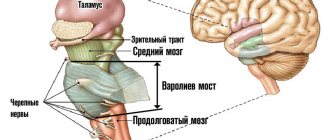
What is paralysis? This is a condition of a person in which he is completely deprived of motor abilities due to lack of strength in the muscles. This circumstance is due to damage to the nerve fibers: the patient is not able to move independently and becomes dependent on the people around him.
Most often, nerve palsy is a consequence of serious negative processes in the body, but some of its forms can act as independent diseases: Erb's palsy, Bell's palsy, Parkinson's disease, polio, cerebral palsy.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of a disease caused by damage to nerve fibers consists of:
- examination by a neurologist;
- fluoroscopy;
- computed and magnetic resonance imaging;
- myography;
- neurosonography;
- testing the reflex abilities of the lower extremities (Achilles, plantar, knee reflexes and Jendrasik maneuver).
Diagnostics
The neurologist examines the patient, reflexes and muscle strength, collects medical history data, to clarify the diagnosis, separate paralysis from similar diseases (brain cancer, muscular dystrophy) and identify the cause of the pathology, prescribes the following additional examinations:
- Neurosonography (ultrasound of the brain) is prescribed for children up to 1.5 months, until the fontanel is closed, if asphyxia, hypoxia, or congenital defects are suspected. The procedure is rarely performed on adults.
- X-ray of the skull - examination of bone structures, deformations, injuries, areas of hemorrhage.
- Myography is the study of electrical activity of muscles and nerves.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) – evaluates the state of the white and gray matter of the brain to identify lesions and circulatory problems.
- Blood test - with inflammation, ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) and leukocyte levels increase.
- Toxicological analysis is a blood test for poison if poisoning is suspected.
- Electroencephalography (EEG) – assessment of the functioning of the cerebral cortex and blood vessels.
In some cases, narrowly targeted diagnostics are carried out:
- Bell's palsy : hearing test (the degree of nerve damage is revealed), vestibular apparatus, lumbar puncture (examination of the spinal cord).
- Cerebral palsy : monitoring the baby in the first 1-2 years of life, regular examinations by a neurologist.
Consequences of immobility
What is paralysis? How to care for a patient who finds himself in a state of immobility? Prolonged bed rest caused by forced inactivity negatively affects the health of a paralyzed person. When the patient remains in a supine position for more than 4 days, a decrease in muscle tone occurs, problems with blood pressure arise, and joint mobility decreases. Along the way, metabolic processes in the body are rearranged, an increase in glucose levels is observed in the blood, and the nitrogen-calcium balance is disturbed.
Due to the paralysis and recumbent position caused by this condition of the body, the rate of bone liquefaction rapidly increases, the risk of infection of the urinary system increases, urinary incontinence occurs, dizziness and fainting occur, especially when changing body position and sharp turns of the head. During breathing, the volume of the lungs is partially used, blood circulation is disrupted, which subsequently threatens thrombosis.
Paralysis concept
After paralysis of a person’s limbs, life changes dramatically, and the concept itself is interpreted as a loss of motor functions, when the strength of muscles regulated by the nervous system sharply decreases. Partial paralysis is called paresis.
By finding out the cause of the movement disorder, you can understand the essence of the disease. Incoming information from the sensory organs, after processing in the postcentral gyrus, enters the prefrontal cortex, from where the signal goes to the dorsal cortex. It is from here, after the receipt of an electrical impulse to the motor neurons, that a discharge occurs to the muscle fibers, and as a result, movement occurs.
When the signal transmission process is disrupted, paralysis occurs. In medicine, artificial immobility is used, for example, epidural anesthesia or general anesthesia.
Polyneuropathy
Polyneuropathy is a group of diseases that are manifested by muscle weakness and sensory disturbances.
There are organic and functional subtypes of paralysis, and the first appears due to the formation of tumors, injuries or lesions in blood vessels, and the second can occur after mental disorders, which most often leads to partial immobilization.
These processes can be reversible and transient, it all depends on the location of the lesion in the brain and the severity of the disease. Paralysis occurs only against the background of an existing disease, as a complication; it is a symptom of a tumor formation or circulatory disorders in the brain.
Caring for a Paralyzed Person
A patient who needs special care during this period should be aware that stiffness in the joints should not cause complete immobility. Even with paralysis, you need to move and perform various exercises to the best of your ability.
