A stroke, regardless of its form (except for transient ischemic attack - TIA) and causes, leads to the death of brain cells. Side effects of stroke (acute cerebrovascular accident) can be varied and depend on the location of the vascular accident. Thus, seizures after a stroke often occur when the frontal lobe is affected.
The consequences of stroke cannot be avoided, but conditions can be created for a speedy partial or complete recovery
Cortical neurons are extremely sensitive to a lack of oxygen, but they are the ones responsible for higher nervous activity. Their death means that a person ceases to exist as an individual, even if vital functions are preserved. Changes in the cerebral cortex can lead to cognitive and mental disorders. Their degree of expression varies. In severe form, these disorders can make a person’s life in society extremely difficult.
Ischemic stroke: general characteristics
The nosological description of ischemic stroke includes three different pathologies that characterize the localization of the circulatory disorder:
- ischemia – lack of blood flow in a local area of an organ;
- heart attack - organ damage caused by a lack of blood supply;
- stroke is a disturbance in the blood supply to one of the areas of the brain, caused by progressive ischemia of one of the vessels and accompanied by necrosis (death) of brain cells.
Another name for ischemic stroke – cerebral infarction – fully corresponds to the ongoing pathological processes in the brain. It is important to note that tissue destruction occurs even after normal blood flow is restored.
That is why a person who has suffered a stroke needs qualified medical supervision and subsequent rehabilitation.
Among the causes leading to ischemic stroke, two groups can be distinguished:
- unmodifiable , i.e. untreatable (for example, genetic predisposition, age-related risks);
- modifiable , the influence of which can be controlled (bad habits, excess weight, diabetes, high cholesterol, sedentary lifestyle and others).
Many adverse factors can be corrected or minimized by following the rules of a healthy lifestyle.
Some other consequences of stroke
- Seizures after a stroke are a manifestation of damage to neurons in the brain. The occurrence of a convulsive syndrome may mean that an area of sclerosis or a cyst has formed in the stroke area. If a person begins to complain that he is dizzy, has weakness and a headache, this is a reason to suspect problems with blood flow. The occurrence of seizures against this background may indicate recurrent stroke.
Convulsive seizure due to the consequences of a stroke
- Hallucinations after a stroke indicate the involvement of the cortical centers of the sensory organs in the process. ACVA leads to disruption of their activity with the occurrence of disorders of perception of the surrounding reality. Hallucinations after a stroke may also indicate mental disorders, which often occur against the background of insufficient blood supply (atherosclerosis and vascular sclerosis contribute to this).
- Behavioral disorders are consequences that usually occur when the right hemisphere is damaged. Unmotivated aggression in such patients complicates life not only for them, but also for those around them. If the patient begins to complain of hallucinations or begins to demonstrate behavioral disorders, care should be taken to involve a psychotherapist or psychiatrist in the treatment process.
- Salivation. Usually associated with impaired swallowing function, as well as the inability to completely close the mouth due to paralysis of the facial muscles. Saliva is not released due to its increased secretion, but as a result of its excessive accumulation in the oral cavity. Treatment should be aimed at eliminating the cause, but it is also possible to prescribe drugs that reduce salivation.
- Reddish spots on the body are signs of blood flow disorders in these areas of the body in bedridden patients. Bedsores occur due to improper care, when the patient remains in one position for a long time. This contributes to compression of the soft tissues, as a result, characteristic bluish-red spots first appear, and then areas of necrosis. To avoid this, it is important to know and take preventive measures against bedsores.
Anti-bedsore mattress
- After a stroke, your legs may hurt. These sensations are associated with damage to the thalamus, as well as muscle spasms in the paralyzed limb. Legs may also hurt due to peripheral circulatory disorders due to vascular pathology (atherosclerosis) accompanying stroke. What to do in this situation? For thalamic pain, the administration of antidepressants and anticonvulsants, as well as drugs that improve blood flow in the vessels of the brain, is effective. If your legs hurt due to muscle spasms, great importance is attached to exercise therapy, massage, physiotherapy, and if necessary, muscle relaxants and analgesics are prescribed.
The consequences of a stroke are varied: sclerosis, brain cyst, dementia, mental disorders, hallucinations, pneumonia, drooling, convulsions. All of them, one way or another, are associated with changes that occur in the brain after the death of neurons and the formation of a focus of necrosis. Therefore, measures aimed at restoring blood flow in the vessels of the brain are important for preventing the occurrence of these disorders.
