Preliminary examinations and preparation
As a rule, the patient is asked to undergo several examinations beforehand and only after this is bypass surgery performed.
- Angiography.
Can be magnetic resonance, intra-arterial or computed tomography. It is carried out not so much for diagnosis, but so that the doctor can determine the most suitable type of surgical intervention in a given case. - Duplex ultrasound scan checking the great arteries of the head.
It helps determine the condition of the arteries and how narrowed or blocked they are, as well as the characteristics of blood flow. At the same time, it allows you to check the vessels that will be used for a successful outcome of the operation. - Temporary arterial occlusion balloon test.
Checks the possible reaction of the brain to a temporary stop of blood flow in the operated artery.
Consent to the operation
Only a neurosurgeon with a specialization in neurovascular surgery can perform such an operation.
When the examinations are carried out and the operation is scheduled, the patient can agree to it or refuse it. He signs a document stating that he is fully informed and agrees. The contract must be read carefully: possible complications are indicated there, and if they occur, there will be no one to blame.
And yet, such operations are not simply prescribed: refusal in most cases carries with it an increase in health problems, even an ischemic stroke. Whether the patient signs the contract or refuses, the choice must still be balanced and well thought out.
Pre-operative procedures
If you are taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, you should take a break and stop using them a week before bypass surgery. When you can start again will be decided by your doctor. During the same week, you should avoid drinking alcohol and smoking, as this can cause bleeding during surgery.
You also need to follow some rules:
- It is necessary to wash the entire body (in a hospital setting - take a shower) in the evening, then in the morning before the operation. Wash your hair with shampoo twice. Change into clean clothes.
- Your doctor may prescribe pills on the day of surgery. They should be washed down with a small amount of water.
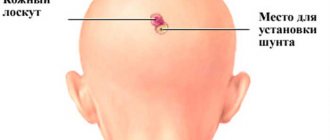
- On the eve of the operation, the surgeon will prescribe to shave the entire head or a separate section of it. This procedure is performed by a nurse.
- All foreign objects on the head, be it piercings, earrings and even lenses or removable dentures, must be removed.
- You also need to transfer all mobile communication devices to your relatives. After the operation, regardless of the patient’s condition, he will spend at least a day in intensive care, and such devices are prohibited for use there.
Rehabilitation and recovery
All patients who have undergone bypass surgery are sent to intensive care for a day. You can get out of bed and walk only after two days, when the patient’s condition has returned to normal. The day after the procedure, an MRI is performed to determine how the surgery went. If no complications are observed, then after a week the patient is sent home. Painkillers and anticonvulsants may be required immediately after discharge.
Restrictions after surgery
During the first weeks of rehabilitation, a number of restrictions should be observed:
- Do not engage in housework or other physical activity without your doctor's permission. The only type of acceptable activity is walking. It’s better to start with 10-15 minute walks, gradually increasing their duration;
- do not drive a car until the doctor gives permission;
- do not lift anything heavier than 2 kg;
- Avoid alcohol until you stop taking medications prescribed by your doctor. You should also give up coffee;
- Swimming in ponds is not recommended, but taking a bath and washing your hair is acceptable. It is better to use baby shampoo and avoid touching the area where the intervention was performed. It is enough to treat it with a sponge with light movements.
For the first 2-4 weeks after the intervention, you should stay at home, going outside only for walks and if absolutely necessary, and also avoid exertion. All restrictions should be observed for a month after surgery. It is then recommended to consult a doctor if you plan to play sports or other activities.
A mandatory element of rehabilitation is mental work. Taking care of yourself in everyday life and solving various everyday problems contributes to a speedy recovery.
How to understand that complications have begun
In the first days after bypass surgery, the patient may feel discomfort and nausea. These are normal consequences of bypass surgery and will subside within a few days. But there are symptoms that, if they appear, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor:
- increased body temperature above 38°;
- after taking medications prescribed by a doctor, a rash or itching appears;
- when walking, the patient feels unsteady and dizzy;
- constant drowsiness;
- the postoperative scar is swollen or red;
- feeling of weakness and pain in the neck;
- increased headache and nausea;
- vomit.
Often complications arise due to the patient’s failure to comply with the doctor’s instructions. The risk of seizures can be reduced by taking medications prescribed by your doctor.
A common type of complication is clogging of the shunt two to three years after shunting. The main symptoms of “congestion”: headache, focal neurological symptoms, intracranial pressure levels above normal.
