Disorders of work, functional activity, anatomical changes in cerebral structures are represented by a wide list of deviations that can be deadly.
This is often how it turns out: without proper medical care, the patient risks dying or suffering irreversible changes in the nervous tissues and becoming deeply disabled. This cannot be allowed, we need to act faster.
Brain edema is an acute condition in which the amount of intra- and intercellular fluid in the structures of nerve fibers increases. It occurs against the background of many diseases and conditions of a neurological, traumatic nature, and damage to the cardiovascular system.
The clinical picture is specific, therefore it is quite difficult to confuse the pathological process. Time is running out. Treatment takes place in a neurological hospital, intensive care unit. Depends on the patient’s condition, the current state of affairs.
The forecasts are vague. If you can help in the first few hours, there is a high chance of total recovery without critical complications and consequences.
Development mechanism
There are several pathogenetic pathways for the formation of the disorder. As a rule, they do not intersect with each other; they exist and arise in isolation.
What exactly are we talking about:
- Acute inflammatory processes. May be infectious, such as meningitis or encephalitis. Autoimmune variants of the disorder are slightly less common. They give about the same complications.
We are talking about an increase in fluid concentration as a result of stagnation of cerebrospinal fluid, which also leads to a rapid increase in intracranial pressure.
Attention:
If the inflammatory process is not eliminated in a short time, the likelihood of developing a complication, cerebral edema (CED), increases every hour.
- Oncology. Malignant tumors most often. Mainly glial astrocytomas. Oddly enough, this also includes benign neoplasms. Provided that they are large enough to compress the drainage pathways of cerebral structures.
The likelihood is debatable. It is impossible to predict in advance what the risk of developing this pathological process is. But it’s better to play it safe and start treatment quickly.
- Hydrocephalus. Increased amount of fluid in the skull. It develops as an independent pathological process or as a result of the influence of an external factor. For example, inflammation, trauma or tumor development.
Congenital forms of the disorder cannot be eliminated radically. It is necessary to combat the symptoms and normalize the functioning of the drainage system. For these purposes, diuretics are used.
- Suffered damage. The traumatic mechanism is considered one of the main ones. A very common factor in the development of the pathological process.
Post-traumatic cerebral edema can occur suddenly, some time after a skull injury. Therefore, it is strongly recommended to treat TBI in a neurological hospital. There you can get sufficient supervision and the necessary care.
- Stroke. Acute disturbance of cerebral blood flow. Especially when it comes to the hemorrhagic form. When a blood clot forms, it shrinks, thickens and compresses the tissue. Including a drainage system that distributes cerebrospinal fluid. Dangerous and unpredictable consequences are possible in the form of necrosis of most of the cerebral structures, wedging of the trunk into the foramen magnum and the death of the patient.
These are the main mechanisms for the development of the pathological process.
Children are worth mentioning separately. Newborns experience cerebral edema during severe pregnancy in the mother. It is necessary to observe for some time after birth. At least a week.
Classification
Cerebral edema is divided into vasogenic, interstitial and cytotoxic. They have slightly different formation mechanisms and require a separate approach to therapy.
Vasogenic
The essence of the disorder is the penetration of positively charged ions into the brain tissue. Normally, they cannot enter the cerebral structures. The blood-brain barrier interferes.
As a result of inflammatory processes, tumors and other conditions, the degree of protection decreases. Charged particles lead to an increase in osmotic pressure. Accordingly, the fluid leaves the cells into the intercellular space.
The next noticeable step is compression of the tissues of cerebral structures and the development of cerebral tissue edema itself. The clock is counting. In some cases - for days. If you are lucky, you will be able to react and help the patient.
Cytotoxic
Simply put, the concentration of fluid in this case increases inside the nerve cells themselves. They are mostly composed of water. Immediately the volumes grow even more.
Cytological units lose the ability to respond normally to stimuli and work as usual. Swelling develops relatively slowly over several days. There is time to help the patient.
