The main danger of a cyst is that it appears most often in the brain. This human organ is the most vulnerable and is easily damaged by any bruises. What then can we say about the neoplasm? Of course, if the cerebrospinal fluid cyst arose in another place, it would not have received so much attention. Its peculiarity is that in most cases it is asymptomatic and is discovered by chance. Such a formation can develop in any part of the brain. It should be noted that a cyst of this type is quite rare.
Localization
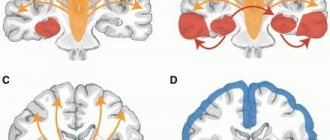
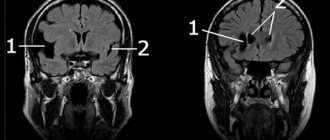
A cerebrospinal fluid cyst is a neoplasm located between the dura mater and the arachnoid membrane of the brain. Arachnoid cystic formations are most often localized above the sella turcica, in the area of the Sylvian fissure or cerebellopontine angle. They are located in both hemispheres of the brain, sometimes only in the left hemisphere, sometimes in the right part of the crown or middle cranial fossa.
Basically, these cavities are single in nature (80%), and multiple locations occur (12%). The diagnosis is confirmed 4 times more often in men than in women.
Why is it dangerous?
Untimely treatment of the disease leads to serious consequences that significantly worsen the quality of human life. First of all, a large cystic tumor begins to put pressure on various parts of the brain, causing a disruption in the functioning of vital systems. Damage to one or another part of the brain can result in lifelong disability or even death of the patient.
Another serious complication of a cerebrospinal fluid cyst is a violation of the integrity of its membrane. In this case, the fluid accumulated from the inside pours into the brain and provokes the development of infectious pathologies.
Monitor your health and well-being very carefully. Negligent attitude to the manifested symptoms, in the presence of a tumor, is fraught with death.
Classification
When diagnosing a pathology, the causes of its occurrence, morphological features and clinical manifestations are identified. Based on these indicators, they are divided into types and subspecies:
- primary, congenital – arising at the stage of intrauterine development;
- secondary, acquired – triggered by pathological processes (injuries, hemorrhages, infections);
- simple - consisting of cellular cerebral exudate;
- complex, or retrocerebellar, consisting of arachnoid tissues and neurons;
- frozen - not growing, without obvious clinical signs;
- growing - with increasing size, the manifestation of neurological symptoms increases.
Surgical treatment
This method is suitable for eliminating large cysts. Also, if the mass enlarges and shows symptoms, surgery is also recommended. It comes in four types:
- craniotomy;
- cyst shunting;
- drainage;
- endoscopy.
Craniotomy is the most effective method of all of these. However, there is one drawback - during this operation there is a high probability of injury. Shunting, which is the removal of fluid, is a less dangerous surgical procedure. But during the operation, an infection may occur and complications may arise.
Endoscopy is used quite rarely. As for drainage, this method is not entirely reliable. There have been cases when, after such an operation, the patient experienced a second relapse.
Causes of primary neoplasms
The formation of a cystic form occurs when the intrauterine birth and development of an organ goes wrong. This happens due to the negative impact of certain factors on the body of the expectant mother:
- exposure to toxic substances;
- infectious diseases;
- heat provocateurs, including sunstroke;
- hereditary pathologies: Marfan syndrome;
- radiation.
Women who are carriers of infectious and parasitic diseases are at risk of developing cavitary cysts in a newborn. Rubella, herpes, cytomegalovirus, and toxoplasmosis are especially dangerous.
Cyst in the temporal lobes
Why does pathology develop? The cerebrospinal fluid cyst in the right and left temporal lobes increases due to concussions, inflammation of the meninges, and circulatory disorders. In this case, surgical intervention will not be enough; it is necessary to identify and understand the cause of the formation.
CSF cyst of the temporal lobe tends to recur again and again after elimination. To prevent such situations from arising, you need to take medications aimed at restoring the body’s defense system. Doctors prescribe different medications for specific situations. For example, to restore cerebral circulation, you should take blood thinning medications. If there is a lack of oxygen and you need to improve metabolic processes, experts recommend taking antioxidants and nootropics. To resolve adhesions of the meninges, doctors recommend using special medications like Karipain.
Secondary cysts
Acquired arachnoid cystosis appears as a result of:
- Bruise, concussion, trauma due to:
- a directed blow to the head against a stationary object;
- falling a heavy object on the head;
- rupture of large cerebral vessels due to a fall on the legs or buttocks.
- Surgical interventions.
