Down syndrome is a genetic disease that crosses out a person’s future. Many mothers who learn about fetal pathology during pregnancy decide to have an abortion, but not all. And some do not even imagine that their baby will be born sick. Therefore, sometimes parents have to face a problem when they learn about the terrible diagnosis of a recently born and long-awaited child. It is important for every person planning to have a baby in the future to know the causes and description of Down syndrome, as well as the prognosis with diagnosis and treatment features.
Features of the phenomenon
The disease is considered one of the most unusual; it has not yet been fully studied, because... It is not possible for modern medicine to identify all the features of its origin. This has led to the formation of a large number of speculations and myths that confuse and form misconceptions about the syndrome among desperate parents.
The main change in the body with such a disease is a non-standard number of chromosomes. This is what completely changes a child’s life. The patient has not 46, but 47 chromosomes, with the extra one being part of 21 pairs, into which the third unit fits. There are also types of disease in which the number of chromosomes does not change, but their deformation or movement occurs. This first became known in 1886, when the scientist D. L. Down presented the results of his research concerning pathology. Therefore, the syndrome received his last name as its name.
Sunny children - this is what people with this syndrome are called. This is due to the fact that all people with this disease stand out from the rest because they are especially kind and tender. They never show negative emotions, do not get angry with others, and you can almost always see a sweet smile on their face. Unfortunately, despite such friendliness, people with Down syndrome cannot live a full life, they lack the necessary skills, and forming normal relationships with other people becomes an almost impossible task for them.
Medical statistics show that in the modern world, approximately 0.1% of people are born with this diagnosis. It would seem that the number is very small, but behind it are hidden millions of children whose lives will never be the same as everyone else’s. Most often, the syndrome manifests itself in babies whose mother became pregnant at a late age, and every year the likelihood of having a sick child increases significantly. If at 25 years old the risks are not so high, and only 0.05% of newborns with this syndrome appear, then 40-year-old mothers give birth to children with this pathology in 0.5% of cases. And when the father is over 40 years old, the risk of the disease increases even more.
A child with such a diagnosis will not be able to live without outside help. Parents who keep their baby must be prepared for all the difficulties that may arise in the future. To do this, doctors conduct special consultations and prescribe courses where they teach how to care for a sick child and the correct approach to raising him.
The largest number of children born with Down syndrome was recorded in early 1987. The reasons for this surge in pathology are still unknown.
Classification
Doctors have created a classification of Down syndrome, according to which there are three types of this disease. Each of them differs in the characteristics of the development of the disease and changes within the human brain. Their symptoms are identical, but treatment approaches may differ slightly under certain circumstances.
There are three forms of the syndrome:
- Trisomy. The most common type of syndrome. It is characterized by the presence of an extra chromosome in pair 21, which disrupts the functioning of the brain. This anomaly is associated with pathological cell division during the development of an egg or sperm. It is often caused by chromosome nondisjunction during the formation of the egg. The result is a negative effect on all brain cells.
- Translocation. The translocation form of the disease is quite rare. When it occurs, a fragment of one chromosome is displaced towards another or a slight deviation from its initial location. The carrier of this mutation is a man, which is why transmission of the syndrome can only occur on the father’s side.
- Mosaicism. This type of syndrome occurs in only 1% of cases, making it the rarest. It is distinguished by the presence of 47 chromosomes only in some cells, while in the rest there are 46. This anomaly is caused by a defect in cell division after the birth of the fetus in the mother’s egg. This is often associated with a disorder of meiosis. Children with this type of syndrome have slightly more developed brains.
Dividing the syndrome into forms is not the only method of classifying this disease. Additionally, in medicine there are degrees of Down syndrome, which describe the severity of a child’s mental retardation. There are 4 of them in total:
- Lightweight;
- Moderate;
- Heavy;
- Deep.
A weak degree is not so scary, because... children who encounter it are almost no different from those around them and are able to achieve their goals. Moderate levels make the child’s life more difficult. Severe and deep deprives a person of any opportunity to fully understand what is happening and make any plans for the future. Therefore, it is very important to promptly identify chromosomal abnormalities and begin treatment without waiting for the pathology to worsen.
The chance that a woman with Down syndrome will become pregnant does not exceed 50%. Men are much worse off in this regard - they succeed in becoming a father only in isolated cases. This is due to partial disruption of the functioning of the genital organs.
Raising a child with Down syndrome
Parents who are informed that their child has a serious chromosomal pathology and refuse to terminate the pregnancy often overestimate their strength, not realizing how difficult this is for the whole family in general and for the unborn baby in particular.
