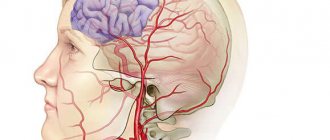
Diagnostic features
There are several criteria that distinguish paranoid psychopathy from character accentuation of the same type. These signs were identified by P.B. Gannushkin and are common to each type of psychopathy: the totality of the external manifestation of character traits, its stability over time and, as a consequence, serious difficulties in social adaptation.
The totality of character becomes obvious when a patient observes an exorbitantly high assessment of his person. This assessment applies in all circumstances. He considers all his actions undeniable, and desires and needs must be quickly and unconditionally satisfied. Overestimation can concern not only the sphere of supervaluation of one’s own personality, but also all phenomena that a psychopath encounters. The same can be said about constant suspicion, “hyper-vigilance,” about a vigilant search for enemies, intrigues, and persecution.
Inflated self-esteem, characteristic of paranoid development, does not completely exclude an inferiority complex. But at the same time, this complex turns out to be repressed into the unconscious, blocked through overcompensation by inflated self-esteem.
As for stability of character, it is relative. Usually, over time, there is an increase in paranoid characteristics and a complication of symptoms. It is for this reason that this form of psychopathy has received the name paranoid development among specialists. However, transformation of character type or smoothing out of negative characteristics, as a rule, does not occur. This is only possible with timely drug treatment and completion of a course of therapy.
Possible reasons
Psychopathy often stems from childhood
This condition can develop under long-term influence of unfavorable factors in the social environment that affect the formation of personality. Psychopathy is not considered a disease; it is believed that it is a reflection of pathological character deviations that could be caused by the following reasons:
- trauma during embryonic development or childbirth;
- congenital defects of the nervous system;
- genetic predisposition;
- brain damage that affects its functioning;
- alcoholism of one of the family members;
- past infectious diseases;
- regular exposure to social pressure.
The development of psychopathy can be influenced by errors in parental upbringing.
- Manifestation of overprotection. Parents take excessive care of their child, depriving him of the opportunity to become independent and withstand life's difficulties.
- Permissiveness. The situation when parents allow their baby to do whatever he wants, satisfies all his whims. As a result, a person grows up who considers himself overly significant, with inflated self-esteem.
- Free upbringing or neglect. The lack of necessary attention forces the child to adapt to life in society without anyone's help. This can lead to isolation in adult life.
- Despotic form of education. A child deprived of care and support, who is regularly punished and kept in fear, grows up as an insecure, weak person.
Symptoms of paranoid psychopathy
P.B. Gannushkin noted that until a psychopath began to openly quarrel with others, he could be an extremely useful employee. In a certain professional field, a paranoid person will work with all tenacity, accuracy and pedantry, without being distracted by extraneous interests and hobbies. In fact, such cases should be classified as character accentuations, and according to Gannushkin - “latent psychopathy.”
K. Leonhard identified the so-called “stuck” personality type as one of the norm options. A typical quality of this type is “stuckness”. First of all, it concerns emotional affect, which can be maintained for a long period of time. The affect is not eliminated and the individual cannot react to it. However, even with success, “getting stuck” makes itself felt. In this case, it turns into arrogance and narcissism. This type equally carries the possibility of both positive and negative personality development. The main driving force of paranoids is ambition. They can achieve great success in their careers, but when they encounter an obstacle, they easily become embittered, suspicious and vindictive.
Gannushkin believed that the main feature of this type is a penchant for so-called super-valuable ideas, the dominant position among which is occupied by the idea of the special meaning of one’s own “I”. Close to this judgment were the ideas of I. Lange that the main feature of this type is “hypersensitivity of the self.”
This is where paranoid patients become convinced that everything they do is always right; everything they say is always true; and what they claim is their unconditional right. It is for this reason that they are rarely inclined to ask for advice. Patients are impervious to the most benevolent forms of criticism and never listen to objections. A paranoid person is touchy and easily vulnerable. When faced with an objection, he very quickly begins to show aggression.
