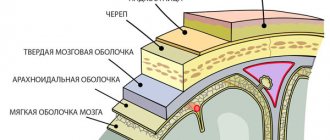
Ceraxon tablets: composition and action
Ceraxon is sold in several forms:
- injections;
- pills;
- solution for systemic use.
The tablets contain the main active ingredient – citicoline sodium. In addition to this, the composition includes:
- talc;
- castor oil;
- magnesium stearate.
Tablets are packed in 5 pieces in a blister, each box contains 4 blisters. The solution intended for drinking contains the same basic substance - citicoline, and along with it glycerin, sorbidol, sodium citrate, sodium saccharinate, strawberry flavoring. This composition is packaged in unpainted glass bottles with plastic caps. The volume of one bottle is 30 ml. It is convenient to dose using the syringe included in each package.
The drug for administration into a vein is packaged in glass ampoules, with a break line marked. One cardboard package can contain 3 or 5 pieces. Ceraxon mainly acts on brain cells, strengthening membranes, improving the functions of ion exchange pumps of the nervous system, which is due to the production of phospholipids.
In case of severe swelling, the action of the drug relieves pressure at the site of the lesion, which returns the cognitive functions of the brain. In addition, the ability to concentrate is restored and memory improves. If Cerakson is applied promptly at the first symptoms of a stroke, it will be possible to minimize the area of spread of necrotic tissue.
Citicoline is one of the constant elements of the human body, which does not make it possible to evaluate its pharmacokinetics. The substance entering through the gastrointestinal tract is absorbed almost completely. As a rule, 1-2% of the total ingested volume remains unabsorbed. Citicoline is excreted through the kidneys in the urine.
As a result of hepatic metabolism processes, two substances are formed: cytidine and choline. Citicoline is first concentrated in the structures and tissues of the brain. At the same time, fractions of the resulting choline pass into phospholipids, and cytidine derivatives into the composition of nucleic acids.
Substitutes for therapeutic effect
In some cases, medications are required that have a different active substance (for example, if you are intolerant), but have a similar therapeutic effect.
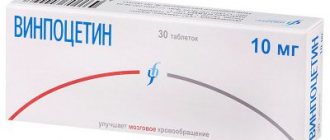
Vinpocetine
The action of a medicine based on vinpocetine is aimed at improving cerebral blood flow and metabolism, as well as normalizing blood viscosity. The spectrum of action of the product is very wide, in particular:
- stroke;
- TBI;
- cerebral atherosclerosis;
- encephalopathy;
- spasm of cerebral vessels;
- vascular dementia;
- motor and cognitive disorders;
- thrombosis of eye vessels, glaucoma, retinal changes;
- hearing impairments of various nature;
- vasovegetative disorders associated with menopause.
This medication is prohibited for use in the presence of heart problems - coronary artery disease, severe arrhythmia, as well as in children under 18 years of age; pregnant and breastfeeding women.
Piracetam
Piracetam, which is the basis of the drug of the same name, is a nootropic substance that is a cyclic derivative of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Its main effect is to improve connections between the hemispheres of the brain and synaptic transmission in neocortical structures, as well as improve cerebral blood flow. It is used for the symptomatic treatment of intellectual-mnestic disorders (if there is no diagnosis of dementia) and for myoclonus (involuntary muscle contractions).
Contraindications for its use are:
- intolerance to piracetam and pyrrolidone derivatives;
- hemorrhagic stroke;
- Huntington's chorea;
- severe chronic renal failure;
- age up to 3 years;
- severe hemorrhagic disorders.
Noobut
This is a psychostimulant and notropic drug based on phenibut. Available in the form of tablets for oral administration of 100 or 250 mg of the active ingredient. The main advantage is its mild action and lack of pronounced toxicity. It can be prescribed to children to treat stuttering, urinary incontinence, and nervous tics.
For adults, the medicine helps cope with insomnia, emotional lability, stress, nervousness, and asthenia. The drug is also prescribed to prevent motion sickness and to eliminate withdrawal symptoms.
Glycine
Glycine is an amino acid that is produced by the human body. To compensate for its deficiency, a synthesized analogue is used. When consuming the substance, there is an improvement in metabolism in the brain.
Glycine has antidepressant, antitoxic, antioxidant and sedative effects. It is prescribed to improve intellectual and thinking abilities, eliminate neuroses, sleep problems, and also as part of a comprehensive treatment of alcoholism.
