The full functioning of human reflex activity is largely determined by the functioning of the nervous system.
If the nervous system is affected, then the human body malfunctions - all its basic functions are disrupted: the frequency and rhythm of the heart, breathing, coordination of movements and walking skills, as well as nutrition.
If the disorder occurs in the brain, the person may lose all basic life skills such as speaking, writing, and reading.
Despite the fact that medullary gliosis is not a disease, this abnormal process contributes to the occurrence of serious disturbances in a person’s normal life.
White matter gliosis - what is it?
This process is a fairly severe morphophysical disorder of a pathological nature, which occurs in the tissues of the brain under the influence of certain environmental factors that are traumatic in nature.
This process is accompanied by a significant growth of the scar formed in the injured area where neurons have died.
This scar is medically called neuroglia.
This term refers to the additional tissue substance of the brain, which makes up about 30% of the total mass of brain tissue. The main function of neuroglia is to protect the brain matter from the effects of pathogenic microorganisms and various damages. Neuroglia also produce useful substances and take part in metabolic processes.
When brain cells are injured or infected, the volume of neuroglia increases. Scar tissue usually forms in the damaged area of dead neurons.
However, neuroglia excludes its formation, since it itself becomes a kind of bioconductor.
The main problem is that neuroglia are not able to function like natural nervous tissue. This in turn causes serious health problems.
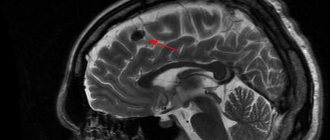
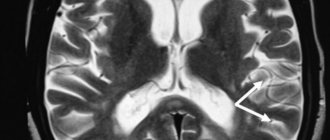
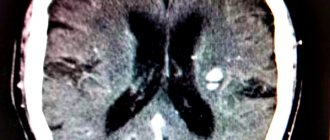
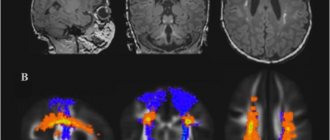
Foci of gliosis are very clearly visible on MRI of the brain.
When brain tissue is damaged, the following symptoms are observed:
- Fatigue that is chronic. A person experiences causeless bouts of fatigue, even while at rest.
- Prolonged and unremitting headaches, which may be accompanied by dizziness, nausea, fear of light, and vomiting.
- Sudden jumps in blood pressure, including conditions of arterial hypertension of varying degrees of complexity.
- Epileptic seizures and convulsions. If a large lesion is present, neurological symptoms may also be observed.
- Impaired motor coordination associated with cerebellar disorders, which leads to injuries of varying severity.
- Problems with short-term and long-term memory.
- The occurrence of sound and olfactory hallucinations.
- Lack of ability to clearly express one's thoughts out loud and in writing, which is caused by the formation of a lesion in the brain in the area responsible for the formation of oral and written language.
- Sudden mood swings, which can be accompanied by increased aggression, depressive states, and absolute apathy towards everything.
White matter damage
Modern medical capabilities and the latest technologies make it possible to determine the pathology of white matter or a violation of its integrity in the early stages. This significantly increases the chance of coping with the problem.
White matter injury can be traumatic or pathological. Caused by any disease or congenital. In any case, this leads to serious conditions. It disrupts the coherence of the body.
Possible disturbances in speech, visual field, and swallowing reflex. Mental disorders may begin. The patient will no longer recognize people and objects. Each symptom corresponds to white matter damage in a specific area.
Thus, knowing the symptoms, we can already guess the site of damage. And sometimes the cause, for example, with a skull injury or stroke. This makes it possible to provide the correct first aid before a full diagnosis is carried out.
Neural reactions are transmitted at the required speed only if the white matter is intact. Any violations can lead to irreversible processes and require urgent contact with specialists.
In the range of 30 - 50 years, the largest number of quality connections occurs. Further, the activity of impulse transmission decreases every year.
Types of disease
Because, due to the pressure of developing neuroglia, necrotic cells gradually die and die.
Against this background, small areas of gliosis of different sizes and shapes appear, which can be located in any area of the brain.
The pathological process is classified into 7 forms:
- Intraventricular - lesions form inside the ventricles of the brain, which contributes to a significant reduction in their volume, as well as the volume of cerebrospinal fluid.
- The formation of lesion islands that form around atherosclerotic vessels, which are severely compressed under pressure.
- Regional - involves the formation of single lesions that are concentrated outside the brain tissue (this type of neuroglia is the simplest, since it does not affect the central region).
- Fibrous - gliotic foci can be filled with fibers, which can have different lengths and sizes.
- Massive neuroglia - multiple foci are formed in different areas of the brain tissue (when scanning, the image is displayed as a large spotted field).
- Intrathecal – altered areas are located under the inner membranes of the brain, which significantly complicates the diagnosis of the disease.
- Anisomorphic - altered lesions are located chaotically.