Types of psychopathy
There are several classification options, but the classic one identifies the following types:
- cycloids - the mood changes to the opposite with different frequencies, from several hours to months;
- schizoids - live in their own world, incapable of empathy, secretive, easily vulnerable, external sign - angular movements;
- epileptoids are incredibly irritable, angry, intolerant, stubborn, touchy, cruel, ready to “explode” at any moment, scandalous;
- asthenics - quickly “light up” and go out just as quickly, irritable, indecisive;
- psychasthenics - constantly doubt the correctness of their actions, insecure, hesitant;
- paranoiacs - complete egoists, stubborn and absolutely self-confident, consider themselves the “center of the earth” and never doubt that they are right;
- hysterical - mannered and demonstrative, can only live in the center of interests, always strive to attract attention to themselves;
- unstable - they act and think like the crowd, do not have deep interests;
- organic - smart in words, but cannot apply theoretical knowledge in practice, interests are limited to everyday life, banal, not a way to creativity.
Only a psychiatrist can determine whether a person suffers from psychopathy based on a combination of signs. No other doctor has any legal authority to use this term.
What is character accentuation?
Literally, this is the sharpening of personality traits. The accentuation is worse than the norm, but does not reach the level of psychopathy. A healthy person with accentuation of character may exhibit such traits as a psychopath, but in a much weaker, lighter form.
You can distinguish a psychopath from a person with an accentuated character by how their social adaptation proceeds. Accentuation of character allows you to stay in society, take your rightful place among people, build a family, raise children, and have permanent friends. Accentuation is not perceived as something painful; society evaluates such people as original. Accented people never go beyond universal human values and boundaries.
Psychopaths, unlike accented ones, always oppose themselves to society. The inability to “fit” into the logical and smooth flow of life results in the loss, first of all, of family and related ties, and the inability to build a career. In many cases, this ends in social rejection in its most extreme form, namely the loss of freedom.
In women, all psychopathic traits have their own characteristics.
Female hysteria
Hysterical psychopathy in women is more common than other types. This is facilitated by the properties of female nature - the desire to please and artistry, the innate ability to feel people’s weak points, intuitive perception of the world around us.
However, what makes a woman sensual and irresistible in everyday life, in the case of hysterical psychopathy, exhausts those around her. This is best described by the phrase “one-man show.” At the first contact with such a woman, it may seem that life has confronted you with a miracle, the woman presents herself so attractively and vividly and describes everything that happens to her. True hysterical psychopaths (according to Karl Jaspers, a German philosopher) suffer from a “thirst for recognition”; it is vital for them to “appear more than they really are.” There is nothing behind their words except the desire to show off.
The main passion that overcomes them is vanity. They seem to forget that they live in an ordered world and behave like children, always admiring themselves. It is important for them to be talked about, and it does not matter whether it is positive or negative. The main thing is the focus of attention, and the reason is not important.
Such women hint at mysterious patrons and will persuade anyone with the help of delicately used eternal female tricks - tears and “innocent” blackmail. They are short-sighted - what will happen tomorrow worries them little, the main events of their lives happen in the moment of communication.
A hysterical psychopathic woman easily breaks up with a man if he can no longer provide for her financially. She has already chosen her next victim.
Female epileptoids
The German psychiatrist Emil Kraepelin said the most colorful thing about these people: “With the Bible in his hands and a stone in his bosom.” In these women, ostentatious hypocrisy and evil vindictiveness coexist. Despotism, capriciousness, explosiveness and authority are the main features. These are domestic tyrants, from whose gaze and persecution there is nowhere to hide.
As a rule, such a lady chooses as her husband a man who is conscientious, gentle and shy, with a weak character. If such a couple gets along together for a long time, then the man often goes into alcoholism from unbearable daily pressure.
Such women are excellent housewives, because they have pedantry included. But along with a routine that runs like clockwork, such a woman brings callousness and vindictiveness, hypocrisy and cowardice. She knows exactly who can be oppressed and who needs to be curried.