If a firm decision has been made to leave the pregnancy, the couple must realize that they now have a serious responsibility. You should not deny that a child has abnormalities and consider him normal, because such an attitude can deprive him of necessary medical care. Parents should surround such a child with affection and care no less than other children, because he perfectly feels the attitude towards him.
Children with Down syndrome should be regularly monitored by specialists, take medications prescribed by a doctor, go to special procedures and follow a regimen. Inpatient treatment is prescribed only if necessary. Often all this costs a lot of money and not every family has the financial means to provide a special child with everything necessary.
Children with Down syndrome experience rapid fatigue, impaired coordination and fine motor skills, and delays in physical and mental development. Parents must be patient and strive to make daily efforts for their child's development. Only in this case will he be able to acquire all the skills necessary for life, even with a delay. There are also rehabilitation programs developed by qualified psychologists and pediatricians that can significantly help in solving the problems of raising special children, but even their use, unfortunately, does little to ease the burden of parents.
Causes
The answers to many questions regarding Down syndrome remain unknown, and the causes of its occurrence are no exception. Nevertheless, doctors continue to actively research this disease, regularly learning something important and new. Perhaps much more will be known about her soon.
The main reason for the development of the syndrome is considered to be heredity. It depends on the parents whether their child will suffer from such a terrible illness. At the same time, scientists are absolutely sure that environmental factors or the lifestyle of parents before fertilization and during pregnancy do not have any effect on the likelihood of the disease occurring. Therefore, there is no direct guilt on the part of mom or dad, and all self-flagellation is absolutely pointless.
If we talk about hereditary causes in more detail, they are associated with the age of the parents, and are not the only factors pushing towards this problem. In total, there are 5 points that can lead to illness, which are known to scientists:
- Age of parents. The older the mother, the higher the risk that she will have a baby with Down syndrome. Every year the probability increases, which forces many women not to delay pregnancy and have a child earlier. It is advisable to do this before the age of 35. The age of the father is no less important - if he is over 40, then the risks will also increase.
- Accident in the formation of pregnancy. A huge number of different processes occur in the body; in any of them, an unexpected failure can occur, which will lead to unpleasant anomalies. One of them is Down syndrome. It can arise as a result of random coincidences during the interaction of male and female reproductive cells, as well as the first stages of pregnancy.
- Lack of folic acid. An insufficient amount of this component can lead to disorders within the body, which is especially dangerous when carrying or conceiving a baby. However, this fact has not yet been proven by scientists and is speculative. However, it can still cause illness.
- Presence of illness in previous children. If parents have already given birth to a baby with this syndrome, then the likelihood of encountering this problem again when conceiving another child is somewhat higher. This is due to the fact that there are definitely reasons for such a result, as proven by a previously born baby.
All these factors deserve special attention. If they are present in the life of a couple who has decided to have a child, it is worth visiting a geneticist so that he can conduct all the necessary tests and talk about the likelihood of having a healthy baby. But it is worth understanding that even in the absence of any cause of downism in life, the good health of the unborn child cannot be guaranteed.
D. L. Down, having identified Downism, first called it “Mongolism.” The cause was epicanthus in sick people, which resembled the appearance of people of the Mongoloid race.
Advice for parents of children with Down syndrome
- Remember: a child with Down syndrome is an individual who, like any individual, has his own hopes, dreams, rights and dignity.
- A child with Down syndrome has the same basic needs as any other child.
- Don't focus on the needs of the child with Down syndrome; remember the needs of all other family members. Your family should be harmonious.
- A child with Down syndrome should not completely occupy your life. Don't treat it like a heavy burden.
- A child with Down syndrome needs the love of his family and always responds to them in kind.
- Respond with calm and dignity to the curious looks of strangers.
- Try to answer questions from friends and passers-by without hesitation and honestly.
- Make new friends if necessary to make both you and your child feel comfortable.
- In conversations with specialists, ask any questions about your child, even if they may seem trivial to you.
- Meet other parents of children with Down syndrome and talk to them about how they felt when a child was born into their family.
- Remember that parents are always the experts in matters affecting their own child.
- In order for a child to learn to interact with the world around him, he needs to attend a regular public school. If a child is taken to some other school, he immediately becomes different from everyone else in the eyes of the public. In this case, it is difficult to find friends and establish relationships with people.
- Due to their narrow social circle, children with Down syndrome are strongly attached to their parents. Friendship is a special value for them. By imitating other children, these children can learn valuable social skills.