Interstitial
Develops against the background of hydrocephalus. Stagnation of intracranial fluid, cerebrospinal fluid, leads to compression of the brain and spinal cord itself, and then to focal disorders that are dangerous to health and life.
Each option requires its own, special approach to therapy.
Recovery
The processes of complications, their severity and severity, will directly depend on the quality and efficiency of medical care. Restorative measures after the operation are carried out in the hospital. If during the development of brain swelling the visual and speech centers and the area of the musculoskeletal system were affected, then the person will have to learn to walk and talk again.
The consequences after the acute stage of the disease will not always be serious, but in some cases there is a possibility of death. A pathology of this type, taking into account the individuality of clinical manifestations and the many causes of its occurrence, almost always remains unpredictable for doctors, therefore, in any case, three main paths of the disease are always considered:
- Subsequent development of pathology, compression of brain structures by edema, death of a person.
- Elimination of swelling, patient disability.
- Elimination of edema without any serious consequences.
According to world statistics, five out of ten patients who have been diagnosed with cerebral edema die within a few days after the onset of the pathological process.
Causes
The main factors in the formation of the process will be as follows:
Traumatic brain injuries
Bruises, concussions and many other pathological conditions. They can provoke stagnation of cerebrospinal fluid and cerebrospinal fluid. Which will ultimately become a factor in the development of the disorder.
Recovery is carried out under the supervision of a neurologist. Minor damage can be corrected at home.
More serious ones, in order to avoid unnecessary risk, are best dealt with in a hospital, in the neurological department of the hospital. We will consider treatment issues further.
Inflammatory processes
Mostly infectious. These are well known to many encephalitis and meningitis. Of course, they do not always lead to the named pathological process. But this is possible, the risks increase as the condition worsens, the temperature rises, and the number of pathogenic organisms increases.
Autoimmune lesions of cerebral structures are slightly less common. They lead to the same consequences.
Treatment of these disorders takes place strictly in an infectious diseases or neurological hospital, under the supervision of a group of doctors. Otherwise there will be complications.
Intoxication, some forms of poisoning
For example, damage to the body by salts of heavy metals. Lead, mercury and others. Toxic vapors of volatile substances: hydrogen sulfide, phosphine and many others.
Everything that has the potential to slow down metabolic processes in cerebral structures and disrupt cellular respiration.
This may also include some medications. As a rule, cerebral edema as a side effect is prescribed directly in the annotation itself, the instructions for a specific drug. All that remains is to look and estimate the risks.
In any case, you cannot prescribe medications on your own. Leave this job to the doctor.
Malignant tumors
Less commonly, benign oncology. In the first case, a couple of factors influence the brain.
- On the one hand, neoplasia grows through healthy tissue, destroying and killing cells. Causes the release of cerebrospinal fluid into internal structures.
- On the other hand, if the size is sufficient, it compresses the fibers. As for benign forms, we are talking only about the mass effect, compression of cerebral structures.
The only way to help the patient is to remove all or most of the tumor. And then, no one guarantees that a relapse will not occur.
Stroke
Acute weakening of the nutrition of nerve tissues. The cause of cerebral edema is the disruption of local blood circulation, the release of fluid from cells into the external space and the increasing phenomena of tissue compression.
The process is closed; the vicious circle can only be broken through medical intervention. A stroke can be ischemic or hemorrhagic, when the vessel cannot withstand it, bursts, and a large hematoma forms.
The result is the same. In the second form, an additional pathogenetic factor appears, extensive hemorrhage. The chances of recovery and even survival are much lower.
Severe allergies
It’s interesting, but even banal immune reactions, false responses of the defense forces can cause brain edema.
Most often, the culprit of the pathological process is anaphylactic shock. The same result occurs with Quincke's edema.
Edema-swelling of the brain is a consequence of stagnation of cerebrospinal fluid, accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the intercellular space against the background of damage to cells of cerebral structures by one’s own antibodies.
Fortunately, this is an infrequent problem, and there is every chance you won’t encounter it.
Alcoholism
Long-term alcohol consumption increases the permeability of small and large vessels. The liquid fraction seeps into the intercellular space and literally bursts apart the cerebral structures.