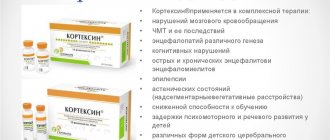
Cortexin
A drug based on polypeptides from the cerebral cortex of cattle is classified as a neurostimulant. It is available in the form of a lyophilized powder, from which a solution for injection is prepared. The main actions are nootropic, neuroprotective, antioxidant.
Cortexin is prescribed as an adjuvant for:
- stroke and TBI;
- asthenia;
- encephalopathy;
- epilepsy;
- cerebral palsy;
- delayed speech and psychomotor development in children.
When is Cerakson prescribed?
Treatment with Ceraxon is indicated in the following cases:
- first 4 hours during primary stroke;
- for rehabilitation after a stroke;
- emergency assistance and to restore the condition impaired as a result of severe head injury;
- cerebrovascular diseases that reduce cognitive function and provoke behavioral changes.
If the patient was administered Ceraxon in the first hours after a traumatic brain injury, the duration of post-traumatic coma will be less than without the help of the drug. In addition, there is a high probability of reducing the severity of neurological abnormalities typical of this type of injury.
If chronic hypoxia has become the reason for the predominance of lack of initiative in a person’s behavior, complete inability in matters of self-care, the drug effectively affects certain areas of the brain, restoring cognitive functions.
Main properties of the medicine
Citicoline has a neurometabolic, nootropic spectrum of action. Due to him:
- the rate of cell death is prevented or reduced;
- damaged membrane films are restored;
- accelerated formation of free radicals, etc. is prevented.
In case of acute stroke, the drug helps the amount of tissue damage and stimulate the functioning of cholinergic receptors. The medication accelerates the recovery process after TBI, reduces the time of coma after injury, and suppresses neurological symptoms.
With constant oxygen starvation of parts of the brain, effectiveness is noted in relation to:
- to cognitive disorders;
- self-care problems;
- forgetfulness issues.
The medicine is used for the treatment of neurological, motor pathologies, with vascular or degenerative origin.
The product has high bioavailability; processing processes take place in the liver tissues. Choline and cytidine, which arise during metabolism, are embedded in the membranes of cellular structures and form parts of phospholipid fractions. Up to 15% of the medication is excreted through the kidneys, the remaining part is excreted together with exhaled carbon dioxide. After 36 hours, the components completely leave the body.
Ceraxon 1000: instructions
Intravenous administration of the drug Ceraxon 1000 should be carried out slowly and evenly, avoiding the creation of a strong stream of flow. When administering drips, the lamb should be in the middle position, which provides up to 60 drops per minute. Jet injection, including into an elastic band, is carried out by applying gentle pressure on the syringe piston. The effectiveness of the drug directly depends on the time of treatment. The sooner the patient was admitted to the care of physicians, and the earlier drug treatment was started, the more positive the result will be.
Ceraxon 1000 is a classic dosage for the treatment of stroke of various etiologies and to minimize the consequences of traumatic brain injuries, which is administered every 12 hours for 6 weeks. After which, if the patient has not lost the swallowing reflex, intravenous administration is replaced by systemic administration through tablets.
If treatment involves taking the solution orally, it must be diluted in 100 ml of drinking water. Drink the medicine with meals. Children may be prescribed the drug in cases of damage to the central nervous system. The dosage for the child is prescribed by the attending physician, depending on his weight, age and condition.
Analogs by mode of action in tablets and ampoules
Cerakson's therapeutic effects are similar to medications that have different ingredients in their composition, but have one therapeutic direction - restoration of cerebral blood flow and brain function.
Bilobil Forte
Bilobil Forte is a herbal medicine based on a substrate from the leaves of Ginkgo Biloba. The herbal medicine blocks platelet adhesion, which significantly improves blood flow to the brain.
Bilobil is prescribed for a number of diseases:
- cognitive impairment due to stroke, brain injury, encephalopathy, age-related dementia;
- sleep rhythm disturbances and decreased intelligence;
- decreased attentiveness, concentration and memory;
- diabetic retinopathy;
- obliterating atherosclerosis and Raynaud's disease;
- decreased functioning of the visual and auditory organs.
The herbal medicine is not prescribed for allergies to plant components, as well as for children, nursing and pregnant women.
Take the drug one capsule three times a day. The duration of treatment depends on the pathology. On average it is 2-3 months.
Possible side effects:
- dizziness, fatigue, fainting;
- dyspepsia;
- itching of the skin, urticaria, rashes, hyperemia, Quincke's edema.