Paranoid psychopaths
Such women rarely have a family. The selfishness of such ladies takes such ugly forms that it is not easy for ordinary people to stay close to them. They do not recognize anyone's rightness except their own. Selfish self-will - that’s what you can say about them. They joyfully walk “over heads like watermelons” for the sake of their goal. Parents still somehow tolerate this, but husbands and children - if they do appear - cannot stand it for long.
Women of this type are incredibly quarrelsome and vindictive. If on the path of such a woman she meets a man whom she considers an enemy, then any means will be suitable for revenge, including physical violence, hired killers or litigation. Logical arguments do not work here; only the unhealthy person’s own conclusions matter.
These are jealous women who can cripple the one who arouses the sympathy of her man. Moreover, there may be no reason for this.
Their main difference from the others is the formation of highly valuable ideas or fixed ideas. For such a woman, all the people around her are divided into two camps - friends and enemies. For enemies - even social workers or cashiers - there is no mercy. It is better not to stand in the way of such a woman if there are no reliable levers of influence on her.
Psychasthenic psychopaths
These are women who spend their whole lives fighting their own complexes, and the fight goes on with varying degrees of success. They constantly delve into themselves, so they have little time and energy for pleasure and joy. They perceive any criticism addressed to them extremely painfully, not understanding in principle that many say nasty things out of banal envy.
These are unresponsive “horses” who do not know how to stand up for themselves. They silently pull everything that is loaded onto them. They may do someone else's work at the expense of their time or family. They most often forget that a woman should have pleasure and personal time. At the same time, they do not have any career heights or special achievements.
The psychopath and society
The psychopath quickly benefits from the morals accepted in society, various laws and rules. He endlessly refers to existing moral principles, existing norms. His demagogic references to existing laws are not always openly rude, but are presented taking into account current circumstances and are carefully planned.
Another symptom of paranoid psychopathy is that the patient is able to find in each of his friends the characteristics of a fraudster or an attacker watching him. People often attribute envy to others. It seems to them that others want to harm them - even if these others are doctors. Painful symptoms often manifest themselves in obsessive ideas of jealousy, fanatical monologues, and incessant complaints. It is quite logical that the relationships between paranoid people and others are full of quarrels and misunderstandings.
What is pathology?
Patients with hysterical psychopathy strive to stand out from the crowd and try in every possible way to attract the attention of relatives, acquaintances, and colleagues. They often commit rash and unexpected actions.
Stage personality disorder occurs in 2–6% of the world's population. It is typical for both the stronger sex and women. All patients with such a deviation are united by increased egocentrism. These people find it difficult to come to terms with the lack of interest and attention to their person. Patients do not even care what reactions they provoke in others - positive or negative. Such individuals can be compared to artists playing for the audience.
Hysterical psychopathy does not always lead to disturbances in adaptation to society and failures in the professional sphere. Many patients with this disorder achieve great success in activities that require creativity. However, an increased desire for attention and praise, painful perception of comments and suggestibility often provokes troubles: deterioration of reputation, separation from a partner, loss of property.
Type of illness: excitable psychopathy
Psychopathy is a persistent personality disorder that develops at a fairly early age and lasts almost until the end of life. Any of these pathologies is expressed in a violation of the integrity of the individual, adaptation disorders, and complex relationships with the social environment. Another fairly common type of this disorder is paranoid psychopathy of the excitable type. What exactly is different about this disorder? Its characteristic features are uncontrolled outbursts of aggression and actions inappropriate to the current situation.
Psychopaths suffering from this disorder are very demanding of others, extremely touchy and selfish. They care very little about the opinions of other people; in advanced forms of the disease, patients are not capable of compassion. At the same time, the patient may often be overcome by depression and despair. Most often, the excitable type is found among alcohol addicts, drug addicts and socio-pathological elements (thieves, bandits and other offenders). It is among this type that the largest number of offenders is found, as well as persons who are examined at a forensic medical examination institution.