This is very dangerous because it can cause the brain to move and cause death. Such pathological complications develop not only in binge alcoholics and experienced drinkers.
Anyone can encounter a problem by simply exceeding the dosage. If you give up alcohol, the likelihood of a pathological condition will gradually decrease. You need to be observed by a neurologist for at least six months. Just in case.
These are only some of the possible reasons. In fact, the number of pathogenetic factors goes into dozens.
Thus, during the experiments, information was obtained about the swelling of cerebral tissues after intense exposure to cold. The causes of cerebral edema can be liver disorders, cirrhosis and subsequent dysfunctional phenomena.
But these are the main ones. The issue should be considered in its entirety and the pathogenesis clearly delineated. This will help in developing a treatment strategy. You won't be able to figure it out on your own. The participation of a specialist is required.
Etiology of the phenomenon and symptomatic manifestations
There are quite a few reasons that cause peripheral edema of the extremities;
- Decreased protein synthesis due to liver dysfunction.
- Excessive capillary permeability.
- Impaired kidney function, leading to large loss of protein through urine.
- Chronic heart failure.
- Varicose veins.
- Vein thrombosis.
- Disease of the body's endocrine system.
- Allergic reaction.
- An infectious disease leading to an inflammatory process.
Sometimes swelling can be caused by reasons not related to any disease:
- Injection of a medication.
- Limb bruise.
- Eating disorder, hunger or, conversely, overeating.
- Side effect from a medication.
- Exposure to the body of poisons of certain insects or animals.
- Crushing a limb.
- A person staying in one position for a long time without moving.
Peripheral edema is manifested by several symptoms:
- The volume of fingers, ankles, and forearms increases.
- The skin on swollen limbs is red or, conversely, pale.
- When you press on the skin above the swelling, a clear mark remains, since the elasticity of the skin is sharply reduced.
- There is pain in the area of swelling.
- Body weight rapidly increases, sometimes up to 1.5 kg per day.
- The volume of urine passed during the day decreases.
These symptoms occur in various diseases; therefore, it is impossible to diagnose the disease that caused peripheral edema based only on these signs.
Causes in children
Factors for the development of edema in younger patients may be those described above. With some exceptions for obvious reasons. But there are also provocateurs that are found only in children in the early period of life.
This may include:
Congenital traumatic brain injuries
The bone structures of a newborn are too soft and pliable. Therefore, it is very easy to get damaged. As a rule, it can be avoided.
This is due to insufficient qualifications or outright negligent attitude of medical personnel, obstetric nurses, obstetricians, and doctors.
The most common occurrence is a concussion. There are also fractures of the skull bones and severe deformities.
Recovery is not always possible. The prospects for correction are considered individually, based on the situation.
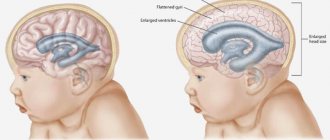
Hydrocephalus
This condition has already been discussed. The concentration of cerebrospinal fluid increases, in different volumes.
Recovery is carried out in a neurological hospital, after undergoing primary therapeutic measures. Emergency assistance.
In fact, the child is transferred from the maternity hospital to the hospital. Further, systematic measures of drug correction will be required. And this will continue indefinitely.
Eclampsia in mother
The so-called late toxicosis. The exact reasons for the development of this dangerous pathological process are not fully understood. It is impossible to say anything concrete, there are only assumptions.
Among them are disorders of the liver and kidneys of the expectant mother, unhealthy diet, physical overload, stress, bad habits.
The disorder is characterized in a rather specific way. Blood pressure increases, and significantly: tonometer readings of 200 to 120 are not the limit. If nothing is done, both mother and child will die. There is a risk.
After birth, dangerous complications begin. Almost all children born in such a difficult way end up in intensive care and fight for their lives.
Fortunately, with sufficiently qualified doctors, the chances of recovery are high. Over 70%.
Newborns are monitored for a week or more when there are risks.
