The structure of the human body is complex and unique, this is especially true for the gray and white matter of the brain. However, it was precisely thanks to such features that people were able to achieve existing advantages over other representatives of the animal world. The study of the structure of intracranial structures, their functions and features has not yet been completed. However, knowledge about their location and significance for people’s health helps specialists understand the nature of diseases of the nervous system and select optimal treatment regimens.
Structure
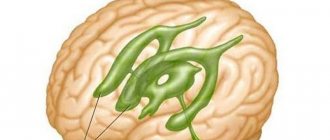
Each brain cell has a body and several processes - a long fiber in the axon and a short fiber in the dendrites. It is they who determine the color of different parts of the organ by their color. Thus, gray matter in its structure contains neurons, glial elements and blood vessels. Its branches are not covered with a shell - this is why it has a dark shade.
Most of this substance is present in the following sections:
- cortex of the anterior hemispheres;
- thalamus and hypothalamus;
- cerebellum and its nuclei;
- basal ganglia;
- cranial nerves and brainstem;
- pillars with spinal horns extending from them.
The entire space along the periphery of the gray structures is occupied by white matter. It contains a huge number of nerve fiber processes, on top of which the myelin sheath is placed. It gives a white tint to fabrics. It is these structures in the central nervous system that form the pathways along which information signals move to dependent organs, or from them back to the central structures.
Main types of white fibers:
- associative - localized in different parts of the spinal nerves;
- ascending - transmit information from internal structures to the cerebral cortex;
- descending - the signal comes from the intracranial formations to the spinal horns, and from there to the internal organs.
It is more convenient to consider how the nervous system is structured, what white matter or gray matter is, on educational models - detailed sections with color images will clearly demonstrate the features of the arrangement of tissues and structural units.
White matter damage
Modern medical capabilities and the latest technologies make it possible to determine the pathology of white matter or a violation of its integrity in the early stages. This significantly increases the chance of coping with the problem.
White matter injury can be traumatic or pathological. Caused by any disease or congenital. In any case, this leads to serious conditions. It disrupts the coherence of the body.
If the structure changes or is damaged, paralysis of the muscle mass of one side of the body or face and memory loss may occur.
Possible disturbances in speech, visual field, and swallowing reflex. Mental disorders may begin. The patient will no longer recognize people and objects. Each symptom corresponds to white matter damage in a specific area.
Thus, knowing the symptoms, we can already guess the site of damage. And sometimes the cause, for example, with a skull injury or stroke. This makes it possible to provide the correct first aid before a full diagnosis is carried out.
Neural reactions are transmitted at the required speed only if the white matter is intact. Any violations can lead to irreversible processes and require urgent contact with specialists.
In the range of 30 - 50 years, the largest number of quality connections occurs. Further, the activity of impulse transmission decreases every year.
A little about gray matter
Gray cells, in contrast to the conductive function of the white matter of the brain, have different types of tasks:
- physiological - formation and movement, as well as receiving and subsequent processing of electrical impulses;
- neurophysiological – speech and vision, thinking and memory with emotional reactions;
- psychological - the formation of the essence of a person’s personality, his worldview and motivation with will.
Numerous studies by specialists have made it possible to establish how the gray matter and white areas of the brain are formed and their role in the central nervous system. However, even today many mysteries remain unsolved.
However, the nuclei of gray matter in the topic of the intracranial hemispheres and such structures in the spinal cord were anatomically structured. In fact, they are the main coordination center through which human reflexes and higher intellectual activity are formed. For example, if you know where the gray matter of the cortex and its dependent organ are located, you can cause the necessary reaction to a stimulus. Doctors use this to restore patients after certain neurological diseases.
Of course, what the white matter and subcortical nuclei of the forebrain consist of will directly determine the speed of impulse transmission and their processing. This is how people differ from each other. Therefore, all subcortical lesions in the white matter must be considered separately.
What is it and what does it consist of
White matter of the brain is a collective concept that refers to a complex of nerve structures through which electrical and chemical impulses are transmitted. The nerve cell can be thought of as a trading post where travelers sell and buy goods, relax and discuss prices. However, for successful commercial activities, traders need roads, thanks to which they make long journeys from one point to another, delivering valuable cargo. It’s the same in the brain: the white substance ensures the delivery of nerve impulses.
The white matter of the nervous system serves as a springboard for the gray matter. The latter, unlike white, acts as a generator and collector of information. The white substance transmits the nerve impulse and is not responsible for its creation. On the other hand, there are opinions of many experts that white matter determines the speed and quality of brain functioning, namely the number of formed nerve pathways. Indeed, the development of the mental component of the mental sphere in children usually means the formation of white matter in the brain.
The white substance is opposed to the gray one. Gray matter is a collection of nerve cell bodies and their appendages (glial tissue, capillaries, partially short processes and early axons). The functions of gray matter include providing programs for higher nervous activity, such as thinking, memory, and perception. The contrast is not only functional, but also anatomical. If the gray matter is the cortex (the final layer of the brain), then the white substance is located between the cortex and the deep structures of the brain.
