The human brain is the main center from where signals are sent to the periphery, to other organs, and the organs respond to orders from the brain. However, under certain circumstances, signals may not travel at the right time to one or more parts of the human body. And then this part of the body gradually atrophies if the necessary treatment is not found.
This is how a person experiences unpleasant symptoms - paresis of the limbs, arms or legs. The complex mechanism of this phenomenon requires detailed consideration.
Paresis of the limbs as a symptom of the disease
Paresis of the limbs occurs due to dysfunction of the brain or spinal cord. Those parts of it that are responsible for motor activity. At the same time, the muscles of the arms and legs cease to obey, which does not allow the person to move freely. Very often this condition provokes a stroke.
In the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10), sometimes such pathology is classified as code R 29.8 - other and unspecified symptoms and signs.
When the leg and foot are paralyzed, it is very difficult to bend the hip, and sensitivity disappears. If paresis of the arms occurs, a decrease in movements becomes noticeable. A person cannot even make a normal handshake.
With prolonged paralysis, the muscles begin to atrophy, and it will become increasingly difficult to restore their functions. This will require special treatment, massage and exercise therapy.
Muscle atrophy with limb paresis
Prices
| Disease | Approximate price, $ |
| Prices for diagnosing migraine | 7 060 – 8 260 |
| Prices for diagnosing childhood epilepsy | 3 100 – 4 900 |
| Prices for brain shunting for hydrocephalus | 33 180 |
| Prices for treatment of Parkinson's disease | 58 600 |
| Prices for migraine treatment | 9 680 |
| Prices for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis | 6 550 |
| Prices for diagnosing epilepsy | 3 520 |
| Prices for rehabilitation after a stroke | 78 300 – 82 170 |
| Prices for treatment of childhood epilepsy | 3 750 – 5 450 |
| Prices for treatment of multiple sclerosis | 4 990 – 17 300 |
Types of paresis
Experts classify several types of paresis.
This depends on several factors:
- muscle strength;
- lesion sites;
- depending on the number of affected limbs.
Muscle strength is divided according to a point system:
- The countdown starts from 5 points. In this case, no motor disturbances should be noticeable. The patient is completely healthy in this regard.
- At 4 points, a slight disruption of muscle function appears , but they are barely noticeable. This is a mild paresis.
- If a score of 3 is given , the deterioration in muscle functionality has become more noticeable. There are times when part of an arm or leg does not obey.
- With a score of 2, it is difficult to bend your arms and legs.
- 1 point characterizes a severe stage of paralysis. Any movement requires a lot of willpower.
- Complete paralysis means 0 points and the person becomes completely immobilized.
When determining the location of the onset of paralysis, the following are distinguished:
- Spastic paresis , also called central. In this case, a person becomes paralyzed on one side of the body. In this case, the arm and leg will be paralyzed, on one right or left side. This variant of paresis is characterized by an uneven or partial change in muscle tone.
- Peripheral paresis (or flaccid paresis) occurs due to damage to brain cells. With it, all reflexes disappear, the muscles do not obey. Another person becomes completely immobilized. Subsequently, the muscles completely atrophy.
- Mixed paresis combines the signs of flaccid and central paresis.
Peripheral or flaccid paresis
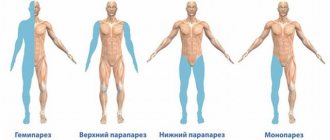
Types of paresis can be determined by the number of affected limbs:
- Monoparesis . In this case, only one limb is affected.
- Hemiparesis . Then one side is affected. Left-sided or right-sided paresis.
- Paraparesis . This is when the top or bottom is paralyzed, upper paresis and lower paresis.
- Tetraparesis. In this case, complete paralysis of all arms and legs occurs.
Types of paresis are characterized by characteristic symptoms.
What diagnostics is needed for a patient with paraparesis?
It is extremely important not only to identify paraparesis in a patient, but also to determine its true cause, since treatment tactics depend on the etiology of paraparesis.