In case of cerebral edema, if the child has recovered from the pathological condition, he is registered with a neurologist. It is necessary to examine a young patient at least once every six months.
Prevention Tips
No less effective than the treatment of edema is its prevention.
- It is necessary to undergo medical examinations to maintain your health.
- Perform feasible physical exercises to reduce the risk of edema.
- Use compression garments.
- Review your diet and exclude foods that cause swelling.
- Monitor your body mass index and lose weight if necessary.
- Do a warm-up every hour if you are sedentary.
- Monitor your medication intake so that it does not cause swelling.
- Give preference to loose and comfortable clothes and shoes.
- Get rid of bad habits that aggravate the formation of edema.
- Purchase orthopedic pillows and a mattress.
- Periodically raise your legs above your heart to prevent swelling.
Simple measures can minimize the accumulation of excess fluid in tissues or completely avoid it.
Symptoms, clinical picture of cerebral edema
The manifestations of the pathological process are obvious and typical enough to immediately understand the essence of the disorder.
Among the signs:
- Disorders of consciousness. Symptoms of cerebral edema in adults in the acute phase, with rapid development, include stupor and coma. They differ from simple fainting in depth and duration. If nothing is done in the first few hours, the patient will most likely never regain consciousness.
- Cramps. Attacks of muscle contractions. Like an epileptic seizure. The manifestation is typical for both acute and gradually increasing edema of brain tissue.
- Unbearable headache. In some cases, a person does not lose consciousness immediately. Then this debut is preceded by pronounced evidence of central nervous system dysfunction.
Associated signs of cerebral edema include dizziness, weakness, a feeling of unreality of what is happening and a weak body. This is the result of sharply weakened blood circulation in the nerve tissues.
- Nausea. Not always.
- Vomit. Similar.
- Visual impairment. Double vision due to compression of nerve tissue. They grow gradually.
- Hallucinations. Visual or auditory deceptions of perception.
- Movement coordination disorders.
- Symptoms of cerebral edema include problems with breathing and heart function. Especially in the later stages.
Brain edema in children is accompanied by a drop in blood pressure, apathy, and lack of reactions to stimuli, which should not be normal.
Diagnosis is complicated because it is impossible to know how a person is feeling. It is not immediately clear what is happening.
Symptoms
In the early stages, the manifestation of the disease is not typical. Often the pathology progresses quickly, so symptoms appear unexpectedly.
The most important symptom of edema is an unbearable headache, which has a pressing character. It spreads quickly throughout the entire head, so it is almost impossible to determine the original location. There is high intracranial pressure, neck numbness and confusion. The pain is often accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
There are more indicative and specific symptoms of the disease, which depend on which part of the brain has been damaged. So, if there is deterioration in vision, then probably the main source of the disease is in the area of the visual analyzer in the brain.
Focal symptoms may also include:
- confusion of temporal-spatial orientation;
- cramps of the arms and legs;
- difficulty speaking;
- impaired coordination and functioning of the vestibular apparatus;
- speech disturbances and sudden loss of consciousness;
- amnesia;
- coma.
If any of the symptoms occur in a person who has previously had a stroke, emergency medical attention is required. Also, people who have had injuries or concussions should pay attention to such manifestations.
First aid
We can do little on our own. You need to call an ambulance. While the brigade is driving, it’s worth following a simple algorithm:
- Lay down or make the patient sit. Under no circumstances should blood rush to the head. Therefore, find the optimal position for the victim.
- Provide fresh air. Open a window or window.
- Create conditions of complete peace. No noise, no intense light irritation. Nothing that could lead to the release of excess hormones.
- Carefully monitor your breathing, the condition of your pupils, and your heart activity. If this is possible, then also blood pressure.
What do doctors do after they arrive on site? First, conditions are provided to transport the patient to the hospital.
Several types of drugs are used:
- Osmotic diuretics. The favorite of this type is Mannitol. The concentration is selected individually.
- Electrolytic solutions to restore basic functions of the central nervous system and heart.