Symptoms
To recognize a female psychopath, it is worth paying attention to such signs as a deterioration in the ability to perform purposeful activities and emotional disturbances. Deviations in the volitional sphere also indicate the presence of mental disorders. Patients are not able to engage in result-oriented activities for a long time, especially if successful completion of work does not occur immediately.
Emotional disorders include lability (frequent mood changes, instability of emotions, inability to control emotional manifestations), euphoria (state of bliss, elation), a tendency to inappropriate, vulgar jokes, increased irritability, uncontrollable attacks of aggression, anger, apathy (detachment, indifference to the environment reality). Other symptoms of psychopathy in women:
- Disinhibition of drives. The patient does not take into account generally accepted rules, does not adhere to social norms of behavior, and is not able to foresee consequences. More often, violations are expressed in neglect of hygiene procedures, overeating, and committing antisocial acts (theft, fraud, sexual harassment).
- Deterioration of cognitive functions (memory, mental activity).
- Behavior that is inappropriate to the situation (excessive suspicion, illogical thoughts, delusional ideas).
- Preoccupation with a certain idea (religion, penchant for moralizing, moralism).
- Changing the nature of speech. It manifests itself as hypergraphia (verbosity, pedantic precision of presentation), pathological thoroughness (detailedness, inertia - indifference, passivity, torpidity - slowness of reaction, assessment of information, mental activity), perseveration (sustained repetition of a certain word, phrase).
- Sexual disorders (hypersexuality, changes in preferences).
A psychopathic girl has weakly expressed or absent character traits such as empathy (the ability to consciously empathize), the ability to repent of committed offenses, and regret. She is not capable of taking responsibility for her behavior; in making decisions, she is guided by her own benefit and the desire to achieve the goal by any means.
Signs of a female psychopath include excessive talkativeness, inflated self-esteem, a pathological tendency to deceive, a need for mental stimuli (emotions, impressions), and a desire to manipulate other people. A psychopathic wife is distinguished by superficial emotional reactions, does not know how to show sympathy or support her husband in a difficult situation.
Such people tend to lead a parasitic (dependent) lifestyle; they are characterized by irresponsibility and impulsiveness, and often maintain promiscuous sexual relationships. For female psychopathy, manifestations of sociopathy are typical (rejection of other people, ignoring, violation of their rights and freedoms).
Hysterical psychopathy in women is manifested by a need for outside attention and extreme egocentrism. Patients use external data, clothing, and provocative actions to attract the attention of others. Patients have a reduced ability to self-control. To keep other people's attention, they behave obediently and are easily influenced by other people.
Patients with the hysteroid form tend to stage demonstrative suicide attempts. Typical manifestations in a stressful situation: fainting, disturbances in breathing, hearing and speech. In the stage of decompensation, neurosis of the hysterical type develops.
In the emotionally unstable form, after an affective attack, patients enter a period of partial equilibrium, when they tend to criticize their behavior. Outbursts of aggression alternate with episodes of dysphoria (depressed, depressed, gloomy mood), when patients are prone to drinking alcoholic beverages and drugs.
The asthenic form is characterized by typical manifestations: emotional sensitivity, timidity, excessive sensitivity, self-doubt, which intensifies at the moment when it is necessary to make important decisions. Throughout their lives, patients are characterized by suspiciousness, increased anxiety, and a tendency to doubt.
There is often a pathological craving for introspection. On the basis of constant doubts and the inability to make a decision, neurosis develops, and anxious and suspicious personality traits worsen. In the paranoid form, patients exhibit signs of resentment, vindictiveness, lack of emotional attachments and sympathies, suspicion, and a tendency to conflict.
The schizoid form is characterized by the following symptoms: isolation, secrecy, emotional disharmony. Such people are categorical in their judgments, they tend to make extreme, unconditional decisions. Intelligence level is not a diagnostic criterion. Some patients have high intellectual abilities, others have mental retardation, sometimes even debility.