Reason to see a doctor
There are different reviews about brain shunting for hydrocephalus: some people are afraid of the operation because they do not have complete information about it. Most patients establish normal, full-fledged lives, only occasionally visiting a doctor to monitor the functioning of the system. However, sometimes you need to see a doctor immediately. So, you need to go to the hospital if you have the following symptoms:
- an increase in body temperature - this indicates the development of an inflammatory process that contributes to a deterioration in the functionality of the brain;
- the appearance of skin allergies - most likely, it is provoked by medications, so the list of prescribed medications needs to be reviewed;
- change in gait;
- confusion;
- weakness in arms and legs;
- nausea, vomiting, headache (this is a sign of increased intracranial pressure, that is, the shunt has stopped functioning).
Hydrocephalus is a complex and dangerous disease that can make a person disabled or lead to death. Installing a shunt allows you to solve the problem and provide the patient with a full life. But it needs to be installed in a good clinic and by an experienced doctor.
Possible risks and complications
Shunting for hydrocephalus can lead to serious complications. 20% of patients have to undergo repeated intervention in the first year.
After surgery you may:
- An infectious process will develop. In most cases, this occurs due to staphylococcus entering the body.
- A subdural hematoma will form, which will resolve in the future without medical intervention.
In addition, the established conductive system may fail as a result of natural processes (for example, the growth of a child). In some cases, after craniotomy, patients may experience:
- Blockage of the shunt at any site.
- Development of epilepsy.
- Consequences of damage to brain tissue during surgery.
- Kink or bending of the shunt
- Excessive or insufficient outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from the brain cavities.
- A stroke, which is a consequence of constriction of the arteries or the formation of a blood clot in a blood vessel.
When bypassing cerebral vessels, the following may occur:
- Arrhythmia.
- Cardiac ischemia.
- Heart attack.
- Chronic pain in the area of surgery.
- Infection.
- Arterial thrombosis.
Despite the complexity and danger of this type of operation, specialists’ forecasts about the future condition of patients are quite favorable and optimistic. The shunt, being a kind of prosthesis that replaces the cerebrospinal fluid pathways, helps to significantly improve the well-being of patients and avoid the development of serious consequences.
Contraindications and rehabilitation
When the procedure is completed and the shunt is in the head, the patient will begin to feel unwell. It is often accompanied by mild nausea, dizziness, headaches of varying intensity, and mild numbness of the limbs. All these sensations can be expressed with different strengths. This is the norm.
On the second day after the operation, the doctor should assess the success of the bypass. To do this, the patient needs to undergo an MRI, which will help check the condition of the brain and eliminate the likelihood of complications developing after the intervention. If everything is in order, then repeated examinations are carried out another week and immediately upon discharge from the hospital. The total recovery time in hospital is 14 days.
Rehabilitation process
The person recovering is required to follow simple rules:
Complete cessation of alcohol and cigarettes until the body is completely restored. Avoid any physical activity. A complete ban on lifting heavy objects and all kinds of household or country work. Refusal to drive a car and all types of work that require concentration. There is a risk of an inadequate reaction to stressful situations, which will also lead to complications. Home regime for 30 days. At the same time, it is prohibited to visit swimming pools and ponds, or to stay outside for longer than necessary, especially if the weather conditions seem unfavorable. No touching of the head in the area of the postoperative opening. Any contact with this area can cause injury and rapid infection. It is also prohibited to try to remove the shunt yourself. Take all prescribed medications according to the doctor's instructions. The patient is prescribed anticonvulsants
At the same time, it is important to monitor your well-being, because... they have a number of side effects.
Throughout the entire rehabilitation period, it is very important to strictly follow the instructions of your doctor. This is the only way to avoid problems in the future and return to normal life as quickly as possible.
The patient will live a full life for a very long time with virtually no restrictions. The life expectancy of those who had to undergo shunting is practically no different from the average statistical indicators of healthy people.
The need for a shunt remains forever. Therefore, a shunt patient should take his problem as seriously as possible. This is not as convenient as most patients would like, but the result with the ability to live peacefully is much more important.
From time to time the shunt needs to be changed. Gradually it loses its effectiveness. The reason for this is blockage, wear, and various accidental damage. It is impossible to say how long the shunt will last. They are designed for a service life of up to 10 years. However, they often have to be replaced much earlier, regardless of quality. Especially when it comes to children. Along with their gradual growth, lengthening and a shunt will be required. Replacement is very quick and painless.
If you first need to check the equipment or replace it, you should immediately contact your doctor, because specialist intervention will be necessary. It can only be removed by an experienced employee of a medical institution.