Vinpotropil
Vinpotropil is a complex nootropic with cerebroprotective effects. The medication dilates the membranes of the cerebral vessels, which ensures uninterrupted blood supply to all parts of the brain. The active ingredients in the medicine are vinpocetine and piracetam.
Instructions for taking the medicine:
- rehabilitation process after a stroke;
- parkinsonism;
- asthenia and intoxication;
- treatment of dizziness and migraine.
- encephalopathy of various etiologies;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- decreased cognitive abilities;
- withdrawal syndrome;
- Meniere's syndrome.
It is not recommended to take Vinpotropil in the following cases:
- allergies to medicinal ingredients;
- cardiac arrhythmia and ischemic heart disease;
- acute phase of hemorrhagic stroke;
- kidney and liver dysfunction;
- lactase deficiency and glucose malabsorption.
Vinpotropil is not used during lactation, pregnancy and childhood.
Prescribed with restrictions for the following pathologies in patients:
- disturbances in hemostasis and severe open or internal bleeding;
- hyperbilirubinemia and hepatitis;
- alcohol damage to liver cells;
- epileptic seizures.
The medication is administered using a dropper - 1-2 ampoules diluted in 500 ml of sodium chlorine. The speed of movement of the medicine through the dropper is 80 drops per minute. Therapy continues - from 10 days to 2 weeks.
Treatment regimen with capsules and tablets – 1 tablet (capsule) 2-3 times a day. The last dose of medication should be 4-5 hours before the patient goes to bed. Therapy can last from 2 weeks to 6 months. Dosages are reduced gradually so as not to provoke the development of withdrawal syndrome.
Vinpocetine and Vinpocetine Acree
Vinpocetine eliminates disturbances in cerebral blood flow and is used in neurology, psychiatry and cardiology. The active ingredient in the medicine is vinpocetine. The drug is produced in solution for injection and in tablets, and Vinpocetine Acre is only in tablets.
Medicine is prescribed for the following diseases:
- encephalopathy of various types;
- cerebral ischemic attacks;
- ischemic stroke and atherosclerosis of cerebral arteries;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- migraine;
- Meniere's syndrome;
- dementia and alcohol (medicine) intoxication.
It is not recommended to take the medicine for the following reasons:
- abnormal heart rhythm and ischemic heart disease;
- allergy to the components of the medication;
- acute phase of cerebral hemorrhage.
It is strictly prohibited to take during pregnancy and breastfeeding, as well as in childhood.
Despite the ban on the use of the drug in pediatrics, children from 3 months of age with cerebral hypoxia are prescribed Vinpocetine.
Tablets should be taken 1-2 tablets three times a day for 14-60 calendar days.
The injection solution is administered intravenously. Standard dosage for stroke treatment:
- 20 mg Vinpocetine + 500 ml infusion solution – for 2-3 days;
- from day 4 it is necessary to increase the dose to 1 mg and carry out the entire therapeutic course with this dosage;
- The duration of the course of therapy is 10-14 days.
If necessary, the doctor may prescribe pills.
Cavinton
Cavinton is a vasodilator that is effective in the treatment of cerebrovascular pathologies. The drug prevents the development of hypoxia, restores metabolism in brain cells and improves cognitive functions.
Cavinton is prescribed for the following conditions:
- ischemia and hypoxia of the brain;
- decreased memory, attention, concentration and intelligence;
- encephalopathy;
- vestibular disorders - dizziness, Meniere's disease and tinnitus;
- eye diseases due to vascular damage.
Medicine is not prescribed in the following situations:
- arrhythmia, ischemic heart disease, blood pressure fluctuations;
- kidney dysfunction;
- lactation period and pregnancy.
Take one tablet 3 times a day, after meals
The solution is administered only using a dropper - 20 mg of Cavinton + 500 ml of sodium chloride. Droppers are placed once a day; as the pathology progresses, the doctor may increase the number of injections.
Children are given the medicine by drip at the rate of 1 ampoule + 200 ml of solution for infusion with glucose.
Intravenous therapy continues for 2-3 weeks, then the patient is transferred to taking tablets.
The drug may cause side effects:
- fluctuations in blood pressure and heart rhythm disturbances;
- dizziness and drowsiness;
- dyspepsia;
- skin allergies and bronchospasms.
Cogitum
Cogitum is a medication based on acetylaminosuccinic acid, which is found in the central nervous system. Regulates the activity of the brain and central nervous system.
The drug is prescribed in the presence of the following conditions:
- insufficient blood supply to the brain;
- to restore cognitive functions;
- therapy of asthenic (alcohol syndrome).