Features of this type of disease in men
As for male psychopaths, such individuals often turn into grumpy arguers, starting a conflict over any issue. Psychopathy of the excitable type in men manifests itself in ardor and explosiveness. The patient seeks to prove that he is right not so much by logical arguments, but by the desire to “shout out” his opponent. He is characterized by straightforwardness and rigidity of thinking. A man always strives to present himself as more honest and fair than the people around him. Often he can enter into a quarrel to protect the interests of third parties, but at the same time quickly switch to his own selfish motives.
If something suddenly interests the patient, it means that this thing is extremely important. In the event that someone does not agree with him, this person will turn into enemy No. 1. This is another feature of excitable type psychopathy in men. Why is such a person dangerous? First of all, it is very difficult to live with him. A psychopath constantly has to be petted, and his whole life will have to be sacrificed to his highly valuable ideas. For a paranoid person there will always be a large number of “enemies”. If we are talking about a married couple, a paranoid husband may prohibit his wife from communicating with her mother, sister or brother. All instructions should be carried out in the way that seems right to him - for example, waking up the child at 5 am or forbidding him to communicate with friends.
Paranoid men are very jealous and constantly look for “signs of infidelity” in their wives. The background to such ideas is not at all inflated self-esteem, but an internal conviction of one’s own sexual inferiority or unattractiveness. At first glance, aggression caused by jealousy should be directed at third parties - more attractive rivals. But such an orientation occurs only in women. The target of jealous aggression in men is primarily his partner. The psychological background of this phenomenon has not yet been fully studied.
Features of pathology in women
It is believed that paranoid psychopathy in women is less aggressive than in men. According to some studies, the disorder begins to manifest itself in the weaker sex from the age of eleven. In general, the main signs of female psychopathy are similar to the manifestations of the disease in men. However, unlike men, women more often end up not in prisons, but in psychiatric clinics.
Principles of communication with the patient
Often those people whose relatives or loved ones suffer from this disease, the question arises: “How to communicate with such a person?” Paranoid psychopathy is a serious disorder. In addition to treatment, a number of rules in communication should be followed with such a patient. Let's look at the main ones.
Firstly, in the process of communication it is necessary to reduce the expression of aggression on the part of the patient. A psychopath is always unpredictable. Therefore, the person next to him must always be on guard. Even an innocent joke can cause such a person to have an attack of anger.
Secondly, a loved one must be able to distract the psychopath’s attention. If the patient's behavior begins to change in a negative direction, you should distract his attention with books or films, or by talking about a favorite topic.
If there is a threat to health or life, you should call for help and run away. After all, a psychopath practically does not feel pain. You should not use force or gas canisters. In this case, the patient will only become even more angry. If a threat arises, you should immediately run away and call other people for help.
Thirdly, you should not enter into conflict with a psychopath. You must behave extremely calmly and kindly. Also, do not quarrel with other people in front of him. The patient may experience an attack of aggression from other people's screams.
Is it possible to resist pathological development?
Parents need to remember that a child’s social motives are not formed immediately, but over a fairly long period of time, starting from the earliest years. The child should feel a warm attitude towards himself and realize that a similar reaction is expected from him. Sincere love and affection from close people (mother and father, grandparents, siblings) will help develop the right social motives. If a child demonstrates empathy towards other people, this behavior should be encouraged and supported. Only in this case will the chances of pathological personality development be reduced.
Definition and classification
Psychopathy in females is a pathological syndrome characterized by high impulsiveness, inability to become attached to someone, and the inability to create long-term relationships. Such people are characterized by the presence of non-standard experiences, a tendency to obsessive states, and depression.
In most cases, the development of such a pathology is due to improper upbringing; it can also be congenital.
There is no need to think that psychopathy is a disease. These are character traits, and a view of the world, and of oneself in particular. If diseases develop over time, change through different phases, can subside, then worsen, sometimes even be completely cured, then with regard to this disorder, it accompanies the individual throughout his life, and does not change much.