Therefore, from the beginning of bed rest, gymnastics and joint work should be a necessary component of quality treatment. If the patient is unable to do this himself, he should be helped. Breathing exercises are aimed at involving in the process all parts of the lungs that are inactive during paralysis.
Treatment options
- When treating paralysis, it is imperative to treat the underlying disease. For this reason, it is difficult to say unequivocally what exactly you need to do to improve your well-being. For example, if a person is found to have an abscess, neoplasm or hemorrhage, in most cases surgical intervention is required. When it is necessary to normalize blood pressure, a person is prescribed nootropic drugs , as well as angioprotectors . These products can improve blood flow and normalize a person’s well-being.
- If there are infectious lesions of the brain, the person will be prescribed antibiotics. It will be important to get rid of pathogens so that you can improve your well-being. When botulism therapy is required, a person is prescribed anti-botulism serum. If myasthenia gravis is diagnosed, then it will be important to improve neuromuscular conduction.
- In addition, the doctor will prescribe vitamins , as well as medications that are necessary to restore nervous tissue. A person also needs physiotherapy to help develop muscles.
- If treatment is started in a timely manner, then the body can be restored. At the same time, it will be important to strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations if you want to normalize your well-being. Additionally, a person is recommended to adhere to preventive measures, because with their help it will be possible to recover much faster.
- In particular, you will need to lead a healthy and active lifestyle, stop smoking and drinking alcohol. In addition, you will need to follow a certain regime: eat properly and in a timely manner, drink at least 1.5 liters of water , and also get good sleep.
- You will definitely need to consult a doctor in a timely manner if alarming symptoms occur. It is important to promptly treat diseases that are inflammatory and infectious in nature. It is imperative to monitor blood pressure, because it leads to negative consequences, including paralysis.
- A person who is faced with pathology is advised to move more. If this is too difficult a task for the patient, then he will need outside help. It is also necessary to perform breathing exercises that will engage the lungs. As you know, this organ does not work to its full potential during paralysis.
During treatment, you must be observed by a doctor so that you can monitor the progress of treatment. Your treatment regimen may need to be adjusted to help it work better. Under no circumstances should you start the disease unless you want to face irreversible consequences. These include muscle hardening and joint ankylosis.
What is facial paralysis
Bell's palsy is quite common and is caused by:
- infectious diseases (diphtheria, mumps);
- traumatic injuries;
- hypothermia;
- cancerous tumors;
- impaired blood flow due to hypertension and atherosclerosis;
- consequences of otitis media;
- inflammatory processes in the brain.
Facial paralysis develops at a very fast pace and can occur at any age, but most of all it affects people who have crossed the 60-year mark. The causes of this disease have not been reliably studied; it is only known that the mechanism of its occurrence is due to swelling of the facial nerve, which occurs due to a viral infection or immune failure.
Causes of this symptom
The pathology of “paralysis” has different causes, but they ultimately come down to one thing – brain damage, which occurs as a result of injury, tumor, abscess (ulcer), or inflammation. In addition, paralysis can occur as a result of demyelinating diseases, which are accompanied by the breakdown of the protein - myelin, the function of which is to conduct nerve impulses along the fibers: for example, these are diseases such as sclerosis or multiple encephalomyelitis (infectious). Thus, foci of demyelination appear in the lobes of the brain or in the cerebellum. The causes of paralysis also include other diseases not associated with demyelination:
- myasthenia gravis – a disease with pathology of muscle fatigue;
- myopathy – congenital or acquired metabolic disorders in muscle tissue;
- botulinum toxin poisoning, referred to as “botulism”;
- epilepsy;
- diseases associated with dysfunction of motor neurons, resulting in pathology of muscle function and paralysis of the limbs.
The most common form of this symptom is paralysis of the legs, or paresis, in which it is difficult for the patient to bend the thigh and lower leg due to insufficient strength in the muscles. This occurs due to damage to the motor neurons of the dorsal roots of the spinal cord nerves.
Symptoms of facial paralysis
Symptoms of a dangerous condition are:
- pain behind the ear, often occurring on the eve of the onset of muscle weakness in the facial area;
- lack of facial expression on the affected side and excessive muscle contraction in the opposite part of the face. So, when trying to smile, the patient’s mouth twists to the healthy side;
- muscle weakness that can develop in a matter of hours;
- wide opening of the palpebral fissure. The sick person is unable to close the deformed eye;
- feeling of numbness in the facial area;
- impaired salivation and lacrimation.