- Fungal, viral infections: meningitis, serous meningitis.
Lacunar disease, accompanied by small vascular hemorrhages, also leads to the formation of cysts.
What it is?
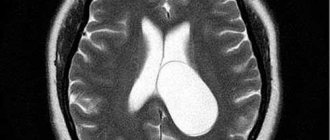
A cerebrospinal fluid cyst is a cavity filled with fluid. This formation belongs to the category of benign. It is worth noting that the cyst has nothing to do with tumors, but sometimes for convenience it is called that. This formation can appear in people of absolutely any age. A cyst is found in a fetus that has not yet been born if certain problems appear during the formation of the embryo.
In addition, it can occur in a newborn child as a result of injury received during birth, or an infection that entered the body immediately after birth. As for adults, such formations can be congenital or acquired. Most often, a cyst appears after a traumatic brain injury or stroke.
Course of the disease
A benign cavity filled with cerebrospinal fluid does not manifest itself in any way if it is in a latent, dormant state. As soon as provoking causes arise that trigger the process of division and growth, the tumor begins to put pressure on areas of the brain and the person experiences discomfort. The clinical course of the disease is increasing. The stages of development are given below:
- Clinical compensation is the stage of a “dormant” cyst: the tumor is localized in the skull, but does not manifest itself.
- Subclinical compensation – the first disturbances of neural functions appear.
- Partial clinical decompensation – neurological disorders become permanent.
- Severe clinical decompensation - the cyst changes location, gradually blocking the large hole at the back of the brain. The patient experiences a disruption in the functioning of organs and systems.
- Impaired cardiovascular activity leading to death.
Medicines for treatment
Some medications help eliminate the cause of this disease and prevent further development and growth of the cyst. In addition to them, antibacterial and immune medications may be prescribed.
The choice of medications is made by the doctor, taking into account the causes and characteristics of the pathology. Therefore, drugs can be very different. There are no specific recommendations here. But in some cases, “Karipain” (for resolving adhesions), antioxidants or nootropic medications, as well as “Pantogam”, “Instenon”, etc. may be prescribed. In some cases, drugs that normalize blood pressure and blood clotting will not interfere. Sometimes medications are required to restore blood formation processes or lower cholesterol. In some cases, the patient also needs other medications. Rehabilitation courses are especially needed after surgery.
Traditional medicine recipes
It is possible to treat such a cyst using traditional methods. Such therapy helps improve the patient’s condition, reduce headaches and slow down the growth of the cavity.
The following means are traditionally used:
- hemlock (A tincture of a mixture of olive oil and crushed grass seeds is used in the proportion of 1 teaspoon of raw material per liter of oil. The mixture stands for 3 weeks in a cool place. Then the infusion is dripped into the nose, 2 drops no more than three times a day);
- Caucasian dioscorea (Take it in the amount of 2 parts of finely chopped root and mix with 700 g of any vodka. Leave for 5 days, after which the vodka is drained and the roots are filled with it again. You need to take the tincture 1 tsp three times a day);
- herbal remedies help reduce pressure inside the skull and the size of the cyst. For example, calendula or chamomile, raspberry leaves or corn silk, elecampane or wormwood are used for this.
Before trying any folk recipe, you should consult your doctor. After all, any herbal tincture has contraindications, just like medications. In addition, many herbs are poisonous, for example, hemlock. And combining herbs with medications can lead to serious consequences, since they do not combine.
Many types of cystic cavities often resolve on their own within the first year after the baby is born and do not require radical measures. But parents should remember that a child diagnosed with such a pathology needs medical supervision.
Symptoms
A retrocerebellar arachnoid cyst manifests itself in the symptoms listed below.
General cerebral
The human brain has a limited volume, so as the tumor grows it begins to put pressure on the soft tissue, which causes:
- headache of a bursting nature, worsening at night and in the morning;
- nausea causing vomiting;
- psychomotor disorders: inappropriate behavior, uncontrolled movements, aggression, suicidal tendencies;
- congestion detected during fundus examination.
Focal
By touching the brain structures, the fluid-filled cerebrospinal fluid membrane creates a lesion and causes:
- In the occipital lobe:
- gradual decrease in vision;
- visual hallucinations;
- agnosia – failure to recognize objects;
- blurred vision, disorientation.
- In the temporal lobe:
- convulsions;
- hallucinations;
- impairment of auditory perception.
- In the frontal lobe:
- speech disorder;
- muscle hypertonicity;
- "drunk" gait;
- In the parietal lobe there is a disturbance of perception and sensitivity.