Methods of combating pathology
Irreversible consequences of brain damage require an integrated approach to treatment and fundamental changes in the usual lifestyle:
- Rejection of bad habits;
- Physical activity - walking and swimming to strengthen the heart muscle;
- Dieting - table number 10 - limiting salt, fatty and spicy foods. Mostly boiled or steamed food;
- Maintaining a rest regime - in case of brain pathologies, it is necessary to increase sleep by several hours;
- Avoidance of stress – an unstable emotional state directly affects the causes of many diseases.
Foci of gliosis
Depending on how focal changes are displayed on film during MRI of the brain, gliosis is divided into the following groups:
- Hypodense - are quite rare, do not have a specific structure and are extremely difficult to paint;
- Hyperintense – characterized by a pronounced structure, easily stained during examination.
Depending on the number of pathological zones, neuroglial foci are also divided into:
- single – when performing an MRI of the brain, single foci of gliosis are very clearly visible;
- multiple – are also clearly displayed during the examination.
Prevention of operational disruptions
Physical activity, even in older people, affects the structure of white matter.
In addition, the load leads to densification of the white matter, which has a positive effect on increasing the speed of signal transmission.
A healthy lifestyle leads to improved brain function, which significantly improves the condition of the whole body. Intellectual activities along with physical activity, games in the fresh air, a variety of active recreation - all this will certainly help maintain memory and clarity of mind at any age.
The brain is the center that regulates the functioning of the entire body and is directly connected to the autonomic nervous system. Focal changes in the white matter of the brain are an irreversible process of death of sensitive neurons, even with slight oxygen starvation.
Unit formations
Such formations are more common in different age groups.
MRI of the brain can detect foci of gliosis in both infants and elderly patients.
In the first case, the formation of altered lesions may be associated with the consequences of postpartum trauma; in the second, it may be the result of degeneration of brain tissue due to age-related changes.
This process is a natural age-related change that is visible in 60% of cases when scanning white matter in people over 85 years of age.
As a rule, such lesions are detected by chance, since they do not cause discomfort. However, when lesions form in the left frontal lobe, they often provoke the appearance of hallucinations.
This phenomenon is due to the fact that in this part there are the most important centers responsible for deep feelings and sensations.
The main feature of such a lesion is that it is not predisposed to proliferation and carries a significant risk in the development and exacerbation of chronic diseases.
What does it consist of?
The volume between the basal ganglia and the cortex is completely filled with white matter. Consists of processes of neurons (axons). Collectively, they represent many nerve myelinated fibers. The presence of myelin determines the color of the fibers. They travel in different directions and conduct signals.
Nerve fibers are represented by three groups:
- Association fibers. Necessary for connecting parts of the cortex only in the area of 1 hemisphere. There are short and long ones. Their tasks are not the same: short ones connect convolutions located in the neighborhood, long ones connect distant areas.
- Commissural fibers. Responsible for connecting certain lobes of both hemispheres. Localized in brain adhesions. The basis of these fibers is represented by the corpus callosum. In addition, they monitor the compatibility of functions in the brain.
- Projection fibers. They are responsible for communication with other points of the central nervous system. Connects the bark to the formations below.
Multiple lesions
Such lesions are much less common compared to single gliosis of the brain. This pathology can develop against the background of various diseases of the blood vessels, the central nervous system (in particular, white matter), as well as connective tissues.
Typically, the cause of such lesions is atherosclerosis, as well as previous strokes and heart attacks. Also, multiple lesions can occur due to traumatic brain injury.
It is important to note that with brain trauma, a process of necrosis occurs, and in different areas and in different areas. As a result, it is the subcortical foci of tissue death that are much more susceptible to gliotic degeneration.
When receiving minor head injuries, the size of the lesions is no more than a few millimeters. Thanks to this, the functions of human thinking remain practically unchanged.
If a patient has even the smallest structural changes, they can easily be detected using an MRI examination.
Functions
Providing a safe environment for the functioning of the nuclei and other parts of the brain and conducting signals throughout the nervous system are the main tasks of white matter.
Constantly, uninterruptedly connecting all parts of the central nervous system is the main goal of the action of white matter. This ensures coordination of general life activities. A signal is transmitted through neural processes, which allows for a variety of human actions.
Tasks in different lobes of the brain
On the cerebral cortex, grooves and ridges that form convolutions can be clearly visible. The central sulcus divides the parietal and frontal lobes. On both sides of this groove are the temporal lobes. The furrows and convolutions separate the hemispheres, forming 4 lobes in each:
- Frontal lobes. They have undergone great changes in the process of evolution. They developed faster than others and have the largest mass. In them, the white matter must provide all motor processes. Here, thinking processes are started, the structure of speech and writing is regulated, and all complex forms of life support are controlled.
- Temporal lobes. They border on all other lobes. The functioning of the white matter in them is aimed at understanding speech and learning opportunities. Allows you to draw conclusions by receiving all kinds of information through hearing, sight, and smell.
- Parietal lobes. Responsible for pain, temperature, tactile sensitivity. They make possible the work of centers that have been brought to automaticity: eating, drinking, dressing. A three-dimensional understanding of the world around you and yourself in space is built.
- Occipital lobes. In this area, functions are aimed at remembering processed visual information. The form is evaluated.