Prevention of paralysis
- Have regular medical examinations once a year.
- Complete exclusion of alcohol and drugs.
- Maintaining a healthy sports lifestyle (moderate physical activity, daily morning exercises, walks in the fresh air, healthy 8-hour sleep).
- Following the rules of proper nutrition (excluding fried and smoked foods, eating fruits and vegetables that are rich in vitamins, moderate consumption of sweets).
- Blood pressure control.
Treatment of facial paralysis
What is facial paralysis and what measures are recommended to be taken to cure it? Treatment tactics for facial paralysis are selected depending on the degree of nerve damage and most often involve drug therapy.
At the initial stages of the disease, the patient is prescribed glucocorticoids, which help reduce the severity and duration of residual paralysis. Antiviral drugs are prescribed: Valacyclovir, Acyclovir, Famciclovir.
Instillation of natural tears or an isotonic solution into the affected eye is used, as well as applying a bandage. After a week of treatment, vitamin complexes and agents to improve nerve conduction are prescribed.
In parallel, the following procedures are applied:
- physiotherapy;
- acupuncture;
- massage of the collar area;
- laser therapy;
- ultrasound;
- UHF electric field.
In severe cases, surgical intervention is used, which must be performed no later than 3 months from the moment the disease is detected. Otherwise, the pathology may remain forever. During surgery, microscopic decompression is performed to remove the bone covering the facial nerve. This is necessary to open the nerve sheath. Then the doctor prescribes certain exercises for the facial muscles, thanks to which it is possible to fully recover in most cases.
Symptoms
Main symptoms of paralysis:
- Complete or partial immobility of the limbs of the body, depending on the affected area of the central nervous system or peripheral part.
- Changes tone , which is accompanied by constant tension or weakening, cramps.
- Strengthening or weakening of tendons.
- Absence or decreased abdominal reflexes.
- Changes tone .
- Complete or partial loss of sensation.
- atrophy .
- Changes in gait .
- hanging forward.
- Difficulty lifting or standing up.
- Development of strabismus.
- The appearance of incoherent speech.
- Protrusion of the tongue due to weakness of its muscles.
A separately isolated psychogenic factor of the disease has symptoms of central and peripheral paralysis; they can manifest themselves throughout the entire illness or be periodic.
The danger of lack of motor ability of the limbs
Paralysis of the limbs is the result of damage to the spinal cord. In the full form, the integrity of this organ is compromised. The degree of its damage affects the muscle failure of a certain area of the body.
Damage to the spinal cord at the level of the 4th, 5th and 6th cervical vertebrae leads to tetraplegia - paralysis of all 4 limbs, but the patient can bend and raise his arms. If there is damage in the area of the 6th and 7th cervical vertebrae, the legs are taken away, the hands and wrist joints are paralyzed; The patient can only move his shoulder and move his arms very slightly.
If the lesion occurs at the level or above the 4th cervical vertebra, breathing is paralyzed, which in most cases ends in death.
Paraplegia is paralysis of both legs that occurs due to transverse lesions of the spinal cord in the area of the lumbar and thoracic vertebrae.
All situations of spinal cord injury are characterized by impaired sensitivity of the affected areas.
Causes of paralysis
The pathology is based on a disruption of communication between the central nervous system (brain) and the peripheral one. This situation is due to 3 factors:
- failure of the central nervous system (CNS);
- pathologies of the performing organ;
- problems in the communication system - neural conduction channels.
The following reasons lead to paralysis:
- dystrophic-degenerative diseases of the central nervous system;
- injuries - cranial or spinal injuries with damage to nerve endings, rupture of muscle-ligamentous structures;
- toxic factors - poisoning with lead, mercury, botulinum toxin, alcohol, drugs;
- cerebrovascular accidents;
- oncology;
- metabolic disorders;
- inflammatory processes;
- infections;
- mental disorders (cause functional paresis).