Signs
You can suspect the presence of a pathology in the head based on characteristic manifestations. Some people can ignore warning signs for a long time, explaining them by fatigue, individual characteristics of the body, weather changes and other safe factors.
Such behavior cannot be considered correct, because if any unpleasant symptoms appear, it is important to consult a doctor.
Manifestations of a cyst:
- Constant headaches. They are extremely difficult to eliminate with the help of various analgesics.
- Nausea and vomiting that does not bring relief.
- Insomnia, anxiety during sleep.
- Mental disorders. A person may suffer from apathy, negative thoughts, and increased aggression.
- Noise in ears.
- Problems with coordination, it is difficult for a person to maintain balance.
- Speech disorders.
- Decreased sensitivity of the skin.
These signs can be noted in adult children. At the same time, it is more difficult to find out about the presence of a neoplasm in newborns . This is due to the fact that they cannot talk about their condition, so they have to judge only by external signs. These include lethargy of the limbs, excessive regurgitation, and blurred vision.
As soon as characteristic signs are detected, you will need to consult a doctor. A specialist will be able to conduct an examination and also refer you for the necessary examinations. Based on their results, it will be possible to clearly understand what kind of pathology we are dealing with.
Diagnostics
The cyst is detected in only 4-5% of patients who apply for an MRI with other problems. Early diagnosis, in the first stages of development, gives a high percentage of recovery. To identify the disease, a comprehensive examination and consultation with specialists is carried out:
- neurologist;
- neuro-ophthalmologist;
- pediatrician;
- psychologist.
After compiling an anamnesis, the following is carried out:
- ultrasound diagnostics;
- echoencephalography (Echo-EG);
- radiography;
- rheoencephalography (Rheo-EG);
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- electroencephalography (EEG).
Images with contrast injection allow you to accurately determine where the cyst is located and distinguish it from a malignant tumor. Only after studies and laboratory tests are carried out, a course of treatment for the disease is prescribed.
Treatment of pathology
An arachnoid cerebrospinal fluid cyst does not necessarily need to be treated in all cases. If it does not bother you, then nothing can be done, but nevertheless, periodic monitoring should be carried out to see if there are any changes associated with its increase.
And, on the contrary, if the size of the tumor is large enough, then it is worth starting its treatment immediately. Experts distinguish 2 directions for treating pathology:
- operational;
- conservative.
In the second referral, the patient is seen by a doctor as an inpatient and undergoes drug treatment, which includes:
- medications whose action is aimed at resolving adhesions;
- nootropic drugs to prevent metabolism in the brain;
- medicines to improve blood supply;
- immunostimulants and modulators;
- medications to prevent ischemia.
After carrying out this type of treatment and determining its ineffectiveness, as well as if the cyst grows, it is necessary to carry out surgical interventions.
List of possible operations:
- Drainage of the cyst.
- Carrying out endoscopy.
- Bypass surgery of the cyst cavity.
- Radical excision.
Endoscopy is considered less dangerous but is not suitable for every disease pattern. If bypass surgery is performed, there is a risk of infection. And radical intervention is a very dangerous operation, which is why craniotomy and amputation of the cyst are performed.
Some methods are chosen individually, depending on the disease itself and the patient’s well-being.
The danger of a cerebrospinal fluid cyst
These types of cysts do not manifest themselves clinically and do not pose a threat to human health. They are determined randomly during magnetic resonance imaging. Sometimes these formations make themselves felt, for example, from external influences on the brain during concussions, inflammation and the presence of infections.
As the size of the cyst increases, the patient begins to experience discomfort associated with periodic headaches caused by the internal pressure of the tumor on the brain. Periodic circulatory disorders contribute to the occurrence of irreversible processes, which ultimately causes cell death. If there are no diagnoses to improve the condition, then partial or complete paralysis may occur, and after this, death cannot be ruled out.
The most serious manifestation is considered to be rupture of the cyst cavity, because the fluid immediately envelops the brain, and this leads to saturation of the body with toxins and death.
An arachnoid cyst, which has a transparent septum, with a slight increase in size can cause severe headaches. This kind of tension can be relieved with the help of diuretics.
Treatment
Even knowing about the presence of a simple, congenital, frozen cyst, the patient should not worry. The following drugs are prescribed against liquor cysts to improve metabolism:
- vitamins;
- to reduce cholesterol levels;
- for resorption of adhesions;
- to normalize blood pressure;
- anti-inflammatory drugs.
Further observation and supportive therapy will be required. It is important to be systematic in treatment and follow doctors’ recommendations.