Video
Symptoms
The medical description of the syndrome is quite clear and includes specific manifestations, which makes it possible to detect its presence in children immediately after birth. But modern technologies have made life much easier for doctors and parents of children suffering from this disease. They make it possible to determine the development of Down syndrome in a child who is still in the womb. The symptoms will be different, but this does not have a negative impact on the effectiveness of identifying the disease.
Symptoms during pregnancy
Some signs of the development of the disease can be seen on ultrasound already in the first trimester of pregnancy, but they all require separate diagnostics that will confirm their presence. No doctor can say immediately and absolutely about the presence of symptoms indicating possible downism.
In the womb, a baby with this syndrome may have the following symptoms:
- Complete absence of nasal bone;
- Fairly short length of bones in shoulders and hips;
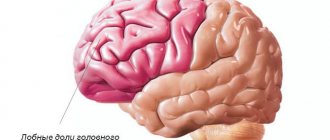
- Reduced cerebellum, insufficiently large frontal lobe of the brain;
- Thickened collar space;
- Heart problems;
- Hyperechoic spots on the heart;
- Tumors of the choroid plexus;
- Enlarged renal pelvis;
- Hyperechogenicity of the intestine;
- Infection of the duodenum.
None of these symptoms can be accurate evidence of the development of Down syndrome in the fetus. Even if they are present, the child can be born completely healthy. However, it is still worth thinking about and carrying out all the necessary diagnostics along with treatment in order to avoid problems with the baby’s health in the future.
Symptoms after birth
Signs in newborns are more obvious, but their presence also does not mean that the baby has downism. If they are detected, then you should urgently take the child to the doctor and tell them about your suspicions. After this, he will be sent to various genetic tests that will help give an accurate answer to whether he has such a syndrome.
These symptoms include the following phenomena and disorders:
- The plane of the face, the back of the head or the bridge of the nose;
- Deformation of the chest, ears;
- Insufficient length of the skull, nose, limbs;
- The presence of a skin fold on the neck, the length of which is relatively short;
- Short finger length associated with low development of phalanges;
- Transverse palmar fold;
- Slight curvature of the little finger;
- Large distance between the first and second toes;
- Unusual structure of the palate in the form of an arch, often an open mouth;
- The presence of grooves on the surface of the tongue;
- Pigment spots on the iris of the eye;
- Strabismus, Mongoloid eye shape;
- Hypermobile joints;
- Hypotonicity of muscle tissue;
- Heart diseases;
- Congenital anemia;
- Psychical deviations;
- Narrowing or overgrowth of the duodenum.
If a baby has downism, then most likely he will have almost all of the listed symptoms from the moment of birth. The nature of the disease is such that it begins to manifest itself already at the stage of fetal formation, which makes its detection much easier. It is worth noting that when growing up at primary school age, children may develop: cataracts, dental problems, mental retardation, stuttering, reduced immunity, and obesity.
Down's surname is similar to the English word down, which is why many people mistakenly believe that the disease was named for its decreased intelligence.
Forecast
Children faced with such a disease can live completely differently. It all depends on the degree of negative impact on their mental development and the effectiveness of treatment, which includes regular activities with the baby. In most cases, children can live quite well. They are able to learn, even a certain lag behind their peers does not become such a serious problem. Many fully walk, read, write and perform other everyday tasks. Speech may be difficult, but most children can learn to express themselves and communicate with others. Therefore, sometimes children with such a problem are not sent to a special school, preferring a regular general education institution. Having matured, some of them can start a family, creating strong relationships with a member of the opposite sex. Of course, we are not talking about the usual idea of everyday life, but it can be almost complete.
Unfortunately, the prognosis is not as positive as many parents would like. Children often face many more serious problems than developmental delays and communication difficulties. Among them:
- Dementia – the likelihood of developing dementia with Down syndrome is quite high; many older patients experience it, most often it occurs before the age of 40.
- Infections – the immunity of sick children is very weak, which is why they are susceptible to various infectious diseases that can harm their health.
- Digestive disorders - the effect on the intestines with downism can be quite serious, which will make the patient’s life very difficult.
- Heart failure - more than 50% of children with this disease have congenital heart defects, which sometimes lead to dire consequences and may require surgery.
- Leukemia – some patients develop leukemia in childhood, which is a malignant disease and can be extremely dangerous.
- Bone weakness – underdeveloped bones become a serious problem that requires a special approach to lifestyle and maximum safety for the baby.
- Problems with the sensory organs – some people with this syndrome suffer from severe hearing loss or visual impairment.