Patients who have undergone brain shunt surgery can expect to be assigned a degree of disability. This is determined by a commission that makes a decision based on the research conducted. Both a child and an adult can be recognized as disabled if they are identified as having impairments in the main categories of life activity, which include the following abilities:
- self-service;
- orientation in space;
- movement;
- education;
- self-control;
- communication;
- work activity.
Disability will need to be continually confirmed through examinations.
Kinds
In modern medicine, 2 types of bypass are practiced: an autodonor bypass and a bypass from the scalp arteries. The appropriate option is selected based on a number of parameters (required blood flow speed, the state of the patient’s cardiovascular system as a whole, the presence of concomitant diseases) and for each patient individually.
In autodonor bypass surgery, a vessel is taken from the patient, usually from the radial or ulnar artery of the arm or part of the great saphenous vein of the leg. One end of the taken vessel is sutured to the external carotid artery, then passed subcutaneously and through a previously prepared trepanation window sutured to the blocked vessel above the site of stenosis. This option is used for main arteries with high blood flow speed. For smaller vessels, through which blood circulates with less intensity, shunts are used from the vessels of the soft tissues of the head (scalp). This method is less traumatic due to the smaller volume of surgical intervention.
Only one end of the selected vessel is isolated, passed through the trepanation window and sutured to a small vessel on the surface of the brain. After surgery, blood supply to the brain improves.
Shunting for hydrocephalus
Brain shunting for hydrocephalus has a number of features, since it redistributes cerebrospinal fluid rather than blood in the vessels.
Hydrocephalus is a severe pathology, a characteristic feature of which is an enlargement of the cerebral parts of the skull due to excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the cavities and a violation of its drainage.
Epidemiology of hydrocephalus. Regardless of the etiological factors, congenital hydrocephalus occurs in two newborns out of 1000. If the child is not operated on in time, the mortality rate is 75% in the first year of life.
This disease affects both newborns and adults, and has various causes (infectious diseases in the mother during pregnancy, birth trauma, consequences of meningitis, congenital anomalies, traumatic brain injury, arachnoiditis, cysts and tumors of the nervous system).
Hydrocephalus is a dangerous disease. Regardless of the etiology, it has a high percentage of mortality and disability among newborns. At this stage of development of medicine, shunting is the only effective method of treating hydrocephalus, despite the high percentage of complications, among which are:
- infection of body cavities depending on the location of the shunt;
- development of epilepsy;
- inadequacy of the drainage system itself, namely insufficient or excessive outflow of cerebrospinal fluid.
The peculiarities of such operations in newborns with hydrocephalus, in addition to the risk of complications, include the need for repeated operations.
In the first year of life, a newborn grows very quickly, and over time the shunt ceases to cope with its functions; in addition, as the child grows, the shunt can become dislodged, which threatens damage to the brain and its structures. Hydrocephalus requires dynamic treatment.
Intervention methods
The main purpose of shunting for hydrocephalus is the redistribution of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricular system of the brain.
The main types of shunting for hydrocephalus:
- Ventriculoperitoneal shunt.
- Ventriculoatrial shunting.
In the first method, the neurosurgeon makes a burr hole in the newborn's skull, into which a special tube is inserted. Its lower end is inserted into the ventricular cavity, and the second end is connected to the abdominal cavity. Excess fluid is absorbed, but the risk of complications is high. The second type is less dangerous in terms of complications. The shunt itself is more complex in its structure; it has a number of valves, on which its reliability and functionality depend. Such a shunt requires replacement every six months, and accordingly another surgical intervention is performed.
Postoperative period
In the postoperative period, a patient with hydrocephalus is prescribed painkillers and anticonvulsants, which are selected by the doctor, who also sets the dosage.
As you recover, drug therapy changes depending on the dynamics of the disease.
Rate this article:
4
Total votes: 238
How is it carried out?
There are two types of procedures: ventriculoperitoneal and ventriculoatrial shunt insertion.
The essence of the first type is a complex shunt made of a special soft material. It needs to be changed twice a year. Despite a number of inconveniences associated with the features of the shunt, this method is considered to be as safe as possible. If a patient is diagnosed with shunt-dependent hydrocephalus, this method is usually used.
The method is based on removing excess cerebrospinal fluid into the patient’s abdominal cavity. The peculiarity of the structure allows you to regulate the amount of cerebrospinal fluid absorbed by the stomach using valves. Due to the fact that the catheters and valves are located subcutaneously, such a shunt is completely invisible to others.