If a person develops symptoms that indicate paraparesis, the diagnostic program should include:
- MRI (sometimes CT) of the brain, spine and craniovertebral area;
- radiography of the spine and skull;
- lumbar puncture and cerebrospinal fluid examination;
- neurological examination;
- myelography;
- electromyography;
- general clinical blood and urine tests;
- blood chemistry;
- serological diagnosis of possible infectious agents that can affect the nervous system;
- determination of vitamin B12 and folic acid levels in the body;
- consultation with a geneticist;
- study of tumor markers and other examinations for the purpose of cancer detection.
Symptoms of limb paresis
Paresis, like any other disease, has its own symptoms. They can be identified by examining the patient and conducting research.
Symptoms of limb paresis:
- A person's gait changes. She becomes unsure and begins to waddle from side to side. The patient finds it very difficult to get up. There are difficulties with any movement or movement, loss of coordination (ataxic syndrome).
- The muscles in the arms and legs weaken. Muscle tone sharply decreases or increases.
- The foot sags and does not obey.
- A pathological foot reflex may appear.
- When running along the soles of the feet, the fingers may suddenly straighten.
- The functioning of the circulatory system deteriorates. This occurs due to a sedentary lifestyle and atrophy of the vascular walls. Because of this, the heart will work poorly.
- Paralysis of the limbs may be accompanied by paralysis of internal organs . The digestive system is especially susceptible to this.
Even a non-specialist can determine that a person’s limbs are paralyzed. But only a doctor will determine the cause and prescribe treatment.
Symptoms
Let's look at common motor dysfunctions.
Spastic diplegia
The most common form of cerebral palsy. The clinical picture shows spastic tetraparesis, that is, the function of the arms and legs is impaired, but the lower extremities are more affected. Patients have increased tone not only of the muscles of the arms and legs, but also of the body, as well as the tongue. Small children cannot sit or walk. The majority have pseudobulbar syndrome - articulation (articulate pronunciation), phonation (sound production), swallowing and chewing suffer. This form may be complicated by convulsive syndrome. Pathological attitudes are noted and a spastic gait with a cross is formed. Due to muscle tension, the patient has difficulty bending his legs at the knee joints and does not lift his legs off the floor.
Patients develop early deformities of the arms and legs, contractures , and curvature of the spine . High muscle tone causes pathological attitudes - crossing the legs and bending the knee joints. Characteristic poses develop: the triple flexion pose and the ballerina pose.
Children's intelligence is normal or reduced, and there may be hearing impairment. The degree of increased tone varies from mild to severe. Depending on this, some patients can walk independently, others with support, and others need to move in a wheelchair.
Spastic hemiparesis
With this form, the movements of the arms and legs on any one side of the body deteriorate. In the clinic it can manifest itself as left- or right-sided hemiparesis . At the same time, its expression is greater in the hand. This form is characterized by the fact that spasticity is more pronounced in the leg extensors and arm flexors. Therefore, the affected arm is bent at the elbow and brought to the body, the hand and fingers are also bent (the expression “the hand asks”) is used.
If we talk about cerebral palsy, then from birth the baby has a difference in movements in the arm and leg on the affected and healthy half. Limbs with paresis lag behind healthy ones in growth—the difference in their length is noticeable. The standing posture becomes incorrect and the foot is placed “on its toes”. Shortening the limb leads to poor posture and pelvic distortion.
When a child begins to walk confidently, he develops a hemiparetic gait. When walking, he “circles” a circle with the affected leg: it is extended at the knee joint and performs circular movements outward, and the torso deviates in the opposite direction. This bent position of the arm and leg, which makes circular movements when walking, is called Wernicke-Mann pose .
Hemiparetic gait occurs with lesions of the brain and spinal cord: strokes , abscesses , encephalitis , brain trauma , tumors , toxic injuries and hereditary degenerative processes. In patients, the muscles on the affected side are dense to the touch and their relief is sharply contoured. If several passive movements are performed in a limb in a row, then muscle tension decreases. When examining a patient, a “jackknife” symptom is often encountered - with passive movement in the elbow or knee joint, the patient feels muscle resistance, and then it decreases.
Inferior flaccid paraparesis
This form of motor dysfunction is associated with damage to peripheral neurons and is characterized by:
- decreased or complete loss of muscle tone;
- amyotrophy;
- degeneration of nerves;
- decrease or disappearance of reflexes;
- muscle degeneration.