Speaking of structure, the substantia alba differs from the gray matter: the white matter of the brain consists of bundles of long processes - axons, covered with a myelin sheath. This layer, consisting of fat components, provides a person with an electrical impulse transmission speed of up to 100 m/sec on average. An axon that does not have myelinated fibers transmits information up to 10 m/sec. The white color of the substance is provided by myelin, and on a section the subcortical ball of the substance looks whitish-cream.
So, the white matter of the brain is represented by myelinated axons that connect different parts of the brain. Anatomically, the processes are divided into long ones, responsible for communication between distant parts of the brain, and short ones, connecting nearby structures (brain convolutions). They are located as follows:
- Short . They lie directly under the cortex of the brain and are called subcortical.
- Long or intracortical. This part of the white matter is located in the deep parts.
In addition, white matter is conventionally divided into 3 types, depending on anatomical features:
Associative connections . Fibers of this type of white matter provide a general connection between areas of the cortex, but located in the same hemisphere. For example, association fibers connect the area of general sensitivity (parietal cortex) with the frontal cortex.
Commissural fibers . These structures are represented by cerebral adhesions and articulate similar areas, but on different hemispheres. For example, the hearing area on the temporal cortex of one hemisphere with the same area in the other part of the brain. The largest structure here is the corpus callosum. In the physiological aspect, the structure ensures the interconnection of both hemispheres. The corpus callosum has not been fully studied.
Projection fields . This type of white matter connects the cerebral cortex with structures morphologically located below. Functionally divided into two subtypes:
- Efferent fibers. Along these pathways, the nerve impulse is sent from the cortical centers to the underlying structures;
- afferent. These fibers ensure the delivery of electrical signals from underlying structures (internal organs, tissues) to the brain.
There are phenomena where people who do not have this unifying structure (corpus callosum) have phenomenal memory. Experts say that this is due to the corpus callosum, which acts as a kind of barrier that limits the flow of electrical impulses. In the case where it is not present, the areas are connected to each other directly, without any collector system or filters.
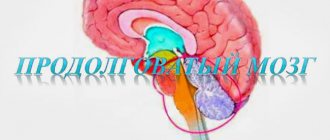
The white matter of the medulla oblongata is represented by short and long fibers. The latter include the pyramidal tracts running through the anterior clusters of the spinal cord. The fibers of the medulla oblongata form several tracts:
- Rubrospinal;
- Vestibulospinal;
- Reticulospinal tract.
Through these structures, information flows from the nuclei of the medulla oblongata, reticular and vestibular nuclei to the spinal cord.
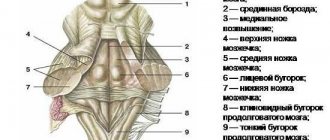
The white matter of the midbrain forms a cluster represented by the cerebral body, located deep in the cerebellum. Branching, the fibers of the body pierce all the convolutions of the coordinating center of the brain. The fibers of the white matter of the cerebellum form pathways leading to the cerebral cortex and neighboring brainstem structures.
Topography
Fibers of gray and white neurocytes are represented in both the central and peripheral parts of nervous regulation. However, if in the spinal cord the gray matter is topographically localized in the middle - its outline resembles a butterfly that surrounds the spinal canal, then in the cranial region it, on the contrary, covers the main hemispheres. Its individual sections, the nuclei, are also located in depth.
The white matter is localized around the “butterfly” in the spinal part of the brain - nerve fibers surrounded by membranes, and in the central section - under the cortex, representing separate white clusters and cords.
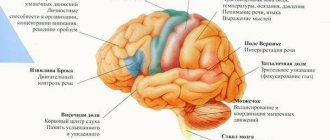
Highly differentiated cells of the gray matter form the cerebral cortex - the cloak. They are the human intellect. An increase in the area of the cortex is possible due to many folds - grooves and convolutions. The thickness of the cloak is ambiguous - it is greater in the area of the central gyrus. Its gradual decrease can be observed towards the spinal cord, the transition to which is designated as the medulla oblongata.
The percentage of white and gray matter in different parts of the brain is ambiguous. As a rule, there are more non-enveloped white accumulations. It is customary to distinguish structural departments:
- anterior - the cerebral hemispheres, which are covered with a cortex of gray matter, inside the nucleus surrounded by white matter;
- middle - many cranial nuclei of dark cells with pathways of white brain fiber;
- intermediate - represented by the thalamus, as well as the hypothalamus, to which impulses move along many white fibers to the nuclei of the autonomic system located in them;
- cerebellum - resembles the cerebral hemispheres in miniature in structure, since the cortex and subcortex can be distinguished, but not in terms of functional responsibilities;
- oblong - gray matter predominates, which is represented by many nuclei and brain centers.
Many scientific works are devoted to the study of the representation of one or another part of the body in the brain. However, their research is incomplete - nature presents people with new discoveries.
Functions
Thanks to the complex and unique structure of the nervous system, the brain substance is able to perform many functional duties. In fact, he is entrusted with managing the entire variety of processes occurring inside the body.