Types of stroke
Ischemic stroke is a pathological syndrome , the manifestations of which vary depending on the type of disease. If we consider the mechanism that led to the development of pathology, we can distinguish five types of stroke:
Atherothrombotic
Atherothrombotic stroke - its development is based on atherosclerosis, in which blockage of a vessel in large or medium arteries is caused by cholesterol “plaques”; This condition often develops at night during sleep.
Cardioembolic
Cardioembolic stroke - caused by a special type of blood clot - an embolus, which forms in various heart diseases (arrhythmia, endocarditis, heart disease) and blocks the arteries of the brain; the condition is sudden and develops during wakefulness.
Lacunar
Lacunar stroke - occurs when small vessels are damaged; most often develops in patients with hypertension or diabetes mellitus.
Hemodynamic
Hemodynamic stroke - caused by impaired blood movement through the vessels (for example, when pressure decreases), as a result of which the brain does not receive enough essential nutrients; most often develops in patients with concomitant vascular pathology.
Unknown origin
Stroke of unknown origin - it is not possible to identify the cause of the disease.
Stroke and heart pathology
Cardiac pathology plays a major role in the development of cerebrovascular accidents
One of the causes of stroke is atrial fibrillation. It can also lead to another stroke. The arrhythmia must be eliminated, otherwise the likelihood of emboli forming in the cavities of the heart and moving them into the vessels of the brain will continue.
Typical complaints that suggest the presence of atrial fibrillation:
- My head is spinning.
- The pulse is uneven and frequent (arrhythmia).
- My heart hurts.
- Sweating, fear.
Atrial fibrillation is the result of a disturbance in the conduction of nerve impulses through the myocardium. As a result, the heart muscle fibers contract unevenly. The ejection of blood from the atria is not carried out in full, creating conditions for the aggregation of blood cells with the formation of blood clots. Arrhythmia increases the risk of recurrent stroke, so adequate treatment of this condition must be carried out. The administration of antiarrhythmic drugs can successfully correct atrial fibrillation, preventing the formation of thromboembolism.
Attention! Cardiovascular pathology that led to the development of stroke, if not adequately treated, can cause a recurrent stroke. Sclerosis and atherosclerosis of blood vessels, atrial fibrillation must be treated.
If you feel dizzy, this is a sign of circulatory failure in the blood vessels of the brain. In this case, measures should be taken to normalize blood flow.
Periods of stroke
Ischemic stroke has an individual course for each patient. However, the rapid development of the pathological process is one of the common features inherent in people who have suffered this serious condition.
Sometimes the count is not in hours, but even in minutes, since brain tissue is destroyed very quickly.
There are five periods of stroke:
The first period - the most acute - lasts no more than 3 days. Timely medical care, consisting of administering thrombolytic drugs to the patient, can slow down the pathological reaction and even eliminate it.
If medical measures are successful, then doctors talk not about a stroke, but about a transient ischemic attack (a less dangerous condition that responds well to treatment).
The second period - acute - lasts from 3 days to 4 weeks. This is an important time to diagnose the extent of brain damage, as well as relieve symptoms of the disease.
This is followed by recovery periods: early (up to 6 months) and late (up to 2 years). At this time, a set of rehabilitation measures and procedures is carried out aimed at restoring the lost functions of areas of the brain (if this is possible).
Troxerutin and Troxevasin, what is the difference
After this comes a period of residual effects that will accompany the person and make themselves felt throughout his life.
Based on the speed of spread of the lesion and intensification of symptoms, experts distinguish the following types of ischemic stroke:
- transient ischemic attack - a small area of the brain is affected, blood circulation is disrupted for no more than a day; the prognosis is favorable;
- minor stroke – attacks of ischemia are severe and can last up to 3 weeks;
- progressive stroke - symptoms do not appear immediately, but gradually increase over several hours or even days; full recovery is impossible;
- extensive ischemic stroke – symptoms are most pronounced and last for a long time; the prognosis is unfavorable.
The possibility of a favorable prognosis is also influenced by the severity of the ischemic stroke.
With mild severity, there are few or only minor symptoms. The prognosis is favorable, rapid recovery is possible.
The average degree is characterized by many signs depending on the location of the lesion. A person’s consciousness does not change, in contrast to severe damage, in which large areas of the brain are involved in the pathological process and many functions suffer.
A sick person requires mandatory hospital treatment followed by a course of rehabilitation.
When a cerebral infarction occurs, certain areas of the brain that are responsible for certain mental and neurological functions are affected. There are several types of stroke depending on the area affected.
Stroke without paralysis or speech impairment
The consequences of a stroke are unique to each patient.
People who have had a stroke are most concerned about loss of body control, visual impairment, and problems understanding speech and pronouncing words.
Ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes kill brain cells. Each of these diseases is catastrophic, but the consequences of a hemorrhagic stroke are usually more severe.
Consequences of stroke: detailed article
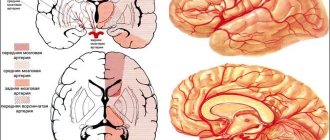
As a rule, a stroke does not affect the entire brain, but only one of its hemispheres - the left or right. The hemispheres of the brain control opposite sides of the body.
When people talk about left-sided stroke, patients mean that they have problems with the functioning of the left side of the body. In reality, a stroke on the left side means that the left hemisphere of the brain is affected and this has consequences on the right side of the body.
If the stroke affects the right hemisphere, there will be problems with the functioning of the left side of the body.
A stroke that affects the right or left hemisphere of the brain can cause the following consequences:
- inability to move, weakening of tactile sensations;
- problems with understanding the structure and written language, numbers;
- inability to select the right words and pronounce them clearly;
- visual disturbances in one or both eyes;
- difficulty swallowing food and liquids;
- weakening of cognitive functions - memory and thinking;
- violations of coordination, orientation in space;
- urinary and fecal incontinence;
- behavioral changes, emotional instability.
In severe cases, the consequences of a stroke make a person disabled. If the stroke was not severe and the patient was lucky to quickly receive medical help, then rehabilitation is possible - restoration of most of the lost functions.
The cerebellum is located at the bottom, towards the back of the skull. This is the part of the brain that receives and processes sensory information from the body. It helps control muscles, make movements precise, and balance the body in space while moving. Ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke rarely affects the cerebellum. But if this happens, the consequences can be serious:
- inability to walk;
- dizziness;
- headache;
- nausea and vomiting.
The brain stem is at the very bottom. It is responsible for the vital functions of the body, which are performed automatically, unconsciously. This area of the brain controls heart rate, breathing, blood pressure, as well as eye movements, hearing, speech, chewing and swallowing.
Consequences of a stroke affecting the brain stem:
- respiratory arrest;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- problems controlling body temperature;
- weakness, paralysis;
- difficulty chewing, swallowing;
- impaired speech;
- vision problems.
If a hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke affects the brain stem, then, as a rule, patients fall into a coma and die. The consequences of a stroke of the left and right hemispheres of the brain are discussed in detail below.
Consequences of a left hemisphere stroke:
- partial or complete paralysis of the right side of the body;
- problems understanding speech and pronouncing words (aphasia);
- “blind spots” in the eyes on the right side;
- inability to engage in planning, logical reasoning, mathematical calculations;
- behavioral changes - depression, caution, indecisiveness;
- problems with reading, writing, mastering new skills.
Consequences of a right hemisphere stroke
- partial or complete paralysis of the left side of the body;
- the patient’s denial of the problems that the stroke caused him;
- “blind spots” in the eyes on the left side;
- violation of the perception of space - in front, behind, up or down;
- inability to identify and recognize body parts;
- the patient cannot navigate using maps, find his clothes, hygiene items;
- behavioral changes - carelessness, impulsivity, emotional instability and depression.
Consequences of ischemic stroke
A dangerous consequence of ischemic stroke is cerebral edema. Hemorrhage, fainting, and epileptic seizures are also possible. Frequent long-term consequences are disability and the need for rehabilitation. One of the arteries supplying the brain is blocked by a thrombus - a blood clot. The larger and more important the artery that is blocked, the more severe the stroke.
In order for the consequences of an ischemic stroke to be minimal, the patient must receive qualified help from doctors no later than 3 hours later. It’s even better if he ends up in a medical facility within an hour.
In this case, doctors will be able to use a special medicine that dissolves blood clots. It's called tissue plasminogen activator.
If more than 3 hours have passed, then it is not used, because the stroke has already caused irreversible damage, and the risk of administering this drug will outweigh the benefits.
In an ischemic stroke, blood does not flow for several hours or days through an artery that is blocked by a blood clot. While there is no blood movement, not only the brain tissue, but also the vessel walls suffer.
Eventually, the clot dissolves and blood flow through the artery is restored. But if this did not happen quickly enough, then the weakened walls of the artery may not withstand the pressure of blood and break through.
So ischemic stroke also causes hemorrhagic stroke.
Watch a video on how to care for a bedridden patient who has had a severe stroke.
If the patient survives the first few days after an ischemic stroke, then the immune system removes the dead brain tissue. In their place, cavities are formed filled with a transparent liquid.
They are clearly visible if you do a computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Unfortunately, the body does not restore damaged areas of the brain.