Acute flaccid paresis was previously associated with polio , but after vaccines were created more than 50 years ago and thanks to mass immunization, the territory of the Russian Federation has been considered a polio-free zone since 2002. This movement disorder can be associated with many other causes and occurs as a symptom in many diseases:
- infectious lesions of peripheral nerves ( myelitis , polyneuropathy , mononeuropathy );
- traumatic neuropathies ;
- encephalomyelitis;
- spinal cord tumors in the thoracic spine;
- spinal cord injury in the cauda equina region;
- demyelinating diseases of the central nervous system;
- transient circulatory disorders of the spinal cord;
- botulism;
- hereditary metabolic diseases (HBD);
- heavy metal poisoning;
- Guillain-Barré syndrome (acute idiopathic polyneuritis - an autoimmune disease);
- toxic effect of drugs ( vincristine , isoniazid );
- the effect of muscle relaxants ;
- myasthenia gravis;
- botulism.
Patients initially develop weakness in the leg muscles, which progresses, and the patient cannot stand or move independently. Movement with great physical stress is possible only with the help of strangers or crutches. Patients cannot maintain an upright posture if their knee joints are not fixed. Attempts to maintain a vertical position lead to bending of the legs. All this leads to the fact that the patient has to stay in bed or in a wheelchair most of the time.
They change their position in bed due to tension in the muscles of the arms and shoulder girdle. Passive movements are performed by patients without muscle tension, but active movements are performed with difficulty, and their amplitude is very limited due to severe muscle weakness. Flaccid paralysis occurs with profound disturbances in muscle movement and trophism. The muscle tone is sharply reduced, the muscles are flabby and atrophic, so the foot acquires the pes equinus (horse foot) position - the foot hangs and is bent towards the sole, which makes walking very difficult.
In acute cases ( encephalomyelitis , acute flaccid paresis ), these phenomena appear within 7-10 days, and in chronic flaccid diseases, muscle weakness and paralysis develop gradually.
How is diagnosis done?
To identify the cause and type of paralysis, you will need to consult several specialists:
- Neurosurgeon.
- Psychiatrist.
- Pulmonologist.
- Psychoneurologist.
- Otolaryngologist.
To identify the full clinical picture, a detailed examination is necessary. The patient must give blood for analysis. His psychogenic reaction is checked.
The following research methods must be used:
- computed tomography;
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- neurosonography;
- fluoroscopy.
Reflexes of the limbs are checked, the brain is examined. After this, the cause of the paralysis can be identified. The main specialist who chooses diagnosis and treatment is a neurologist.
Reflex test
Diagnostics
The presence of lower central paraplegia as a basic symptom and its familial nature are of decisive diagnostic importance. In sporadic and complicated forms, the neurologist has to carry out differential diagnosis with ALS, spinal cord tumor, spinal variant of multiple sclerosis, vascular myelopathy, and neurosyphilis. To differentiate Strumpell's paraplegia from leukodystrophies, an MRI of the brain is performed. In some cases, it reveals atrophic changes in the cerebral cortex. MRI of the spine visualizes degenerative-atrophic processes in the lateral and anterior columns at the level of the thoracic and/or lumbar segments of the spinal cord. An auxiliary method in the diagnosis of Strumpel's disease is electroneuromyography (ENMG) and the study of evoked potentials. ENMG allows you to determine the presence and degree of neuropathy. The study of somatosensory EPs demonstrates a delay in conduction along the posterior spinal columns, while the study of cortical EPs demonstrates a decrease in the speed of conduction along the corticospinal tract. Genealogical analysis and molecular genetic studies are of great diagnostic importance. Due to the great heterogeneity of pathology, the latter are carried out only for the most common types of disease. Prenatal diagnosis is possible.
What is the difference between paralysis and paresis?
Doctors distinguish these two concepts according to the degree of damage to the human body.
Paresis is a deterioration in muscle function and difficulty in movement. But still, with the application of certain efforts, a person can move on his own or with help.
Paralysis is the complete inability to move. The person can be carried, but cannot move their arms or legs.