A specialist can assume the presence of psychopathy based on certain signs:
- apathy;
- indifferent attitude towards others;
- lack of empathy;
- unwillingness to be responsible for actions;
- rejection of society's norms;
- manifestation of social maladjustment;
- lack of shame for misdeeds;
- increased level of conflict.
Depending on which external signs predominate, certain types of psychopathy are distinguished.
- Asthenic. There is an alternation of exhaustion with excitability. Such a person is characterized by increased impressionability, indecision, isolation, and mood swings are often observed. A woman does not tolerate stress well, gets tired quite quickly, and reacts sharply to rude behavior. Such a young lady is characterized by touchiness and silence. Often there is anxiety in the heart area, increased sweating, and sleep problems.
- Psychasthenic. Characteristic signs: endless doubts about the correctness of one’s actions and judgments, suspiciousness, problems making important decisions, introspection, constant control, the presence of fears. It is very difficult for such a young lady to decide on certain life changes, which provoke even more doubts and exacerbate uncertainty.
- Excitable type. Such a girl is characterized by high emotional reactions and aggression. Cases of alcoholism are often reported. A woman with this type of psychopathy is irritable and may experience attacks of rage. After showing an angry mood, he quickly comes to his senses and regrets what happened. Such women often feel dissatisfied with what is happening. They often argue and find something to complain about. There is absolute confidence that one is right, and increased stubbornness.
- Hysterical type. Characterized by the presence of excessive fantasy that replaces reality. A woman lives in pink dreams. Pretentiousness and theatrical behavior are characteristic. Such a young lady will demonstrate what is in her soul, will exaggerate her emotions, and may attribute qualities that she does not possess. Mood swings are typical.
- Paranoid. Overvalued ideas dominate a woman’s experiences. This type of psychopathy is especially acute after the age of 25. Among such women there are jealous people and fanatics. Characterized by the presence of selfishness, stubbornness, self-confidence, straightforwardness. Such a young lady is very conflict-prone and easily causes scandals, both at work and at home. Characterized by the presence of pronounced justice, which they want to restore in any way.
- Schizoid. Such a woman will behave secretly, and is characterized by isolation and isolation from reality. At the same time, her condition is described by increased vulnerability, impressionability, and excessive sensitivity. Such a young lady treats the people around her coldly; she does not care about the problems of other people. Due to the fact that a woman has a non-standard type of thinking, she can achieve good success. In rare cases, he starts relationships with the opposite sex, and there is a tendency towards self-sacrifice.
- Affective. This type combines both hyper- and hypothymic psychopaths. The hypothymic type of women is characterized by despondency, a depressed mood, low sociability, constant dissatisfaction, pessimistic views on life and low self-esteem. The hyperthymic type is characterized by elevated mood, optimism, high activity, and excessive self-confidence. Such a woman does not keep promises and is prone to deceit.
- Unstable. Characterized by a weak-willed character and increased pliability. The life of a young lady directly depends on certain circumstances. Such women often find themselves in bad company and develop various addictions. If a girl is controlled, then she will be able to lead a normal life and work fully.
Paranoid psychopathy: examples of patients
Those suffering from this psychopathy include antisocial individuals. These are individuals who are characterized by cruelty towards other people or animals, fanatical members of totalitarian sects, and recidivist criminals. The described categories will be of interest to those psychology or medical students who need to find an example illustrating this disorder. Paranoid psychopathy also affects those who deliberately endanger others. Such people may deliberately not observe safety precautions: for example, leave exposed electrical wiring, being aware of the consequences this will entail.
Treatment
When the patient’s behavior begins to interfere with his ability to be in society, it is necessary to prescribe drug therapy. Treatment for paranoid psychopathy may include taking antidepressants to correct low mood. This could be Prozac, Fluoxetine, Haloperidol and other medications. Anxiety is relieved with Phenazepam or Mezapam. Depending on individual characteristics, antipsychotics may be prescribed for the treatment of paranoid psychopathy: Tizercin, Sonapax, etc. Medicines are taken only as prescribed by a doctor. Before using medications, you should consult a specialist.
