anemia
This condition is characterized by a low hemoglobin content in the blood and a simultaneous decrease in red blood cells. Anemia is not an independent disease, but a symptom of various pathologies.
With anemia, little oxygen enters the brain, which causes starvation of brain cells (neurons), and as a result, complications in the form of wave dysrhythmia.
Irradiation (poisoning)
Radiological damage does not leave its mark on the body. It undergoes pathological changes, including the brain.
Signs of toxic damage are considered irreversible, can significantly affect the quality of life and a person’s ability to perform daily activities, and require a serious approach to treatment.
Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels
A disease in which plaque builds up in blood vessels, impairing blood flow. The most common cause of BEA disorganization. At the beginning of the disease they are moderate in nature.
In the process of tissue death due to lack of blood supply, the deterioration of neuronal patency worsens, which is manifested by increased disturbances.
Associated abnormalities
Diffuse changes in BEA can be caused by dysfunctions of the lower part of the brain structure: the pituitary gland and hypothalamus. They can also occur in immunodeficiency states.
In newborns, dystrophic foci in the brain can be a consequence of hypoxic-ischemic lesions, which also manifests itself in a violation of BEA.
Symptoms
In most cases, not only those around them, but also the patient himself are unable to replace the manifestations of BEA disorders. Signs of moderately acceptable changes at the initial stage are determined only during hardware diagnostics.
Doctors may say that the bioelectrical activity of the brain is somewhat disorganized if the patient suffers from:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- sudden changes in pressure;
- hormonal disorders;
- chronic fatigue;
- high fatigue;
- dry skin, brittle nails;
- decreased intellectual abilities;
- weight gain;
- decreased libido;
- stool disorders;
- depression, neuroses and psychoses.
Disturbed BEA of the brain leads to personality degradation and changes in lifestyle, while at first the person feels normal. Malaise is often attributed to chronic fatigue, which is erroneous.
Significant diffuse deviations of BEA are detected only by special medical devices.
Diagnostics
Changes in bioelectrical activity of a general cerebral nature are detected during a hardware examination. An EEG will show inflammation, scarring, or cell death. It makes it possible to characterize the pathology and find its source, which is important for diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnosis occurs in several stages:
- Anamnesis. Extensive changes have clinical manifestations, like other pathologies of the central nervous system. During the appointment, the doctor must conduct a thorough examination, find out or diagnose associated injuries and diseases. Important information is about the dynamics of symptoms, what treatment was carried out, and what the patient considers to be the cause of the disease.
- An EEG will help find the disorder and determine its location. It does not allow determining the cause, but the data is used, for example, for early diagnosis of the development of epilepsy. EEG indicates a periodic decrease and increase in bioelectrical activity.
- MRI is prescribed when the bioelectrical activity of the brain is disorganized and irritative changes are detected. The data obtained as a result of the examination will help to establish the reasons for this, detect neoplasms, and vascular atherosclerosis.
- The wording “diffuse change” is not the final verdict. It is vague, and without a clarifying examination it is impossible to talk about the presence of any disease. Each case is considered individually and treatment is prescribed. Vascular diffuse processes are treated with one method, degenerative changes with another, post-traumatic pathologies with a third.
Don't be afraid of a “terrible” diagnosis. More dangerous are suspicious focal symptoms on MRI, which indicate a cyst or tumor and subsequent treatment by surgeons. For diffuse changes, surgery is extremely rare. If you invite 100 random people for examination, then most of them, especially those over 50 years old, will come back from a doctor with a similar diagnosis.
Electroencephalogram of the brain
The research in question is a literal recording of the activity (namely, electrical) of certain brain structures. The results of the electroencephalogram are recorded on paper specially designed for this purpose using electrodes. The latter are applied to the patient's head in a certain order. Their task is to record the activity of individual parts of the brain. Thus, the electroencephalogram of the brain is a record of its functional activity. The study can be carried out for any patient, regardless of his age. What does the EEG show? It helps determine the level of brain activity and identify various disorders of the central nervous system, including meningitis, polio, encephalitis and others. It also becomes possible to find the source of damage and assess its extent.
When performing an electroencephalogram, the following tests are usually necessary:
- Blinking of varying speeds and intensity.
- Exposure of the patient's completely closed eyes to periodic bright flashes of light (so-called photostimulation).
- Deep breathing (rarely inhaling and exhaling) for a period of three to five minutes (hyperventilation).
The tests listed above are carried out for both children and adults. Neither diagnosis nor age affects the testing composition.
Additional studies that the doctor conducts, depending on certain factors, are the following:
- sleep deprivation for a certain period of time;
- passing a series of psychological tests;
- clenching the palm into a fist;
- monitoring the patient throughout the entire period of night sleep;
- taking certain medications;
- the patient is in the dark for about forty minutes.
Danger of diffuse change
Pronounced cerebral changes detected in time are not critical for the normal functioning of body systems. Delayed bioelectrical maturity is common among children; abnormal conductivity is common among adults. The detected changes respond well to restorative therapy. The risk arises when you ignore your doctor's recommendations.