And scientists have not yet learned how to do this artificially.
Consequences of hemorrhagic stroke
The consequences of a hemorrhagic stroke, which can be fatal, are repeated hemorrhage, swelling of the brain, and heart rhythm disturbances.
First of all, doctors try to prevent recurrent bleeding in the brain. In 70% of cases they succeed, in the remaining 30% they do not. As a result of repeated hemorrhage, patients die or become severely disabled.
On the first day after a stroke, the risk of this is especially high, and then it decreases.
The brain normally produces a clear, protein-rich fluid that flows out of it along established pathways. In a hemorrhagic stroke, blood clots block the flow of this fluid. It accumulates, its pressure increases, causing the brain to be pressed against the skull from the inside.
Another way to develop cerebral edema is an inflammatory reaction. Blood clots that appear where they shouldn't attract fluid and white blood cells. The prognosis for hemorrhagic stroke is poor because doctors do not have effective treatments to reduce brain swelling.
The areas of the brain that are often affected by hemorrhagic stroke control the heart. Patients may experience cardiac arrest, rhythm disturbances, and damage to the heart muscle similar to myocardial infarction.
Another consequence is fainting and epileptic seizures, which occur in 25% of cases on the first day after a hemorrhagic stroke.
But if the patient survives, the epileptic seizures will most likely stop over time.
Source: https://ogomeopatii.ru/insult-bez-paralizacii-i-narushenija-rechi/
Types of ischemic stroke
Right-sided ischemic stroke
Right-sided ischemic stroke leads to impairment of motor functions on the left side of the body. Recovery is very slow. One of the most unfavorable consequences is paralysis of the left side.
In addition, there may be speech impairment, as well as loss of concentration and short-term memory.
Signs of a stroke on the right side may include:
- inhibition of reactions,
- body numbness,
- paralysis of the body and facial muscles on the left side.
Left-sided ischemic stroke
In left-sided ischemic stroke, speech functions are primarily affected, while motor functions are only slightly affected. Speech is restored with great difficulty.
When Broca's center is damaged, a person is able to speak only in single words and simple sentences. Other signs include disturbances in perception, difficulty moving and poor coordination.
The main complication of this type of stroke is deviations in the mental sphere, primarily from emotional manifestations. Memory loss and disorientation in space and time may also occur.
Cerebellar stroke
Cerebellar stroke leads to persistent impairment of motor coordination. In addition, at the initial stage of the lesion, the patient may experience attacks of nausea and vomiting, and frequent dizziness.
As the cerebellum begins to compress the brain stem, other symptoms (numbness of the facial muscles) are added, after which the person falls into a coma. The mortality rate for cerebellar stroke is extremely high.
Brainstem stroke
The most dangerous type of ischemic stroke is a brainstem stroke, since it is in the brainstem that the centers responsible for the most important systems of the body’s functioning are located – the respiratory and cardiac ones.
If they are defeated, the chances of recovery are almost zero. Symptoms of this type of stroke are the inability to navigate in space, loss of coordination, dizziness, and nausea.
Major stroke
A major stroke affects large areas of the brain, where there is an almost complete disruption of blood circulation, up to its absence. Brain swelling occurs. Complete paralysis sets in. There is practically no chance of recovery.
Left side stroke consequences
It is generally accepted that left-hemisphere disorders are more amenable to recovery than right-sided ones, but the patient’s relatives are concerned about the question they ask the doctor: left-sided stroke, consequences, how long do they live? Approximately 1/4 of patients do not reach the age of 65 years. Of those who have had a stroke, only 20% remain fully able to work. However, there are cases of recovery from a stroke, with minimal consequences for the person.
If the left hemisphere is affected, this is expressed in such consequences as:
- Paralysis, impaired sensitivity on the right side of the body, paresis;
- Visual impairment – right eye;
- Impaired memory, speech;
- Impaired perception - the patient does not understand what is being said to him;
- The consequence of a violation of the thought process, logic and intelligence;
- Consequences of mental disorders.
Symptoms of ischemic stroke
Typically, an ischemic stroke develops quickly, in just a few minutes. The deterioration of the condition may begin suddenly against the background of complete health. In old age, a gradual increase in the manifestations of stroke is possible over two days.
In order to recognize this life-threatening condition in time, you need to clearly know what symptoms indicate it.
There is a special test that helps identify early signs of cerebral infarction: you need to ask the person to smile or show his teeth, raise his hands and say a few phrases.
When a stroke begins, it is not possible to perform these actions: the patient’s face is asymmetrical or distorted, he is not able to raise two arms at once (one arm will be lowered), speech is unclear.