Thus, the functions of white matter, undoubtedly, are to receive and convey information with the help of nerve impulses - both between individual sections of the brain or spinal cord, and them, as individual structural links of a complex system. In order to present a diagram of the functional responsibilities of white matter, it is necessary to identify the main fibers:
- associative - are responsible for the relationship between different zones of the cortex of one of the hemispheres, for example, short white branches are responsible for the connection between nearby gyri, while long ones are responsible for the interaction of distant areas of the cortex;
- commissural - white fibers connect not only symmetrical zones, but also the cortex in the distant lobes of the hemispheres, which is reflected in the corpus callosum and commissures, which are located directly between the large hemispheric units;
- projection white fibers - are responsible for the quality of communication between the cerebral cortex and the underlying structural units, as well as the periphery, for example, the delivery of information from motor neurons and back to them, or from sensory cells.
The anatomical structure and location determines the functions of gray matter. It is simultaneously able to create and process nerve impulses. Due to them, all internal vital processes are controlled - automatically in the respiratory, cardiovascular, digestive and urinary systems. This is the so-called preservation of the constancy of the internal environment, so that a person as a biological unit can preserve himself as a single whole. Whereas the distinctive function of gray matter can be called the development and increase of intelligence. Every living person has a cerebral cortex. However, the level of development of mental abilities is different for everyone. It is the gray cells of the cerebral cortex that are responsible for receiving, processing and storing information.
Distinctive features
To clearly understand the important differences between the gray and white matter of the brain, what they are and their functional characteristics, experts have developed criteria. The main ones are presented in the table:
| Criteria | Gray matter | White matter |
| structure | nerve cell nuclei and short processes | long myelinated axons |
| localization | predominantly in the central nervous system | mainly on the periphery |
| oxygen consumption | 3–5 ml/min | less than 1 ml/min |
| function | regulating, reflexive | conductive |
| specific gravity | 40% of total weight | more than 60% weight |
In general, the concept of exclusively gray or white in the overall picture of the brain or spinal cord does not exist as such - these organ structures are so closely intertwined anatomically and functionally. Without one, the other cannot exist.
Conventionally, a nerve cell can be imagined as a hotel where people stop to rest and exchange news. This is the gray substance of the brain. However, after this they move on to visit other interesting places. To do this, they need high-quality highways - conductive fibers of white matter.
And if, without the dark nuclei of the subcortical structures and the cloak of the cerebral hemispheres, people are not at all able to perform higher nervous actions - memory, thinking, learning, then without full-fledged white matter it is not possible to quickly make decisions or respond to changes in the world around them.
Preventative measures for brain health
The speed of nerve impulses directly depends on the integrity of the white matter. Its healthy state determines its normal functioning. It has been scientifically proven that with increasing age, the quality of white matter and its functionality decline. Therefore, you need to comply with some simple conditions:
- Exercise regularly at any age - from simple morning exercises to serious sports.
- Monitor your health and consult a doctor on time.
- If diseases that can cause brain damage occur, treat under the supervision of a doctor.
- Remove bad habits from your life that can worsen your health.
- Increase immunity using hardening procedures.
- Keep your emotional state under control.
- Give food for brain activity: read, write, solve crosswords and other puzzles.
- During pregnancy, be under constant supervision of a specialist.
An active physical life and intellectual pursuits in both work and leisure will prolong normal performance and clarity of mind, and maintain strong memory. Teach children to take their health seriously as early as possible. Play sports and games that develop intelligence. It’s good to work together, proving its usefulness by example.
Only humans have higher nervous activity, and this is their direct difference from other species of mammals. The conditioned reflex actions that he masters in the process of life put him at the highest level of development.
Possible diseases
Any violation of the anatomical integrity of the nerve cell does not pass without leaving a trace. However, the severity of the pathological disorder and its duration are directly influenced by the nature of the provoking factor. Thus, when cerebral blood flow deteriorates due to an atherosclerotic plaque, which leads to post-hypoxic changes in the brain, ischemic stroke is characterized by:
- local feeling of numbness;
- partial/complete loss of movement in any part of the body;
- muscle weakness.
If the injuries lead to the death of a large area of the cortex, the person completely loses one of his higher nervous functions and becomes disabled. In the case of tumor damage to subcortical structures, disorders may occur in the regulation of structures dependent on them - autonomic abnormalities, thermoregulation, endocrine disorders.
Of course, diseases of the cortical structures are immediately noticeable. Meanwhile, atrophy of white fibers can occur hidden, for example, with dyscirculatory encephalopathy. Initially, small areas of the brain are affected, which affects a person’s daily activities. Later, the process covers all areas of brain activity - for example, Alzheimer's disease, multiple sclerosis. When performing magnetic resonance imaging, single lesions can be detected in the white matter of the frontal lobes - leukoaraiosis, or their localization in the cerebellum. Then, in addition to intellectual disorders, the patient is characterized by motor disturbances. The selection of optimal treatment regimens should be carried out by a neurologist, taking into account the anatomical and functional characteristics of the gray/white matter of the brain.