Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
about phenobarbital , what it is and what the mechanism of action of this substance is to understand the pattern of the drug’s effect on the body.
Sleeping pills that are addictive with long-term use include barbiturates . In fact, barbiturates to be drugs.
Based on their duration of action, they are divided into three groups:
- short acting;
- intermediate;
- long-acting.
Drugs that belong to the second group are usually abused, less often - to the first. Phenobarbital, in turn, belongs to barbiturates - the third group. Its effect on the body becomes noticeable approximately an hour after application and continues for 12 hours.
The Pharmacopoeia indicates that the molecular formula of phenobarbital is C12H12N2O3. This substance has anticonvulsant , sedative and hypnotic properties.
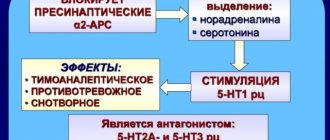
Increases the degree of sensitivity of GABA receptors to the mediator, increases the opening time of neuronal channels for incoming currents of chlorine ions, and promotes their transport into cells. This leads to hyperpolarization of the cell membrane and a decrease in its activity. As a result, the inhibitory effect of GABA , interneuron transmission in the nervous system of the body is inhibited.
In therapeutic doses, it increases GABAergic transmission and prevents glutamatergic neurotransmission . At high concentrations, it prevents the flow of calcium ions through cell membranes.
Acts as a nervous system depressant. It reduces the excitability of motor cortical and subcortical centers, reduces motor activity, causes sedation and sleep.
The medicine can also be used to relieve convulsive attacks of various origins. The anticonvulsant effect is due to the suppression of glutamate , activation of the GABAergic system , and an effect on voltage-gated sodium channels. in the epileptogenic focus decreases , the appearance and propagation of impulses is blocked. The drug inhibits high-frequency repetitive firing of neurons.
When used in small dosages, the drug acts as a sedative . And at high doses it can provoke depression of the centers of the medulla oblongata. In addition, it depresses the respiratory center, reduces its sensitivity to CO2 and the volume of respiration.
After oral administration, it is completely absorbed in the small intestine. The maximum concentration is reached after 1-2 hours. Bioavailability is 80%. About half of a single dose is bound to plasma (20-45%). The substance is evenly distributed in tissues and organs, and is present in lower concentrations in brain tissue. The half-life in plasma in adult patients is 2-4 days. It can pass through the placenta and be distributed throughout all tissues of the fetus and enters breast milk.
Slowly eliminated from the body. It is broken down by microsomal liver enzymes . In this case, inactive metabolites . Excreted by the kidneys as a glucuronide , 25% to 50% is excreted unchanged.
In case of renal dysfunction, the effect of the drug is significantly prolonged.
Phenobarbital is included in various medicinal complexes. For example, in Gluferal , Fali-Lepsin , Teofedrin , Pagluferal , Tepafillin , Bellataminal , Barbexaclone . It is also included in the combined sedative Peppermint leaf oil + Phenobarbital + Ethyl bromizovalerianate. The recipe in Latin in this case will contain the following name: “Oleum foliorum Menthae piperitae + Phenobarbitalum + Aethylii bromisovalerianas.” In addition, this substance is the basis of the drugs Valocordin and Corvalol .
Wikipedia reports that the circulation of phenobarbital is limited in our time. Drugs containing it are prohibited from being imported into some countries. For example, to the USA, Lithuania, UAE.
A lethal dose of phenobarbital is administered to prisoners on death row.
special instructions
Use with caution in patients who abuse medications or have a history of drug dependence; for liver dysfunction, acute or persistent pain, renal dysfunction, respiratory diseases accompanied by shortness of breath or airway obstruction, especially in status asthmaticus. Use parenterally with caution for heart disease and arterial hypertension.
Long-term use may cause liver damage.
Patients who are hypersensitive to one barbiturate may have hypersensitivity to other barbiturates.
Phenobarbital should not be used concomitantly with griseofulvin. With simultaneous use, it is necessary to monitor the concentrations of hydantoin derivatives in the blood plasma.
During the treatment period, avoid drinking alcohol.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
During the treatment period, a slowdown in the speed of psychomotor reactions is observed. This must be taken into account by persons engaged in potentially hazardous activities that require increased attention and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Side effects
Adverse reactions are most often observed with long-term use of the drug. As a rule, this is inhibition of central nervous system activity, allergies , and a pronounced decrease in blood pressure . In addition, agranulocytosis , headache , calcium metabolism disorders, thrombocytopenia , vascular collapse , megaloblastic anemia , bradycardia , nausea, constipation , vomiting, folate , osteomalacia, impotence , hypocalcemia , impaired libido are possible.
Instructions for use of Phenobarbital (Method and dosage)
Children of early and preschool age are given the medicine in the form of a 0.2% solution 30-40 minutes before bedtime. If it is indicated to take Phenobarbital, the instructions for use recommend using it 2 times a day (before nighttime and daytime sleep). This should be done regardless of meals. When using the drug in the form of a solution, it should be taken into account that 1 teaspoon contains approximately 0.01 g of medicine, 1 dessert spoon contains 0.02 g, and a tablespoon contains 0.03 g.