Spinal cord injury
Causes of paresis
Most often, paralysis is caused by damage to neurons in the cerebral cortex.
But other factors can be identified that provoke paresis of the limbs:
- Brain tumors or inflammatory processes in the brain.
- Disruption of the vascular system, cerebral hemorrhage (spinal stroke).
- A nervous disease called epilepsy.
- Diseases of the central nervous system (cerebral palsy, sclerosis, syringomyelia and others).
- Amyotrophy.
- Complex infections that have entered the body.
- A purulent focus in the body that can cause blood poisoning or the spread of inflammation throughout the body.
- Complex injuries that may involve the skull, spine, spinal cord or brain.
- Metabolic disorders (diabetes).
The causes of paralysis may be individual.
Causes of the disease
Paraparesis of the lower extremities develops against the background of various provoking factors. For successful treatment it is necessary to establish the source of the disease. The causes of paraparesis of the lower extremities are as follows:
- Tumors of the brain and spinal cord.
- Herniated discs.
- Myelopathy.
- Back diseases (osteochondrosis, spondylosis, spinal stenosis).
- Injuries to the spinal cord or nerve roots.
- Sclerosis.
- Abscess of the spinal cord and its membrane. The same goes for the epidural space.
- Heredity, congenital or acquired injuries after childbirth.
- Infectious and autoimmune diseases.
- Lack of vitamin B12.
- Vascular factor.
Myopathy can cause paraparesis of the lower extremities. The disease disrupts muscle metabolism. The same applies to demyelinating pathologies, which negatively affect the protein, causing its breakdown. After poisoning with toxic substances and alcoholic beverages, a person develops characteristic symptoms.
It is important to promptly establish the cause of the disease, undergo a full medical examination and treatment prescribed by a doctor. With properly selected therapy, the prognosis is favorable.
Treatment of paresis
Several methods are used to treat limb paresis. They must be selected individually for each patient. Depending on age, health status and cause of paralysis.
For this use:
- medications;
- massotherapy;
- surgical intervention;
- special physical education.
Only in combination can all these measures bring a noticeable positive therapeutic effect. The duration of their use is determined by the doctor individually.
Drug therapy
The choice of medications should only be made by a doctor. They will depend on the cause of paralysis.
For paralysis, they usually use:
- Muscle relaxants - in the form of an injection or ointments Sirdalud, Sibazon, Mydocalm, Tizanidine.
- Antispasmodics - in the form of tablets or injections Oxyvent, Piren, Drotaverine.
- Prosein , which does not have a central effect. It is used for paresis and many other complex diseases.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. There are quite a few names, but only a doctor should select them.
- A vitamin complex must be prescribed . It should help improve the immune system.
Sirdalud tablets
Mydocalm relaxes muscles
Tizanidine
Sibazon
Prozerin
Drotaverine
The dosage and duration of administration will be selected by the attending physician, individually for each patient.
Physiotherapy
Physical therapy may be used to treat paralysis. Any method that the doctor prescribes.
Physiotherapy methods:
Magnetic therapy in children is used for recovery from injuries
- massotherapy;
- galvanotherapy, using low voltage electric current;
- darsonvalization - the use of pulsed alternating high-frequency current;
- inductometry - the healing properties of the magnetic field are used;
- magnetotherapy - low-frequency magnetic field;
- microwave therapy and laser therapy;
- therapy using high frequency electromagnetic fields;
- electrosleep, electrical stimulation, electrophoresis;
- cryotherapy and ultraviolet therapy;
- ultrasonic phonophoresis.
The doctor will select the most suitable and effective procedures. Physiotherapy helps restore reflexes, improve blood circulation and affects the immune system.
DENAS therapy
DENAS is a special device that acts using impulses on the central nervous system. It is used for paresis and strokes. Treatment is carried out in courses.
The device is used for different parts of the body:
- On the scalp.
- From the bridge of the nose to the 2nd cervical vertebra.
- From ear to ear.
- In the area of the carotid arteries.
- Directly on paralyzed limbs. If one is healthy above her also, but in certain doses.
- In the cervical-collar area.
This will help restore motor function and help normalize blood pressure. But before that, it is better to consult your doctor.