To install it, the doctor makes a hole in the patient's skull and inserts the device there. Directly under the patient's skin, a special cavity or tunnel is laid for a catheter, with the help of which the outflow of cranial fluid into the abdominal cavity is carried out.
Indications and contraindications
Indications for surgery:
- Hydrocephalus (water on the brain).
- Tumors that compress the arteries with mechanical pressure.
- Aneurysm of a vessel that cannot be treated with medication.
- Stroke that cannot be treated with medication.
- Impairment of cerebral blood flow that does not respond to conservative therapy.
Contraindications:
- Weak and exhausted state of the body.
- Heart failure.
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases in the acute period.
In 30-70% of patients after brain shunting for hydrocephalus, complications arise:
- Overdrainage. The condition develops in 13.4% of patients. Hematomas form in the brain, and the ventricles of the brain “stick together.” Overdrainage is observed in patients who have had low-pressure shunts implanted. This complication is treated with drug therapy.
- Hypodrainage. It is observed in 5.2% of patients. The condition is characterized by insufficient functioning of the shunt systems, which is why the clinical picture of hydrocephalus remains. Hypodrainage is eliminated by repeated surgery, in which the shunt valves are replaced.
- The ends of the shunt systems are disconnected. Occurs in 2% of patients. The complication develops due to a violation of the location of the two ends of the shunt. The pathology is eliminated by a repeat operation, in which the ends are reconnected.
- Inflammation. In 4% of patients, the brain and its membranes become inflamed. Meningitis, meningoencephalitis or simply encephalitis develops. The ventricles often become inflamed. The likelihood of developing sepsis increases. Pus may accumulate in the cavities. The complication is eliminated by surgery and drug therapy. First, the shunt system is removed from the brain, and then antibiotic therapy is prescribed.
Shunting of the ventricles of the brain in hydrocephalus is not always permitted. Contraindications are:
- Inflammatory processes in the area where the intervention will be performed.
- Severe respiratory disease.
- Heart disease.
- Oncological disease of the brain.
Replacement hydrocephalus of the brain in an adult is an acquired condition and also requires medical supervision and therapy.
The consequences of brain shunting for hydrocephalus can be different. It all depends on the severity of the disease, the quality of the operation and the materials used. The most dangerous thing for the patient is the introduction of infection or bacteria into the brain. The patient may also develop other complications:
- Damage to blood vessels and increase the risk of stroke.
- Infection of the abdominal cavity or gray matter of the brain, with subsequent development of sepsis. The cause of the pathological process is staphylococcus. Antibiotics must be used to prevent infection.
- Damage to an organ causing epilepsy.
- Dysfunction of hydrodynamics. Sometimes the system does not allow normal pressure to be achieved in the ventricles of the brain. Sometimes they change size and become like slits. In this case, therapy will be ineffective.
- Subdural hematoma. In most cases, it resolves on its own. If the outcome is unfavorable, drainage of the specified area or change of pressure using a valve is required.
- Formation of blood clots and blockage of blood vessels.
- Insufficient efficiency of the shunt system, its blockage or damage. This can also be caused by natural changes in the body, for example: the growth of the child, as a result of which the tubes need to be lengthened.
Most of these complications can be avoided if you follow your doctor's advice.
Description and danger of pathology
Cerebrospinal fluid normally circulates constantly in the brain. It not only protects it from infectious agents, but also provides it with nutrients. Under the influence of negative factors, the production of cerebrospinal fluid may increase or its outflow may become difficult.
If the ventricles become overfilled with fluid, their walls become thin, intracranial pressure increases, and tissue rupture may occur. This pathology is characterized by neurological disorders.
Hydrocephalus can cause complications. These include:
- Delayed mental and physical development in infants.
- Psychical deviations.
- Changes in the emotional sphere in children and adults.
- Impairment of cognitive processes (memory, attention), which leads to poor performance at school and learning difficulties.
- Development of epilepsy.
- The appearance of hallucinations.
- Problems with motor functions, which leads to disability.
In the absence of timely treatment, irreversible changes occur in the brain, which cannot be compensated for. The malignant form of the disease often leads to death.
Possible complications after surgery
Replacement hydrocephalus of the brain in adults can appear as a result of trauma and requires careful diagnosis. After surgery is performed, a person may feel general weakness and malaise. This condition is completely normal. Nausea and dizziness also appear.
The success of the intervention can only be assessed the next day after installation of the shunt system. MRI is used to monitor the patient's condition. A repeat study is carried out after 7 days.