The dosage should be controlled by the patient's relatives. This is necessary for the reason that patients with psychopathy often take medications in those doses that they themselves consider necessary. To correct paranoid psychopathy, a course of psychotherapy is prescribed. The most commonly used are behavioral-behavioral therapy, the direction of family systemic therapy, and the Gestalt approach.
Symptomatic picture
A hysterical girl shows the first signs of hysterical disorder already in childhood, at 5-6 years old.
The child needs all the attention of those around him, which he tries to achieve in a variety of ways. The girl is sensitive to criticism and praise from other children. The child prefers to show his abilities in front of adults and communicate with peers. At school, the only motivation is praise and admiration. Without the support of adults, the child quickly refuses to complete assigned tasks and reacts violently to comments and complaints about his behavior. A little girl's hysteria becomes a norm of behavior that allows her to receive compassion, things of interest, or everyone's attention. Failures in studies and sports cause hysterics. Often a nervous breakdown is accompanied by falling to the floor, convulsions, and aggressive behavior.
Symptoms in teenagers
In a pubescent girl, hysteria takes on the most striking features. Teenagers often cut their wrists in an attempt to get attention. Suicidal attempts by hysterical women are not serious, they are of a “show-off” nature. In severe cases (severe nervous shock, physical overload), when a teenage girl becomes hysterical, irreparable things can happen. The suicidal game crosses the border, because the person is not able to control his behavior. It is important for parents not to miss this moment.
Teenagers have a pronounced protest against the opinions of adults. Often teenage girls run away from home, expressing dissatisfaction with punishment. In some cases, this behavior is expected, so parents usually know where to look for their children. Such protests are typical when children want to prove their “coolness” in a company, to be leaders. But, usually in the society of teenagers this is an imaginary coolness, and most children are still aware of the boundaries of what is permitted. Seeing this, hysterics quickly lose interest and begin to look for a new society.
Hysterical girls often run away from home
Manifestations in adults
Women's hysteria in older age acquires special features. Characteristic signs of hysterical women are observed in their behavior and manner of dressing. Demonstrativeness takes on different features depending on the social circle. With one acquaintance a woman looks modest and vulnerable, but with another she behaves arrogantly, familiarly, defiantly. Hysterical attacks designed for a certain audience and aggressive behavior often occur. To attract attention, a woman can use fantasy stories about her past achievements and embellish reality.
Symptoms in hysterical women may vary depending on their mood. It’s easy for them to find a common language with new people, but they quickly become disillusioned with them when interest in their own person dries up. The behavioral line is determined by emotionality and superficial judgment, a painful perception of the surrounding reality. Such features lead to instability in communication, severance of social ties, and irrational behavior with one’s own child and husband.
A distinctive character trait of a hysterical woman is infantilism. Their mental development is at the level of a child:
- they are immature in judgment;
- do not perceive criticism adequately;
- demonstrate violent protests;
- do not try to correct their behavior, citing incorrect perceptions from others;
- It is common for them to quickly succumb to suggestion from third parties and to self-hypnosis.
Forecast
The prognosis largely depends on the severity of the disease. If exacerbations occur frequently, despite treatment, then, most likely, complete social adaptation will not occur.
Symptoms of paranoid psychopathy are not observed among adolescents. It is known that this symptomatology most often manifests itself by the age of 30-40. It is during this period that a person’s social maturity flourishes. Although in some cases the disease can manifest itself at a younger age - 20-25 years.
If we are talking about pathology of the excitable type, symptoms may appear at an earlier age. The prognosis for excitable type psychopathy in adolescents is considered favorable in case of timely treatment. Adolescents, like adults, may be prescribed medications and psychotherapy. A detailed analysis of the patient’s social connections is also necessary in order to exclude interaction with those people who may aggravate his condition.