The drug is not prescribed during pregnancy and lactation, as well as in case of allergies to components in the medicine and in children under 7 years of age.
The oral solution is prescribed to children 7-10 years old - 1 ampoule in the morning, 10-18 years old - 2 ampoules, and adult patients are recommended to take 2 ampoules in the morning and 1 ampoule before going to bed. Therapeutic course – 3-4 weeks. The drug, when used in therapeutic dosages, causes virtually no side effects.
Mexidol
Mexidol is a membrane protector for brain cells. This medication protects cell membranes from the effects of free radicals and has the following properties:
- antihypoxic;
- nootropic;
- antiepileptics;
- anxiolytic.
Mexidol is prescribed for the following diseases:
- impaired blood circulation in the brain;
- encephalopathy;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- systemic sclerosis of cerebral arteries;
- withdrawal syndrome;
- pathologies that provoke brain hypoxia;
- anxiety disorders.
The medication is not prescribed for the following conditions:
- liver failure and kidney dysfunction;
- intolerance to the components of the drug.
The medicine is also not prescribed to children under 12 years of age, pregnant women and mothers whose children are breastfed. Prescribed with restrictions for sharp fluctuations in blood pressure - hypertension and hypotension.
Mexidol is used intravenously or intramuscularly. If cerebral blood flow is disrupted in the acute stage, the medication is administered using a dropper. The dosage for an acute attack of ischemia or stroke is 200-300 mg. After normalization of the patient’s condition, the patient is transferred to treatment with tablets.
Therapy begins with 100 mg three times a day, with progressive dosage increases. The allowed daily dosage is 800 mg.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia and encephalopathy are treated with intramuscular injections - 50-100 mg three times a day.
For dementia, drug and alcohol poisoning, a daily dosage of 300 mg is prescribed, divided into 3 tablet doses.
Side effects:
- dyspepsia, flatulence;
- sleep disturbance;
- headache;
- hives.
Nootropil
Nootropil is produced in the form of a solution for injections, capsules and tablets. The medicine contains piracetam as an active ingredient.
Nootropil is prescribed in the following cases:
- decreased memory and intelligence;
- dizziness and unsteadiness of gait;
- Alzheimer's disease;
- alcoholism;
- sickle cell anemia;
- myoclonus and post-stroke state.
Nootropil is not prescribed to patients with kidney failure, cerebral hemorrhage, when the body is sensitive to the composition of Nootropil, as well as during lactation and infants under 12 months.
The daily dosage of the medicine is divided into 2-3 doses. The dosage is determined depending on the pathology:
- dizziness therapy – 2400-4800 mg;
- Treatment of myoclonus begins with a dose of 7200 mg. The increase occurs by 4800 mg every 3 days. Therapeutic dosage – 24000 mg;
- treatment of dyslexia in children over 8 years of age – a dose of 3200 mg per day is required
Side effects:
- hallucinations, depression and apathy;
- overexcitement and irritability;
- epileptic seizures;
- dyspepsia;
- skin allergy.
Piracetam
Piracetam is produced in tablets, capsules and solution for injections. The active ingredient is piracetam. The medication is prescribed for the following conditions:
- cognitive impairment;
- brain injuries;
- atherosclerosis of cerebral arteries;
- impaired microcirculation of the brain;
- alcoholism;
- dementia;
- neurological pathologies or mental disorders.
Children are prescribed Piracetam for dyslexia (after 8 years) and for the treatment of sickle cell anemia (from 3 years).
It is prohibited to take Piracetam in treatment for the following conditions:
- renal failure;
- hemorrhagic stroke;
- allergy to components;
- the child's age is under 12 months;
- pregnancy and lactation.
For the treatment of cognitive impairment, a dosage of 4.8 g per day is used for 7 days. Maintenance therapy – 2.4 g.
Side effects:
- disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system - lethargy, respiratory depression, depression;
- hives;
- dyspepsia.
Fenotropil
Phenotropil is a nootropic medication and is produced in tablets based on phenotropil.
Indications for the appointment of Phenotropil are:
- decreased mental and motor activity;
- chronic fatigue;
- memory loss and cognitive impairment;
- depression and causeless anxiety;
- impaired blood flow in the brain;
- convulsions;
- schizophrenia;
- alcoholism;
- sleep disorders.
The drug has some restrictions for use:
- hypersensitivity to components;
- pregnancy and breastfeeding of a newborn.
The standard therapeutic regimen is 200-300 mg twice a day. It is permissible to take no more than 750 mg per day. The last dose of medication should be at 15:00.