- Hormones, corticosteroids. Prednisolone, Dexamethasone, Hydrocortisone in individual quantities. These medications reduce the permeability of the blood-brain barrier.
- Psychomotor agitation is almost always present. It is eliminated with tranquilizers. For example, Diazepam.
- Cerebrovascular drugs. Another option is Piracetam.
Also other means at the discretion of the paramedic or doctor. Next, you need to transport the patient to a hospital. It is important to restore all body functions. This cannot be achieved in an outpatient setting.
Diagnostic measures
Since the diseases that cause edema are quite diverse, a number of methods are used for diagnosis, covering almost all functions and systems of the body:
- Heart function is assessed by an electrocardiogram.
- An ultrasound examination of the functioning of the pelvic and abdominal organs is performed.
- The functioning of blood vessels is studied using echocardiography.
- X-rays of internal organs and skeleton are required.
- The patient is weighed and measured.
- The work of internal organs is measured not only at rest, but also under increased load.
- A urine and blood test is taken.
- Magnetic resonance imaging can provide the most complete picture of the functioning of internal organs.
Diagnostics
Neurologists and specialized surgeons examine patients. Other related doctors as needed.
Among the events:
- Oral interview with a person. To identify symptoms of the disorder. Provided that the victim is conscious and able to speak. As briefly as possible.
- Anamnesis collection. Study of the origin of the pathological process. The same. The specialist evaluates the overall picture in a nutshell.
- Auscultation. Listening to breathing and heart rate.
- Blood pressure measurement.
- Basic, routine neurological examination. Analysis of reflexes and their preservation.
- ECG, ECHO.
In fact, there is not much time. An experienced specialist understands everything just by looking at a person and studying reflexes. You can’t delay or delay. We need to act.
After emergency care, you can return to a more detailed assessment of the situation. The anamnesis is studied again, an EEG, Dopplerography of the vessels of the head and neck, and carotid arteries is prescribed. An MRI is performed.
It is important to find the cause and eliminate it. This will prevent relapses.
Treatment
Therapy depends on the specific provoking factor. Here is a sample list of options:
- TBI. They use diuretics (diuretics), cerebrovascular drugs (Piracetam), nootropics to speed up metabolic processes in the brain (Glycine, Phenibut). Next - depending on the situation. Surgery is needed if there are structural changes in the skull or nerve tissues.
- Inflammation. Antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, antiviral agents, stimulators of interferon production, immunomodulators. If the process is autoimmune - glucocorticoids (Prednisolone as a starting point).
- Poisoning. Detoxification solutions, antidotes. It all depends on the toxic component.
- Oncology. Removal of the tumor. If it is malignant - radiotherapy, chemotherapy.
- Stroke. Nootropics, loop diuretics (Furosemide), also Mannitol, cerebrovascular after partial recovery. If a hematoma forms, surgery is required to remove it.
- Allergy. Glucocorticoids, antihistamines (Pipolfen, Suprastin, Tavegil, Cetrin) are usually enough to relieve cerebral edema.
- Alcoholism. Detoxification, coding and rehabilitation. In different variations.
- Eclampsia. Antihypertensive drugs. In the later stages, labor is provoked. The risks are too high.
- Hydrocephalus. Loop diuretics. Then thiazide and potassium-sparing diuretics to support the body. In severe cases, a catheter is installed to drain excess volumes of cerebrospinal fluid.
The strategy is determined by the doctor after a thorough diagnosis.
Possible consequences
Even if the treatment is competent, in 20% of cases some echoes of the past pathology remain. Among the complications:
- Headache.
- Disorders of higher nervous activity.
- Weakness.
- Regular attacks of nausea.
In addition, the consequences of cerebral edema include weakening of thinking abilities, memory, concentration, and a tendency to weather sensitivity.
In the acute phase, movement of the brain in the skull and death are possible. Also potentially fatal respiratory and cardiac disorders, deep coma. Death or severe disability.
The condition is very dangerous. With proper treatment, the probability of survival and complete preservation of central nervous system functions is more than 90%. It is important not to delay.