After the patient is discharged home, he will have to follow some of the doctors’ recommendations:
- Avoid alcoholic beverages for the entire rehabilitation period. Moreover, it is better not to drink alcohol even after the completion of the recovery period.
- Since the patient will have to take medications, and given that the operation was performed on the brain, he should not drive.
- There should be no physical activity. It is prohibited to lift objects heavier than 1 kg.
- You should walk in the fresh air more often, but do not overwork.
In 50% of cases, operations to shunt the cerebrospinal fluid system in children are accompanied by complications that arise due to changes in the body during growth. Most often, several operations are required to replace, restore or correct parts of the system. After a shunt is installed, the child's growth and development depend entirely on its operation.
In adult patients, the need to replace the shunt occurs mainly due to mechanical damage.
The most likely complications after cerebrospinal fluid shunting:
- blockage of the conduction system at any level;
- infection of the body during surgery;
- formation of intracranial hematoma;
- kink or bending of the shunt;
- excessive drainage of fluid from the cavities of the brain (overdrainage);
- insufficient drainage of fluid from the cavities of the brain (hypodrainage);
- damage to brain tissue during surgery;
- the appearance of signs of epilepsy due to the body’s reaction to a foreign body in the brain tissue.
You should know: all modern shunt systems are equipped with valves designed to maintain normal intracranial pressure and prevent fluid from flowing in the opposite direction.
Despite the complexity of the operation, further forecasts are usually quite optimistic. The shunt system, being essentially a prosthesis that replaces the natural cerebrospinal fluid pathways, allows one to avoid life-threatening conditions, improve the quality of life, and in some cases, achieve a complete cure.
Evaluation of the therapy performed is carried out the next day. The patient undergoes an MRI, and repeated examinations are carried out seven days later, and immediately after the patient is discharged.
Doctors check the shunt from time to time and replace it if necessary. The procedure is necessary due to the growth of a small patient or a malfunction of the structure - wear, clogging. Modern systems are designed for a certain time when the tubes will require replacement - it is impossible to predict.
If the system is blocked and the drainage of cerebrospinal fluid is impaired, patients are provided with urgent surgical care - the drainage is replaced with a new one.
The procedure for installing a shunt in the brain is a vital intervention, since cerebral pathologies cannot always be cured conservatively. When installing a shunt, there is a high probability of relieving the severity of the pathology, but the catheters must be carefully monitored. Such patients are forced to constantly visit the clinic for revision of the shunt system. After surgery, it is advisable for patients to give up bad habits, eat right, and protect themselves from stress.
Treatment of vascular blockages
In case of such problems, bypass routes are created to bypass the blood if the brain vessels are blocked. If the arteries are obstructed or narrowed, then they are connected through a jumper with healthy vessels. Thanks to this, blood flow is normalized and brain nutrition is restored.
Types and implementation
Nutrition is provided using:
- Sewing in a section of a vein or artery. To prevent rejection after surgery, shunts are created using the patient’s own blood vessels. If large arteries are affected, the large saphenous vein of the leg or the radial artery is excised. The shunt is sewn in above and below the affected area. Its other end is passed through a drilled hole in the skull and connected to the carotid artery in the neck.
- Sewing in a section of a small vessel. The procedure is carried out using vessels that nourish the scalp. They are removed through a hole in the skull and connected to the damaged vessel. Thanks to this, they supply blood to the brain. If a healthy vessel is not long enough, then fragments of veins and arteries can be sewn onto it.
Carrying out these procedures allows you to completely restore brain function.
Preparing for surgery
Before brain shunting is performed in newborns, parental permission is obtained. The adult patient himself signs a document indicating that the patient has been informed of the possible consequences and agrees to treatment.
After this, urine and blood tests, fluorography, and a cardiogram are performed.
To avoid bleeding, stop taking steroid medications and lead a healthy lifestyle.
The next morning, before the operation, the patient should not eat food, a small amount of water is allowed if you need to wash down the medicine
It is also important to take a shower and wash your hair several times
The patient should be without jewelry, false nails and eyelashes, or removable dentures. His hair is shaved off in the trepanation area. Sometimes it is necessary to remove the entire scalp.
The duration of the procedure is about three hours. It is performed under general anesthesia. After the anesthesia has begun to take effect, the head is tightly fixed.
A microscope is required to stitch the artery and donor vessel. Additionally, clips are installed. Contact Doppler ultrasound is used to check blood flow. If the cavity does not leak, the clips are removed.