Maximum single dosages:
- children under six months – 0.005 g;
- children from 6 months to 1 year – 0.01 g;
- children aged two years – 0.02 g;
- children 3-4 years old – 0.03 g;
- children 5-6 years old – 0.04 g;
- children 7-9 years old – 0.05 g;
- children 10-14 years old – 0.075 g.
As a sedative and antispasmodic , the drug should be taken 2-3 times a day.
Instructions for use of Phenobarbital for adults indicate that a single dosage is selected individually. Frequency of administration – 1-3 times a day. Dose from 10 to 200 mg. The tablets are taken orally.
When used as a sleeping pill, usually take 0.1-0.2 g before bedtime, as an antiepileptic - 0.05-0.1 g 2 times a day, as a sedative - 0.03-0.05 g 2 -3 times/day, as an antispasmodic – 0.01-0.05 g 2-3 times/day.
When using the drug intravenously, a single dosage for adults is from 100 to 140 mg, and intramuscularly – from 10 to 200 mg. For children, intravenous administration is indicated from 1 to 20 mg per 1 kg of weight, intramuscularly - from 1 to 10 mg per 1 kg of weight. The frequency of administration is determined by a specialist individually. After intravenous administration, you need to wait at least half an hour until the drug begins to act.
The maximum dosage for adults at one time is 200 mg. The highest daily dosage is 500 mg.
The drug may become addictive after approximately 2 weeks of use. Physical and mental dependence on the drug is possible. Withdrawal syndrome occurs .
Composition, release form and packaging
| Pills | 1 tab. |
| phenobarbital | 100 mg |
6 pcs. – cell-free contour packages (1) – cardboard packs. 6 pcs. – cell-free contour packages (2) – cardboard packs. 10 pcs. – cell-free contour packages (1) – cardboard packs. 12 pcs. – cell-free contour packages (1) – cardboard packs. 6 pcs. – cell-free contour packages (300) (for hospitals) – cardboard packs. 6 pcs. – cell-free contour packages, 12 pcs. – strips (1) – cardboard packs. 12 pcs. – cell-free contour packages (150) – cardboard boxes. 10 pcs. – cell-free contour packages (180) – cardboard packs (for hospitals).
Phenobarbital overdose
In case of toxic poisoning, symptoms may not appear for several hours. Ingestion of 1 g may cause serious poisoning in adults. In turn, taking 2-10 g leads to death.
Acute overdose is fraught with the appearance of ataxia , severe confusion , agitation, headache , oliguria , hypotension , cyanosis , coma , unusual eye movements, severe weakness and drowsiness , slurred speech, dizziness , Cheyno-Stokes respiration , tachycardia , hypothermia . In addition, nystagmus , constriction of the pupils, weakened or complete absence of reflexes, respiratory depression, weak pulse, and hemorrhages (at pressure points) are possible.
Severe intoxication can lead to pulmonary edema, apnea , death, vascular collapse with decreased peripheral vascular tone, respiratory and cardiac arrest.
If the drug was taken in a life-threatening dosage, suppression of the electrical activity of the brain is likely, which cannot be regarded as clinical death, since the effect is completely reversible if there was no damage associated with hypoxia .
Chronic intoxication with this drug can manifest itself as apathy , constant irritability, insomnia , dizziness , decreased mental abilities and confusion, imbalance, drowsiness , general weakness, confusion of speech. In addition, hallucinations and convulsions may appear, excessive agitation is possible, disruption of the cardiovascular system, gastrointestinal tract and kidney function.
pneumonia , congestive heart failure , arrhythmia , and renal failure may develop .
Acute overdose of Phenobarbital is treated by accelerating the elimination of the active substance and maintaining vital functions.
In order to reduce the absorption of the drug, you can induce vomiting, and then prescribe activated charcoal . In this case, measures must be taken to prevent aspiration of vomit. If vomiting cannot be induced, gastric lavage is performed.
To speed up the removal of the drug from the body, saline laxatives and alkaline solutions are given, and forced diuresis .
Monitoring vital functions and water balance in the body is mandatory.
The following support measures are available:
- maintaining normal blood pressure ;
- ensuring airway patency;
- anti-shock measures (if necessary);
- prescribing antibiotics (if the development of pneumonia );
- use of mechanical ventilation and oxygen;
- use of vasoconstrictor drugs (in case of hypotension );
- prevention of hypostatic pneumonia , aspiration , bedsores and other complications.
It is not recommended to give analeptics ; it is advisable to avoid overloading the body with fluid or sodium.
In case of severe intoxication, shock or anuria peritoneal dialysis or hemodialysis is prescribed . In this case, the content of phenobarbital in the blood should be monitored.
In order to treat chronic intoxication, the dosage of the drug is gradually reduced until complete withdrawal. Therapy is symptomatic. You may need psychotherapy.