Indication for surgery
If the tumor tends to increase, creates pressure on the functional areas of the brain, and neurological disorders have appeared, there are grounds for the use of surgical treatment methods.
Surgical intervention is indicated:
- when convulsions occur;
- if the tumor grows quickly;
- if cerebrospinal fluid accumulates, dropsy occurs;
- when the cavity is located in nearby parts of the brain.
Types of surgical procedures
When treating arachnoid cysts, the following operations are performed:
- Shunting. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia and lasts about an hour. The shunt is installed through small incisions in the head, neck, and abdomen. It removes excess fluid into the abdominal cavity, where it is organically processed by the excretory system. The patient will feel relief of some symptoms immediately after surgery, but it may take weeks for other functions to return.
- Endoscopy. The modern method of neurosurgery makes it possible to remove a pathological formation through a small hole in the skull.
- Trepanation of the skull. Rupture of the cyst shell, spillage of fluid, hemorrhage into the cavity are indications for complete excision. Requires long healing.
- Proton therapy. The modern treatment method has a great advantage over traditional radiation therapy. Gamma rays, along with the source of the disease, also affect nearby healthy tissues of the body. Proton beams, releasing maximum energy, thanks to precise dose programming, stop at a given depth, specifically heal the sore spot, and return back. The harmful effects on healthy tissue are significantly reduced.
- Radiosurgery. It is distinguished by a single dose of radiation, which kills cells in 1 session. Separate beams of radiation, each carrying a small dose, along a certain trajectory reach the desired cavity (intersection point) and collectively release energy without affecting other structures of the body.
What treatment is possible
If the tumor does not have impressive dimensions, and its presence is not accompanied by unpleasant symptoms, no therapeutic measures are prescribed. The doctor simply registers the sick person and examines him with a CT scan once every six months.
If unfavorable signs appear and the size of the formation is small, a conservative method of therapy is prescribed. It consists of using the following pharmacological drugs:
- For resorption of adhesive tissues;
- To stabilize blood pressure;
- To lower the amount of cholesterol in the blood;
- To restore the metabolic process;
- To stabilize the blood clotting process.
All medications must be selected by the attending physician, who is based on the individual parameters of the patient’s body.
If drug treatment is unsuccessful, symptoms are pronounced and the cystic cavity is large, doctors decide to treat the disease with surgery.
The operation can be performed in the following ways:
- Bypass method - the pathology is relieved using a special drainage instrument;
- Endoscopic method - excision of the tumor is performed by piercing the skull with a specialized optical parting;
- Craniotomy is the most difficult type of surgery, since during it the doctor removes a piece of the skull bone and manually cuts out the cystic tumor.
What to suck
To eliminate a benign cavity in the brain, the doctor prescribes the use of drugs for resorption of sutures and voluminous, postoperative scars. Actovegin copes well with this task. In addition to its absorbent properties, it helps the patient reduce the severity of symptoms and improve his general condition. Doctors also often prescribe homeopathic medicines to patients. Their action is aimed at improving blood circulation. Stabilization of blood flow and metabolic process allows the body to restore its strength and independently overcome pathogenic formation.
Traditional therapy
Unfortunately, benign cerebrospinal fluid neoplasm cannot be treated using traditional medicine recipes. Self-medication with plants can not only be ineffective, but also provoke a worsening of the condition. That is why any use of granny drugs should be approved by a qualified medical professional.
Do they take you into the army with a cyst?
The Medical Commission uses the provisions of Article 23 of the Schedule of Diseases. Paragraph “d” describes in detail the examination of conscripts with congenital brain abnormalities. A congenital pathology that does not manifest itself in any way, does not cause pain and does not impair functions, allows the commission to consider the guy fit for service in the “B-4” category. He will repay his debt to his homeland in a certain branch of the military.
Severe damage to the nervous system gives the right to receive a fitness category of “D” or “B”. The conscript receives release, the army does not shine for him.
The secondary nature of the neoplasm is considered under Article 25 of the Schedule of Diseases, on the basis of which the following fitness categories are assigned:
- "D": not fit for service.
- “B”: limited eligibility, receiving a military ID without serving, not conscripted in peacetime. Obtaining this category is possible only if the person is registered, carries out the necessary medical procedures and the treatment does not help.
With or without a cyst, life goes on. A person’s well-being depends only on a responsible attitude towards it. What prevents you from undergoing a medical examination on time, a couple of times a year? The consequences of negligence can be costly. Time is one of the main factors in detecting tumors.