Device for DENAS therapy
Physical therapy and exercise
All exercises should help restore the affected muscles.
There is a general course that is suitable for all patients with lower limb paresis:
- Exercise No. 1. Alternately raise your leg. When the leg is raised, you need to inhale. The patient lies on his back.
- Exercise No. 2. In the same position, the person raises his legs and pulls them to his chest. This is done alternately with each leg. You need to pull it to your chest as close as possible.
- Exercise No. 3. Draw circles or figure eights in the air with your feet. This is done with each leg separately.
- Exercise No. 4. The patient should imagine that he is swimming breaststroke and at the same time making the necessary movements with his legs.
- Exercise No. 5. You need to bend and straighten your toes.
- Exercise No. 6. Pull your feet closer to you as far as possible.
- Exercise No. 7. Twist your feet.
- Exercise No. 8. Imitate riding a bicycle.
Recovery Exercises
The main starting position is lying on your back. But depending on the patient's condition and progress in exercise, the patient may sit while performing some exercises.
It is necessary to engage in physical therapy regularly. The duration of the workout is about 20 minutes. But at first, no more than 10 minutes. Repeat exercises up to 3 – 4 times. The load can be gradually increased. In this case, you need to monitor your blood pressure and not overdo it.
Disease prognosis
If Duchenne palsy is diagnosed in a timely manner and its therapy is prescribed correctly, this allows for a favorable prognosis. During the treatment of the pathological process, parents must strictly adhere to the doctor’s recommendations.
When the nerve pathway is partially damaged, 20 percent of children experience complete restoration of mobility and function of the upper limb, as well as complete recovery. In other children, limb function is restored thanks to a properly selected treatment regimen. The functionality of the hand is restored in children to such an extent that this practically does not negatively affect the quality of life.
If a child has a complete rupture of the nerve trigger, then this does not provide such a favorable prognosis. The earlier surgical intervention is performed and the better the recommendations of the recovery period are followed, the more favorable the prognosis will be.
If the treatment of the pathological process is not carried out in a timely manner, then it is not possible to restore full mobility of the arm, regardless of the therapeutic methods used.
Such negligent attitude towards the child’s health leads to the development of complications. Most often, patients experience contact with the cervix in the joints of the hand. An undesirable consequence of the disease is spinal deformity.
Treatment of newborns
To choose a treatment method, you must consult a doctor. For newborns, only a specialist selects a method of treating limb paresis.
The child is still very small and it is very important that parents make every effort and regularly follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
The specialist conducts an examination and identifies the cause of paralysis. Based on these findings, the following is carried out:
- drug therapy;
- massotherapy;
- physical therapy or gymnastics;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- operation;
In this case, you need to take into account the age of the baby. Some operations can only be performed by adults. But parents should not refuse preventive measures under any circumstances.
Treatment
For treatment, both medication and surgery are used. In the acute period, it is not always possible to determine the need for surgery due to tissue swelling. Therefore, therapy always begins with conservative treatment methods.
Typically, the patient is prescribed a number of medications:
- painkillers – to alleviate the general condition,
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Ibuprofen and others) that relieve inflammation and relieve pain,
- anticholinesterase drugs (Neuromidin, Galantamine) - to normalize the production of hormones involved in the conduction of nerve impulses,
- to improve metabolic processes in tissues - B vitamins, Mexidol, Actavegin,
- improving blood circulation and nutrition - Papaverine, etc. medicines.
It is recommended to combine medication and physiotherapy procedures: electrophoresis, UHF therapy, mud and paraffin applications, electrical myostimulation and others.
An important component of treatment is massage and physical therapy. Massage for babies is carried out very carefully and only by a specialist. Exercise therapy with a special set of exercises is recommended to begin 2 weeks after the start of treatment.
Treatment of Duchenne-Erb's palsy is a long process. The patient and his parents and loved ones will need a lot of patience. The first positive changes usually appear three months from the start of therapy. If the child is recovering, then by the age of 3 months he will have active independent flexion of the elbow and extension of the hand.