Interaction
Combination with drugs that depress the nervous system, as well as ethanol-containing drugs and ethanol can lead to increased CNS depression. Caffeine reduces the hypnotic effects of phenobarbital .
Interaction with MA O and Methylphenidate causes an increase in plasma levels of phenobarbital , so that the toxic effect and inhibitory effect on the nervous system are enhanced.
The intensity and duration of action of the following drugs may be reduced when combined with Phenobarbital: GCS , chloramphenicol , Dacarbazine , Metronidazole , Carbamazepine and anticonvulsants from the succinimide , anticoagulants Indandione and Coumarin derivatives ), Doxycycline , Chlorpromazine , vitamin D , Corticotropin , Cyclosporine , digitalis glycosides , Quinidine , estrogen-containing oral contraceptives , tricyclic antidepressants , Fenoprofen , Phenylbutazone , xanthines .
Concomitant use with acetazolamide can provoke osteomalacia and rickets .
Taking valproic acid leads to an increase in plasma levels of phenobarbital , which can cause pronounced sedation and lethargy . The level of valproic acid in plasma decreases slightly.
Combination with Verapamil , Felodipine , Nimodipine also leads to a decrease in their plasma levels.
Interactions with Halothane , Ftorotan , Enflurane and Methoxyflurane may cause increased metabolism anesthetic drugs , which increases the likelihood of toxic effects on the liver (and also on the kidneys in the case of Methoxyflurane ).
Taking Griseofulvin leads to a decrease in the degree of its absorption from the intestine.
Combination with Maprotiline in high dosages reduces the seizure threshold and the anticonvulsant effect of barbiturates .
The effectiveness of Paracetamol may be reduced when taken with Phenobarbital. Possible development of hepatotoxicity .
A daily dose of Pyridoxine of 200 mg reduces the level of phenobarbital in plasma, and simultaneous use with Primidone and Felbamate , on the contrary, increases it.
If there is a lack of folic acid in the body, taking medications with this acid leads to a decrease in the effectiveness of Phenobarbital.
Combination with other sedatives can lead to severe respiratory depression.
Newborns
For newborns, this remedy can be used in case of hemolytic disease . It increases the detoxification the liver and reduces serum bilirubin .
If mothers use the drug in the last trimester of pregnancy, for newborns this is fraught with the development of physical dependence on the drug and withdrawal syndrome , up to acute withdrawal syndrome , which manifests itself as epileptic seizures and increased excitability immediately after birth or during the first couple of weeks.
Use during childbirth in some cases causes respiratory depression in the infant, especially in premature infants.
Taking this drug as an anticonvulsant during pregnancy can cause bleeding in the baby in the first days after birth.
Contraindications
Before prescribing, the doctor conducts a diagnosis and excludes contraindications. There may be sensitivity of the immune system to the components contained in the tablet, manifested by an allergic reaction. Allergies and intolerances must be ruled out.
Other contraindications:
- Sensitivity to other drugs from the barbiturate group.
- Pathologies of the respiratory system with impaired respiratory functions.
- History of dependence on medications or drugs.
- Carrying a child.
- Breastfeeding period.
- Disturbance of liver or kidney tissue.
- Myasthenia.
- Dependence on ethanol consumption.
- Porphyrin disease.
The use of the drug is limited in the presence of the following factors: depressive disorder, suicidal behavior at the moment or in the past, excessive movements, increased production of thyroid hormones, insufficient secretion of adrenal hormones, pain syndrome, childhood.
Reviews of Phenobarbital
Judging by the reviews, this drug is often used for various intoxications of the body, as it increases the detoxification function of the liver. In addition, you can often find reports that this medicine has been successfully used as a sedative (usually in combination with others), as well as in the treatment of neurovegetative disorders.
Among the negative aspects, reviews of Phenobarbital note the occurrence of side effects. Thus, weakened patients and children often develop excessive agitation after taking it. In addition, attacks of nausea and vomiting, general weakness, constipation, asthenia , and dizziness . Rarely, reviews also talk about fainting, the development of depression , allergies, ataxia , the appearance of hallucinations and hemolytic disorders. Sometimes patients who have taken this drug for a long time report developing rickets .
Phenobarbital price, where to buy
You can buy Phenobarbital in Moscow and other Russian cities only with a doctor's prescription. It should also be taken into account that it is prohibited to import it into some countries. The price of Phenobarbital in tablets 100 mg, 6 pieces per package from 12 rubles. Although in general the cost can vary greatly depending on the manufacturer.
Despite the fact that the price of Phenobarbital can be relatively low, it is not so easy to find in pharmacies, so many people prefer to buy other complexes that contain its active ingredient.
Analogues of the drug
There are other medications based on this chemical compound. When choosing an analogue, you need to pay attention to the content of the active ingredient in the tablet and the instructions. Corvalol and other drugs with several active ingredients are not direct analogues of the drug. The selection of analogues should be carried out under the supervision of a specialist.
Existing analogues:
- Luminal.
- Phenobarbital tablets for children.
Children's analogue with a minimum dose
Any medications based on this substance are prescription drugs.