Adverse reactions - dermatological allergies, blood pressure fluctuations, emotional lability (overexcitement, aggression, tearfulness).
Cellex
Cellex is produced in the form of a solution that is administered subcutaneously. The drug activates synaptogenesis and neuroprotection, and also restores brain cells and improves their reparative potential. The drug is prescribed for cerebrovascular pathologies - impaired blood flow in the brain at different phases of the disease.
It is prohibited to prescribe medicine for the following conditions:
- epilepsy;
- affective insanity;
- delirium;
- up to 18 years old
- lactation and pregnancy.
The medicine is administered subcutaneously once a day for 10 days at a dosage of 0.1-0.2 mg.
Negative effects:
- skin hyperemia and urticaria;
- insomnia or drowsiness;
- headache.
See also:
TOP 12 cheap analogues of Spazmalgon - drug substitutes for the active substance
Contraindications for use
If, as a result of diagnosing the patient’s condition, the following features are revealed, Cerakson is not prescribed:
- individual intolerance to one of the components of the drug;
- tone of the autonomic nervous system, in its parasympathetic part;
- hereditary fructose intolerance.
Adverse reactions during treatment with Cerakson are extremely rare, among them are:
- coordination problems;
- pain in the occipital region;
- diarrhea;
- appetite disorders;
- insomnia;
- rash.
Sometimes short-term changes in blood pressure are observed, as well as loss of sensation, mainly in the arm and leg on the paralyzed side, if the patient has suffered a stroke.
If any of these reactions occur, you should discuss changing the course of therapy with your doctor.
Comparison of the effectiveness of Ceraxon and Neypilept
The effectiveness of Ceraxon is quite similar to Neypilept - this means that the ability of the drug substance to provide the maximum possible effect is similar.
For example, if the therapeutic effect of Ceraxon is more pronounced, then using Neypilept even in large doses will not achieve this effect.
Also, the speed of therapy - an indicator of the speed of therapeutic action - is approximately the same for Ceraxon and Neypilept. And bioavailability, that is, the amount of a drug reaching its site of action in the body, is similar. The higher the bioavailability, the less it will be lost during absorption and use by the body.
special instructions
Treatment with Cerakson is often prescribed to premature babies and newborns with brain tissue injuries received during childbirth. The treatment regimen is determined by the attending physician and depends on the Apgar assessment of the child’s condition. Storing the medicine in the refrigerator may cause crystals to form in the solution. It will take at least two months at room temperature to dissolve them. Despite the fact that this does not reduce the quality of the active substance, the drug should still be stored at room temperature not exceeding +30 C.
The empty packaging of the drug must be used within three years from the date of release.
Features of application
The implementation of the procedure depends on the following indicators:
- intravenous administration - drip (40-60 units per minute), with a duration of at least 3 minutes;
- intramuscular - used less frequently, requires regular replacement of the injection site.
In the acute course of TBI or ischemic stroke, the medication is administered every 12 hours, 1 g. Therapy lasts 6 or more weeks; if the swallowing reflex is preserved, after 3-5 days from the start of treatment, the patient is transferred to oral administration.
During the rehabilitation period, the dosage changes - up to 0.5-2 g per day. The duration of therapy and dosage of the drug are prescribed by a doctor, based on the data of a laboratory diagnostic examination.
There are no special adjustments for elderly patients. The medicine should be used immediately after opening the ampoules; mixing the medicine with isotonic solutions and dextrose is allowed.
For oral use, the product is diluted in a small amount of water. The dose is taken before or after meals, 200-300 mg, three times a day. The duration of the course depends on the general condition of the body and the effectiveness of the procedures.
Comparison of safety of Cerakson and Naypilept
The safety of a drug includes many factors.
At the same time, in Cerakson it is quite similar to Neypilept. It is important where the drug is metabolized: drugs are excreted from the body either unchanged or in the form of products of their biochemical transformations. Metabolism occurs spontaneously, but most often involves major organs such as the liver, kidneys, lungs, skin, brain and others. When assessing metabolism in Cerakson, as well as in Neypilept, we look at which organ is the metabolizing organ and how critical the effect on it is.
The risk-benefit ratio is when the prescription of a drug is undesirable, but justified under certain conditions and circumstances, with the obligatory observance of caution in use. At the same time, Ceraxon does not have any risks when used, just like Neypilept.
Also, when calculating safety, it is taken into account whether only allergic reactions occur or possible dysfunction of the main organs. In other matters, as well as the reversibility of the consequences of using Cerakson and Neypilept.