- Apnea – Most people with this condition experience sleep apnea, which is a short-term stop in breathing and is associated with deformation of the chest.
- Obesity - all people with Down syndrome have a tendency to gain excess weight, which is why many of them cannot avoid obesity.
- Life expectancy - in most cases, children with Down syndrome live to adulthood, often this figure reaches 50 years, after which death occurs, but this is not much.
Other manifestations of the disease cannot be excluded. For example, epileptic seizures. Everything can be very individual, and also depending on the main symptoms, from which various complications arise in the future.
Some people with Down syndrome have managed to obtain higher education. A striking example is the Spaniard P. Pineda.
Signs of Down syndrome
Children with Down syndrome have distinctive facial features.
Not all patients have the same appearance features, but the most common are:
• Short neck. • Small head. • Tongue stuck out. • Flattened face. • Mongoloid eye shape. • Unusually shaped ears.
Patients with Down syndrome also have other signs:
• Poor muscle tone. • Wide, short brushes. • Relatively short fingers. • Tendency to obesity. • Dry skin.
Many patients have malformations of the heart and gastrointestinal tract. Children with Down syndrome may be of average height, but they usually grow poorly and remain shorter than other children their age. In general, patients with Down syndrome reach all important stages in their development (sitting, walking) two times slower than healthy children. Children with Down syndrome have some degree of mental retardation, usually mild to moderate.
Diagnostics
Timely diagnosis will help identify the presence of the disease in the baby at an early stage. The sooner this is done, the more chances parents will have to influence the future of their child. For this, various medical techniques are used. If the baby has already been born, and the parents have suspicions that he has Down syndrome, then you just need to consult a doctor. In most cases, it is enough to undergo a thorough examination, as well as genetic testing, after which a final diagnosis will be made. Sometimes doctors can tell immediately after a conversation whether a patient has such a disease.
During examinations during pregnancy, making a diagnosis is more difficult. To determine the disease, the following may be prescribed:
- Ultrasound - some signs of the syndrome can be detected with its help already in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy;
- Amniocentesis is an analysis of amniotic fluid, which is examined by puncturing the abdomen with a special needle;
- Chorionic villus biopsy is a study of a piece of tissue from the outer membrane of the fetus; to implement the method, a special needle is also used to puncture the abdomen;
- Cordocentesis - testing the fetal cord blood allows you to check for signs of downism in the fetus within the blood composition.
Most often, combined screening tests are used to examine the fetus of a pregnant woman. They include a large number of tests from standard ultrasound to more specific studies of certain venous blood parameters. They are carried out at strictly specified intervals of pregnancy during the 1st, 2nd and 3rd trimester. Based on the results, doctors can accurately determine whether a child has this syndrome, because they will be aware of all chromosome defects.
International Down Syndrome Day is celebrated on March 21. This event first took place in 2006, becoming an annual event.
Diagnosis of Down syndrome
Genetic screening for Down syndrome can be performed during the fetal development of the child.
Maternal age is traditionally considered an indication for such screening. If a child is diagnosed with a pathology before birth, the mother will have more time to think and prepare for caring for a child with special needs. The doctor will tell you in detail about the pros and cons of such screening. Today, the American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends a wide range of tests that can help identify Down syndrome. If the first tests (ultrasound and blood tests) indicate a possible problem, then more accurate but invasive tests (amniocentesis) can be performed on this basis.
In past decades, the United States offered mothers blood tests around 16 weeks to check for Down syndrome and other chromosomal abnormalities. Today, a more effective combination test is recommended, which is carried out in two stages between the 11th and 13th weeks of pregnancy.
The first trimester test includes:
1. Ultrasound.
Using conventional ultrasound, an experienced doctor can examine and measure specific areas of the fetus. This helps to identify gross malformations.
2. Blood test.
The results of the ultrasound are evaluated together with the results of blood tests. These tests measure levels of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) and the pregnancy-associated plasma protein PAPP-A. The results allow us to judge whether there are serious abnormalities in the development of the fetus.
Comprehensive test for the first and second trimester:
American experts recommend conducting a comprehensive test, which consists of tests in the first trimester (as described above) and additional tests in the second trimester. This comprehensive test produces a lower percentage of false positive results. That is, as a result, fewer women will mistakenly believe that their child has Down syndrome.
To do this, in the second trimester, between the 15th and 20th weeks of pregnancy, the mother's blood is tested for 4 indicators: alpha-fetoprotein, estriol, hCG and inhibin A. The results of this analysis are compared with the results of tests obtained at the beginning of pregnancy.