Diseases characterized by paralysis
Motor function is lost in the following pathologies and diseases:
- stroke (often leading to hemiplegia);
- epilepsy;
- myopathy;
- myasthenia gravis;
- botulism;
- Guillain-Barré syndrome (autoimmune damage to peripheral nerves);
- multiple sclerosis;
- polio;
- tuberculosis;
- viral encephalitis;
- cancer;
- tumors near the spinal cord;
- amyotrophic sclerosis;
- inflammation of the brain stem;
- mumps;
- encephalomyelitis
How to restore paralyzed limbs?
Treatment of limb paralysis resulting from an accident involves ensuring the functioning of the circulatory and respiratory systems, which are vital for the body. Artificial ventilation may be used. The patient is prescribed long-term bed rest.
An important factor on the path to recovery is physical exercise and a variety of rehabilitation procedures. During gymnastics, to ensure blood supply to paralyzed muscles, the affected limbs are moved passively. A certain series of exercises is also carried out for healthy muscles. As soon as it becomes clear that the muscle paralysis has disappeared, special motor exercises will be needed.
Occupational therapy is also used - a set of rehabilitation measures aimed at restoring a person’s daily life and usual activities, taking into account the existing physical limitations.
A key role in the treatment process, which lasts quite a long time, is played by psychological support for a paralyzed person who feels inferior. The fight against emerging complexes is carried out using psychotherapy and positive thinking techniques.
Some features
If the disease is caused by impaired blood flow or injury to the brain (spinal, head), paralysis is classified as central. Signs of the disease:
- pathological reflexes;
- increased muscle tension, causing constant maintenance of the diseased area in a specific position.
When identifying peripheral pathology, it is necessary to take into account the features characteristic of this group of disorders:
- decreased muscle tone;
- decrease in trophic conductivity of nerve tissues;
- spontaneous activity of muscle fibers observed at the point where a peripheral nerve begins.
Severe neurological disease: cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy is an incurable disease, the peculiarity of which is the lack of its progress, that is, further development. The main causes of cerebral palsy today are considered to be:
- hypoxia of the child immediately after birth or while in the womb. In most cases, the cause of paralysis is pathologies that arise during gestation (various types of infections, toxicosis, circulatory disorders of the placenta) and lead to incomplete development of the brain areas responsible for the balance of the body and its reflex mechanisms. As a result of these processes, muscle tone is incorrectly distributed in the skeleton, causing the development of pathological motor ability;
- injuries during childbirth. May be due to the structure of the mother’s pelvis, weak labor, rapid or protracted labor, childbirth after a long anhydrous period, abnormal position of the fetus;
- hemolytic disease of newborns, during which the child’s brain is poisoned. It may be caused by liver failure in the fetus or incompatibility of its blood group or Rh factor with the maternal ones;
- chronic or acute diseases of a woman during pregnancy (heart defects, rubella, obesity, anemia, diabetes, hypertension). Factors also dangerous for the child are the expectant mother’s taking medications, in particular tranquilizers, and negative phenomena: stress, physical injuries, alcoholism, psychological discomfort, drug use;
- improper course of pregnancy due to toxicosis, threats of abortion, immunological incompatibility of mother and child;
- complications during childbirth, provoking conditions for the occurrence of asphyxia and mechanical head trauma - secondary factors causing brain damage.
The most severe form of cerebral palsy is considered to be spastic tetraplegia, which is often found in premature babies. Half of these children born prematurely also experience deformation of the torso, epileptic seizures, limited mobility of the limbs, strabismus, atrophy of the optic nerves, hearing impairment, and microcephaly (a pathology of brain development). A child diagnosed with cerebral palsy is not able to care for himself or engage in any simple work throughout his life.
Hemiplegic cerebral palsy is characterized by impaired functioning of the limbs on one side of the body. The arm suffers more than the leg.
The dyskinetic, or hyperkinetic, form is manifested by increased muscle tone, hearing loss, and paralysis. Intelligence is preserved: the child can attend school and university.
The ataxic form of the disease is manifested by the development of oligophrenia and mental retardation.
Types of paralysis
Based on innervation disturbances and clinical manifestations, the following types of pathology are distinguished:
- Peripheral paralysis (flaccid) - motor neurons are affected, which leads to decreased muscle tone. Reflex activity stops or weakens.
- Central (spastic) - develops against the background of disorders of the corticospinal tract and causes hypertonicity of the affected muscles. This form of paralysis most often affects people over 50 years of age.
- Mixed - has characteristics of both forms.