Pronounced changes in the brain are caused by a number of pathologies: softening and hardening of tissues, inflammation and the formation of tumors. This causes the development of diffuse sclerosis, cerebral edema and encephalomalacia. A serious danger is associated with the development of convulsive and epileptic syndromes. Timely diagnosis will help eliminate complications.
Treatment
Diffuse polymorphic disorganization can only be cured in specialized medical institutions. A correct diagnosis allows you to prescribe the appropriate treatment, which will get rid of the pathology and its consequences, and restore the normal functioning of cells.
You should not delay treatment - any delay will complicate it and provoke complications.
The restoration of natural connections largely depends on the degree of damage. The smaller it is, the better the result of the treatment. The usual way of life will become possible only after a few months.
The treatment plan is developed taking into account the causes of changes in BEA. It is easy to normalize brain activity only at the initial stage of atherosclerosis. The most severe cases are considered to be radiation and intoxication.
A set of medications is prescribed. Its action should be aimed at eliminating the root cause (treatment of the underlying disease), psychopathological and neurological syndromes, normalizing metabolic processes and cerebral circulation. To restore normal blood circulation, various groups of drugs are used:
- pentoxifylline to improve blood microcirculation;
- calcium ion antagonists for effects at the cerebral level;
- nootropics;
- metabolic drugs;
- antioxidants;
- vasoactive agents, etc.
Treatment of disorganization of bioelectrical activity may include physiotherapeutic methods: magnetic and electrotherapy, balneotherapy.
Hyperbaric oxygenation and ozone therapy
Vascular diseases - the culprits of oxygen starvation - are treated using hyperbaric oxygenation: through a mask, oxygen is supplied to the respiratory organs at a pressure of 1.25-1.5 atm. At the same time, the tissues are saturated with oxygen and the symptoms of brain dysfunction are alleviated. But the method has a number of contraindications:
- hypertension;
- confluent bilateral pneumonia;
- poor patency of the auditory tubes;
- pneumothorax;
- acute respiratory diseases;
- high sensitivity to oxygen.
Ozone therapy shows good results, but its implementation requires expensive equipment and trained personnel, which not every medical institution can afford.
In severe cases with concomitant diseases, the help of a neurosurgeon is required. Self-medication is life-threatening!
Diagnosis and treatment
BEA dysrhythmia is diagnosed using several methods. The most informative is the electroencephalogram (EEG). Manipulation makes it possible to identify increased or, conversely, decreased bursts of electrical activity.
An EEG should not be confused with an ECG (electrocardiogram). The first method examines the brain, the second - the bioelectrical activity of the heart, its left or right ventricle, and myocardium. Both studies are highly significant for medicine, but have different implications.
A reliable diagnosis is made based on the following studies:
| Diagnostic method | Description |
| History taking | Determines the nature of symptoms in BEA disorders. The doctor conducts a full examination of the patient, paying attention to chronic ailments and head injuries. |
| Electroencephalography | Study of bioelectrical activity of the brain. The method identifies deviations from the norm and establishes the location of localization. The EEG shows abnormalities in BEA, but the cause is not determined. |
| MRI | Finds catalysts for accelerating or decelerating cortical rhythms. Shows irritative changes due to tumors, helps to establish the nature of neoplasms and study the structure of the cerebral hemispheres. |
| Angiogram | Necessary for diagnosing vascular atherosclerosis. |
How is dysrhythmia BEA treated? Therapy is prescribed only after a complete diagnosis of the patient and a control report. Without identifying the causes of the disorder, therapy is ineffective.
The rate of recovery of neural activity depends on how severely the brain tissue is damaged. If the changes are minor, treatment will be quick and effective.
Typically, a person diagnosed with BEA disorganization needs months, even years, to recover. It is easiest to restore brain activity at the initial stage of atherosclerosis; it is more difficult after radiation or chemical exposure, when irreversible changes have occurred in the tissues.
In exceptional cases, for example in the presence of tumors, surgery is required.
Decoding the electroencephalogram
What does the EEG show when electrical conduction in the brain is not organized? The specialist sees BEA dysrhythms immediately, especially if the changes in rhythms are significant.
- rhythms manifest themselves in the form of wave asymmetry;
- disruptions in the distribution of alpha, beta, gamma waves are visible;
- their frequency and amplitude are outside the normal range;
- if the electroencephalograph registers a twofold increase in the beta rhythm, foci of epileptoid activity are visible, this may correspond to the onset of epilepsy.
During the EEG, photostimulation is performed. Normally, the rhythm of the waves should be equal to the frequency of the flashes. It is also considered normal to exceed the rhythm by 2 times. A low or repeatedly exceeded rhythm clearly indicates deviations.
Wave amplitude measures from one peak to another. The rhythm index is used to determine frequency.
In the EEG analysis they can write the following:
- mild regulatory changes, diffuse changes in the brain parenchyma;
- cerebral changes of a residual nature;
- bioelectrical disorientation of a general cerebral nature with the involvement of nonspecific midline structures of the hypothalamic level;
- relatively rhythmic BEA, dysfunction of mid-stem structures with foci of paroxysmal activity.
When deciphering EEG, specialists use a special database that contains normal indicators, as well as deviations, and what diseases they correspond to. Reading an encephalogram is not an easy task, requiring experience and dexterity.