Of all women who are screened, about 5% are identified as at risk. But in reality, the birth rate of children with Down syndrome is much lower than 5%, so a positive test still does not mean that the child will necessarily be born with the disease.
If screening shows a high risk of Down syndrome, it is recommended to undergo a more invasive but accurate test.
Such tests include:
1. Amniocentesis.
During the procedure, a special needle is inserted into the uterus and a sample of the amniotic fluid surrounding the fetus is taken. This sample is then used for chromosomal analysis of the fetus. Amniocentesis is usually performed after the 15th week of pregnancy. Judging by American statistics, in 1 case out of 200 procedures (0.5%) a miscarriage is possible.
2. Analysis of chorionic villi.
Cells that are taken from the mother's placenta can be used for chromosomal testing for Down syndrome and other chromosomal diseases. The test is performed between the 9th and 14th week of pregnancy. The risk of miscarriage after this procedure is about 1%.
3. Analysis of a blood sample from the umbilical cord.
This test is performed after the 18th week of pregnancy. The test is associated with a higher risk of miscarriage than other methods. It is done in very rare cases.
Modern prenatal tests:
1. Analysis of circulating fetal DNA.
This analysis is not yet available in all hospitals, even in the West. A unique method allows you to find and study the child’s genetic material circulating in the mother’s blood. Circulating fetal DNA analysis can detect both Down syndrome and other chromosomal abnormalities. There is absolutely no risk to the fetus.
2. Preimplantation genetic analysis.
This is an analysis that is carried out during artificial insemination to exclude genetic defects in the embryo before it is implanted into the uterus.
Diagnosis of Down syndrome in newborns:
After birth, suspicion of Down syndrome may arise simply because of the appearance of the child. If a newborn has characteristic external manifestations of Down syndrome, the doctor may prescribe a chromosome analysis. If additional genetic material is detected in all or some cells in the 21st pair of chromosomes, then Down syndrome is confirmed.
Treatment
It is important to understand that no treatment will make the child healthy. The syndrome cannot be overcome by any medical measures. Therefore, all therapy is aimed at maximizing the normalization of the sick person’s life and his education. For this purpose, professionals of various categories are involved. But the most important thing for such a child is the help of parents, without which they cannot cope.
If we talk about taking medications, they can support the development of the central nervous system. To do this, medications are prescribed that help improve blood circulation in the brain. The most effective are:
- "Piracetam";
- "Cerebrolysin";
- "Aminalon".
Children are also recommended to regularly take B vitamins. They can be obtained from special complexes purchased in pharmacies, or from regular food. Therefore, parents should think about adjusting their diet.
It is very important to give the baby the necessary care. Parents should be attentive to him, help him adapt to the world around him, and also accept his present. Under no circumstances should you shout at him or show negative feelings. Any desire for independence in such a child should be encouraged, because This is a useful element that allows you to improve its condition.
The parents' task is also to monitor his actions and condition as seriously as possible. Manifestations of the disease, as well as possible complications, are quite dangerous. Therefore, you need to be careful and visit a doctor at the slightest deviation. But even in cases where everything is “as usual”, you need to go to the hospital at agreed intervals for various tests.
It is recommended to contact specialists so that they can develop speech, motor skills, communication skills, as well as everyday abilities. Such functions could be performed by the parents themselves, but professionals will be able to do it much faster and better, because know the right approach and are not so dependent on personal feelings or emotions.
Evelina Bledans, Lolita, the children of Boris Yeltsin, the daughter of Irina Khakamada - all these famous people independently raise children with Down syndrome.
Treatment of Down syndrome
Early diagnosis and proper treatment helps children with Down syndrome realize themselves more fully, and also improves their health and quality of life.
Developed countries have had very strong programs to help children with Down syndrome for many years. These programs may differ, but they usually involve large teams of doctors, psychologists and teachers. These programs focus on developing a child's motor skills, speech, communication and self-care skills.
The team of doctors who should work with these children includes:
• Pediatrician. • Pediatric cardiologist. • Pediatric gastroenterologist. • Pediatric endocrinologist. • Pediatric neurologist. • Development specialist. • Physiotherapist. • Audiologist. • Speech therapist, etc.
What should you expect?
Children with Down syndrome develop with a significant delay and later begin to crawl, sit, stand and talk. Some mental retardation will accompany the child throughout his life. In addition, such children often have severe defects of internal organs, which sometimes require complex operations. But early intervention will help increase the child's chances.