Based on the number of limbs affected, the following types of paralysis are distinguished:
- Monoplegia – 1 arm or leg is immobilized.
- Hemiplegia is paralysis of the left or right half of the body.
- Paraplegia – affects a pair of upper or lower limbs. Often this paralysis develops due to damage to the spinal cord.
- Triplegia – paralysis of 3 limbs.
- Tetraplegia – arms and legs, most of the body are immobilized.
According to etiology (causes of occurrence), there are 2 types of paralysis:
- Organic – associated with damage to the nervous system due to diseases, injuries, tumors.
- Functional – develops due to a stagnant area of inhibition in the brain against the background of movement disorders. Paralysis is complete or partial, occurs in conditions that are traumatic to the psyche, and goes away without treatment.
According to the persistence of the changes that have occurred, the pathology has 2 types:
- Transitory – the disease is treatable, the range of motion returns fully or partially.
- Irreversible – motor function is lost forever.
Sleep paralysis
About 7% of the population experienced this condition, most of them were people 12-30 years old.
Sleepy stupor (another name for pathology) is not a symptom of the disease - it is a short-term complete loss of muscle tone during the activity of consciousness under the influence of external factors.
It is not life-threatening. Paralysis lasts up to 2 minutes and occurs at the following moments:
- Falling asleep , a phase of REM sleep in which skeletal muscle tone decreases and motor skills are suppressed, occurred before brain activity decreased.
- Awakening - consciousness woke up before muscle tone was restored, so there is a feeling of paralysis of the limbs and body.
Sleep paralysis develops against a background of stress, lack of sleep, anxiety, mental and mental stress. The condition is also caused by taking antidepressants and alcohol: this provokes a malfunction in the systems that regulate sleep and wakefulness. Main signs of pathology:
- inability to move;
- panic fear;
- auditory and visual hallucinations;
- feeling of false movements (the feeling that a person has turned over, but remains in place);
- illusion of flight.
Forms of cerebral palsy at an early stage
In 60% of cases, the pathology develops in the perinatal period (in the womb) and is associated with damage to the brain or its structural abnormalities. In almost 40% of children, the disease is caused by factors that affect the child during childbirth. The moment of appearance is the key difference between cerebral palsy and other paralysis. The main causes of this pathology:
- Perinatal : taking medications during pregnancy, infectious and endocrine diseases of the mother, bad habits.
- Natal : birth trauma, asphyxia (suffocation).
- Postnatal (in a newborn): traumatic brain injury, encephalitis, meningitis, antibiotics, brain tumors, severe jaundice.
The clinical picture of cerebral palsy at an early stage contains the following pathological symptoms:
- delayed speech development and motor activity;
- difficulty holding your head up;
- convulsions;
- immobility of arms and legs.
Articles on the topic
- Symptoms of meningitis in adults - how to recognize the infection in the early stages
- Brain stem stroke - first signs and manifestations, drug therapy, surgery
- Exercises after a stroke at home for rehabilitation
In 40% of cases, cerebral palsy occurs in the form of spastic diplegia. It is characterized by spinal deformity and early restriction of movement in the joints. Muscle spasticity most often affects the legs. If hand functions and mental development are normal, the child will successfully undergo social adaptation. Other forms of pathology:
- Double hemiplegia (2% of cases of cerebral palsy) - develops with severe brain damage, the child does not stand, does not sit, has severe mental retardation, and almost does not speak. Half of children experience epileptic seizures.
- Hemiparatic form (32%) – damage to the extremities is unilateral (arm and leg), they shorten over time. Speech, mental development are impaired, and the child masters motor skills late. Hemiparesis most often affects the right side, the arm weakens more than the legs.
- Hyperkinetic (10%) – the child has increased muscle tone and involuntary movements occur. At 4-6 months this can be seen in the functioning of the tongue, and from a year onwards - in other parts of the body. The child begins to move on his own at the age of 4-5, loses balance, but mental functions are normal, learning is going well.
- Atonic-astatic (15%) – the child has decreased muscle tone (hypotonia) and strong tendon reflexes. Intelligence is rarely affected; the pathology is associated with damage to the cerebellum.