The effect of conservative therapy is possible only if the integrity of the nerve fibers of the superior bundle of the brachial plexus is at least partially preserved. If it turns out to be completely torn off, separated from the nerve plexus, only a surgical method can help. The purpose of the operation is to completely restore the attachment of the nerve processes, microsurgical plastic surgery of the nerve trunk. This is a complex neurosurgical operation. In severe cases, muscle tissue transplantation is performed.
After surgical treatment, the nerve fibers (the path for the passage of nerve impulses) are restored. But this does not mean automatic recovery. Then comes a period of conservative treatment and rehabilitation.
The principles of treating an adult after injury or injury are similar. With drug therapy, the doctor has the opportunity to use medications more widely.
The chances of curing a child are quite high if the operation is performed between 3 and 7 months of age. For traumatic paralysis of the shoulder in adults, the timing of treatment should also be very prompt. If surgery is needed, it is better to have it as quickly as possible. In case of obstetric paralysis, it is advisable to do this in the first months, in case of injury - in the first weeks after the development of the disease.
It must be remembered that the period of restoration of limb function after therapy can last for several months (up to a year).
It is important to perform the procedures regularly and follow the doctor’s recommendations. If the disease remains untreated, residual effects will bother the patient longer and more severely. In the absence of treatment or its insufficiency, it is impossible to talk about a favorable prognosis. In adulthood, such a patient will experience disability.
With incomplete rupture of the nerve fiber and timely treatment, about 20% of patients fully recover. The rest have a high chance of restoring almost complete hand function.
ethnoscience
The use of traditional medicine in the treatment of limb paresis at home cannot be ruled out. But this should not be the only treatment. All methods are agreed upon with the doctor and only then applied.
Traditional medicine recipes:
- Ingestion of chamomile decoction. It is drunk as herbal tea.
- Rosehip decoction, you can add hawthorn to it. But you need to control the amount of drink you drink. They have diuretic properties.
- Treatment with celery and beet juice. You can add carrot juice.
- Valerian tincture is useful in the form of a rub . It is rubbed directly into the sore spot.
- Cold and hot shower. You need to start lowering the temperature gradually and increase the duration of the procedure to minutes.
Such measures and procedures can improve the immune system and improve blood circulation. This will help restore the functioning of muscles and ligaments.
Prevention
Limb paresis can be prevented. To do this, you need to do physical exercise all your life and want to exercise. This will promote overall health. But it is necessary to understand that complex diseases can cause paralysis of the arms and legs.
Therefore, after receiving injuries or illnesses, you need to devote more time to preventive measures:
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Monitor your blood pressure.
- Consult a doctor promptly if there are any changes in the functioning of the musculoskeletal system.
- Monitor the functioning of the cardiovascular system. This is especially true for older people.
- Have regular medical examinations.
It is impossible to completely insure yourself against paralysis, but there is a real opportunity to minimize such chances.
Forecast for the development of limb paresis
The prognosis and complete cure of paresis depends on many factors. It is difficult to cure paresis completely, but it is possible. It is necessary to strictly adhere to the advice and recommendations of the attending physician.
This will be affected by:
- patient's age;
- degree of paralysis;
- types of paresis;
- the treatment being taken;
- the willpower of the patient himself.
After the course of treatment, noticeable signs of paralysis may remain, but the patient will be able to move independently. Often younger people completely get rid of paresis and return to normal life. In some cases, a person becomes disabled.
Where is paresis of the lower extremities treated in Moscow and St. Petersburg?
To achieve a positive result, you need to contact specialized clinics. They are in many cities of Russia.
In Moscow, treatment for paresis can be offered by:
- Clinic "Miracle Doctor". Located at: Moscow, st. Shkolnaya 49.
- Clinic "Capital" . It has branches: on Arbat, on Leninsky, on Babushkinskaya, on Yugo-Zapadnaya.
- Medsi Clinic . In Moscow it is located at the address: 3rd Khoroshevsky proezd, building 1, building 2.
In St. Petersburg, such institutions are located at:
- The Altermed Clinic has several branches. They are located on Prosveshcheniya Ave., on Zvezdnaya, in Kupchino, in Devyatkino.
- Medical . Located at: l. Pobedy 17, metro station Victory Park.
Under no circumstances should you contact healers who do not have a medical education. This may be dangerous for the patient.