After the procedure, the hard shells are sutured and the bone flap is installed in place. Sutures and plates are used to fix it. At the end, the muscles and skin are sewn together and treated with an antiseptic.
Recovery period
After the anesthesia wears off, the patient may suffer from dizziness. The patient is also asked to move his limbs and show objects in pictures to check if the brain is damaged during the procedure.
You can get out of bed a day after the session. If the condition is good and the tomography shows that the operation was successful, the patient is discharged a week after bypass surgery.
The patient should avoid any work for a month. Anticonvulsants and non-steroidal medications may be prescribed. Some patients have to take medications throughout their lives to prevent blood clots.
Driving is permitted after a doctor has assessed the condition. Alcoholic drinks in combination with medications are contraindicated. Until complete recovery, you need to walk every day, gradually increasing the distance.
Complications
After the bypass procedure, the following cases occur:
- Stroke. This is possible if the surgeon compressed the vessel too much.
- Epilepsy, if there is a sharp rush of blood to certain areas, which leads to convulsions and swelling.
- Shunt thrombosis.
Bypass cost
Treatment for hydrocephalus should be free. If desired, the patient can go to a private clinic, where the procedure will cost from 15 to 150 thousand rubles.
The patient can receive a quota for brain bypass surgery. But it is only available to certain categories of citizens and only after a full examination. In other cases, you will have to pay a certain amount for the procedure.
Brain shunting for hydrocephalus - what is it?
Shunting is an operation that allows you to cure hydrocephalus and prevent its development in the future. Its purpose is to create an additional path for the outflow of cerebral fluid from the ventricles when its normal circulation is difficult or completely impossible.
The essence of the operation is that a special tube (shunt) is used to connect the affected ventricle of the brain and the right atrium or peritoneum. This ensures the outflow of fluid and the ventricle returns to its normal size.
There are several methods of brain shunting:
- Ventriculoatrial (connection of the ventricle with the right atrium, less often with the left);
- Ventriculo-peritoneal (connection of the ventricle with the peritoneum);
- Ventriculocisternostomy (connection of the ventricle with the cisterns of the arachnoid membrane of the brain);
- Subduroperitoneal (connection of the space under the dura mater with the peritoneum);
- Ventriculo-pleural;
- Ventriculo-urethral (a rare type of shunt, connecting the ventricle to the urethra).
Which method will be used in each specific case depends on:
- features of the patient’s disease course;
- concomitant diseases;
- general condition.
Preparation for bypass surgery
Before the procedure, the therapist fully examines the patient, takes into account his complaints and objective signs of the disease. The main way to evaluate blood vessels in this case is through instrumental research methods:
- Magnetic resonance imaging with angio mode.
- Computed tomography with angiography.
- Ultrasonography.
These methods make it possible to assess the state of blood flow in the brain, study the hemodynamic properties of blood, examine the patency of blood vessels and identify a pathological focus.
If there is hydrocephalus of the brain in newborns, shunting, as already mentioned, is performed immediately. If the procedure is prescribed for an adult patient, and the disease itself is acquired, then he must prepare before the planned operation.
A week before the intervention, the person is prohibited from drinking alcoholic beverages or smoking. You should also completely stop using certain medications (steroids). They may increase the risk of bleeding.
You should not eat food the night before. It is forbidden to drink water in the morning. And before the operation, you need to take a shower, wash well and shave your head in the place where the incisions will be made. All jewelry must be removed before surgery.
Diagnosis of hydrocephalus in children
Consultation with an ophthalmologist: congestive optic discs.
Ultrasound examination of the brain through the fontanel.
CT/MRI: dilated ventricles of the brain, signs of increased ICP.
Lumbar puncture is prohibited. Danger of pinching the brain stem causing respiratory arrest. During the examination for hydrocephalus, the child undergoes neurosonography (ultrasound of the brain), a computed tomography and MRI may be prescribed, an examination by an ophthalmologist, and an electroencephalogram. Diagnosis is often made based on routine prenatal ultrasound. In older children, complaints of headache, uncontrollable vomiting and decreased vision, as well as detection of papilledema during a neuro-ophthalmological examination are indications for examination to exclude hydrocephalus. Similar symptoms can develop as a result of the presence of intracranial space-occupying formations (subdural hematoma, porencephalic cysts, tumors). In children with suspected hydrocephalus, images of the skull should be obtained using CT, MRI, or ultrasound (if the fontanelle is open). CT scan or ultrasound scan of the head is used to monitor the progression of hydrocephalus once an anatomical diagnosis has been made. If seizures occur, an EEG may be helpful.