Treatment of cerebral palsy
Paralysis, the symptoms of which are a good reason to contact a pediatric neurologist in order to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the correct therapy, cannot be completely cured, but the quality of life of a sick child can be significantly improved. In the first years of life, therapeutic measures are carried out to reduce cramps, muscle tone, and improve the motor ability of joints. These actions reduce the risk of skeletal deformation, improve the baby’s ability to maintain balance, make normal movements of the limbs and acquire simple self-care skills.
A child diagnosed with cerebral palsy must be registered with a neurologist, pediatrician, orthopedist, speech therapist, rehabilitation specialist and psychiatrist. It is the integrated approach of the necessary specialists that will determine his maximum adaptation to life.
Paralysis in children is treated by a combination of several methods. This includes taking medications, constant therapeutic exercises, surgical therapy, and treatment in sanatoriums.
Treatment
There are three main directions.
Self-medication is dangerous with complications!
Attention
Despite the fact that our articles are based on trusted sources and have been tested by practicing doctors, the same symptoms can be signs of different diseases, and the disease may not proceed according to the textbook.
Pros of seeing a doctor:
- Only a specialist will prescribe suitable medications.
- Recovery will be easier and faster.
- The doctor will monitor the course of the disease and help avoid complications.
find a doctor
Do not try to treat yourself - consult a specialist.
Surgical
If a benign or malignant tumor is detected, it is performed with a minimal incision, and subsequently implants are installed in the bone. When a blood clot forms, a procedure is performed to suture the vessel to remove the pathology found in order to restore blood patency.
If a foreign body is found in the spine or spinal cord, it is removed and the affected tissue is sutured. Purulent foci are opened and cleaned, and then disinfection is carried out.
Medication
The doctor prescribes medications in cases of teburculosis, myelitis or inflammatory purulent diseases. Antibacterial agents are administered by injection.
Vitamins can be prescribed according to an individual regimen for a long time, which will allow the motor activity of the limbs to be restored.
Symptomatic
This type of therapy is combined with the doctor’s basic recommendations and is prescribed for spinal injuries.
The latter includes:
- Physical therapy or muscle-strengthening gymnastics. A set of exercises is prescribed to the patient to the best of his ability, the program is selected individually.
- massage . Helps relieve muscle spasms, improves blood circulation, the functioning of nerve impulses, and reduces the incidence of bedsores in bedridden patients.
- Swimming in the pool. Helps unload the spine and strengthen joints, which improves motor activity of the limbs.
- Physiotherapy , which helps normalize muscle tone.
- Appointments with a psychologist or psychotherapist. They make it possible to establish the cause of paralysis and associate symptoms with other diseases.
- Use of bandages or corsets to treat spondylosis, spinal instability, or retrolisthesis.
Abroad, the method of getting rid of illness using mirror therapy is very relevant. The innovative method is based on mobilizing the patient’s inner will by watching videos. A person with paralysis is seated in front of a mirror so that in the reflective surface he sees a healthy hand instead of a sick one.
During the session, the doctor asks the patient to make synchronized movements, and, standing behind the glass, he repeats all the actions, and the mirror reflects as if the restored limb. The illusion of a healthy hand is created, which allows you to activate nerve impulses in the brain.
The method of watching videos is based on recording the movement of the patient, as a result of which the person mentally imagines that he is healthy. This is a good incentive to repeat the actions seen in the video, which contributes to the emergence of the power of self-hypnosis.
| Type of paralysis | Lethargic | Spastic |
| What is required in general | Increase muscle tone | Relax your muscles |
| Which massage is better? | Strong rubbing and kneading | Shaking and stroking, light kneading |
| How long and often should the procedures be performed? | Long courses with short breaks | Courses of 25-30 procedures |
How to help patients with different types of paralysis
Bell's palsy
This form of the disease is the most common type of damage to the facial nerve. The symptoms of the disease are quite alarming, but medical statistics show that the pathology is often completely cured within a few months. Usually only half of the face is affected.
The pathology develops suddenly, reaching its peak in just two days. Symptoms vary: there is partial loss of the ability to move, there is complete paralysis.
The following manifestations of pathology are distinguished:
- weakness of muscle tissue;
- twitching of muscle fibers;
- drooping eyelid, inability to close the eye;
- dryness of the mucous membranes of the mouth and nasal cavity;
- loss of sensitivity in taste buds;
- uncontrolled flow of saliva from the corner of the mouth;
- Difficulty in clearly pronouncing words.