If there are one or more signs, then the person should be taken to the hospital as soon as possible and given medical assistance. The first 3 hours are considered the most important for the provision of medical care and a further favorable prognosis.
The variety of symptoms of ischemic stroke depends on the location of the site of damage in the brain. So, if there is a blockage of a vessel located in the front of the neck, then the patient will be bothered by numbness or immobility of an arm (or leg) on one side of the body, speech difficulties, blurred vision in one eye, up to blindness.
The best drugs for men over 50 for potency
If blood circulation is impaired in the vessel along the back of the neck, symptoms such as dizziness, nausea, weakness throughout the body, double vision and blurred vision, feeling hot and sweating may occur.
Forecasts
The prognosis for right-sided stroke cannot be considered favorable. It often returns with lethal consequences. Approximately 5% of patients who have suffered an ischemic stroke die within a month, hemorrhagic strokes die within two weeks. If the patient falls into a coma, there is very little chance of survival. According to statistics, 5 years after a stroke, about half of patients remain alive. However, 10% of stroke survivors still live ten or more years after it. The prognosis for left-sided stroke is somewhat more difficult. 90% of survivors remain disabled (of which about 60% are after a cerebral hemorrhage). Half of patients experience stroke recurrence.
In general, the prognosis depends on the person’s health status before the stroke, the quality and lifestyle of the person, and age. Factors such as adherence to the regimen, compliance with doctor’s orders, stress, and bad habits also play an important role. It is important to understand that a patient who has suffered a stroke is doomed to a different, limited lifestyle. This is a lifelong elimination of harmful foods, smoking, and alcohol. It is also mandatory to take medications that support the functioning of internal organs and systems: blood pressure levels, blood sugar, heart function, etc. Drug therapy will be prescribed by the attending physician and medical specialists, who must be regularly invited to your home or visited independently.
Symptoms of transient ischemic attacks (TIA)
Symptoms of ischemic stroke may be similar to those of transient ischemic attacks , however, the latter are milder and have a good chance of survival and restoration of lost brain functions.
Often transient ischemic attacks precede cerebral infarction, but can also be its consequence.
The clinical picture of TIA when performing an MRI or CT scan of the brain does not suggest the presence of a lesion, and the duration of neurological symptoms does not exceed 24 hours.
The following methods are used in the differential diagnosis of ischemic stroke and TIA:
- clinical and biochemical blood test;
- electrocardiogram (ECG);
- echocardiography (EchoCG) of the heart;
- Ultrasound examination of the vessels of the head and neck using Doppler.
Right-sided disturbance of blood flow in the brain
With a stroke, complications do not always appear. It all depends on the magnitude of the disorder and the type of lesion itself. With extensive right-sided lesions, problems with movement arise: persistent paresis, paralysis, disturbances of sensitivity and muscle tone. Hemorrhage into the right hemisphere causes left-sided hemiparesis. In this case, a persistent violation of muscle tone of the spastic type occurs. As a result, contractures are formed, sensitivity and eye movement are impaired (the head and eyes are turned to the left). During an attack of asphyxia, a tracheostomy is used.
Hemorrhagic intracerebral stroke, or subarachnoid hemorrhage, is characterized by a general cerebral clinical picture. Meningeal signs with episodes of loss of consciousness and cerebral coma are pronounced. Often there is severe pain in the head, attacks of dizziness, unsteadiness of gait, and falls.
Consequences of right-sided hemorrhagic stroke:
- left-sided hemiparesis;
- muscle spasms;
- sensory disturbance;
- significant dizziness in the head;
- vestibular disorders;
- blindness;
- marked decrease in visual acuity;
- ignoring the left half-space;
- left-sided diplopia;
- central pain syndrome;
- neuropsychiatric disorders;
- persistent sleep disturbances;
- problems with swallowing, sometimes the tongue sinks.
Recovery after a hemorrhagic stroke is somewhat difficult. Such patients are paralyzed, have bedsores, and septic ailments (pneumonia, damage to the genitourinary tract). Complex arthropathy, spastic contractures, and sometimes hydrocephalus are observed. Such conditions prolong the patient’s healing and provoke depression and chronic stress. This may cause relapses of the disease.
Features of stroke diagnosis
Modern diagnostic methods make it possible to quickly and clearly identify the signs of an incipient stroke and promptly begin a set of measures to relieve its symptoms, which in the future helps prevent serious complications and reduce mortality from this disease.
The main methods for diagnosing ischemic cerebral stroke include:
- examination of blood and its most important indicators (clinical and biochemical blood tests, study of lipid composition, detailed coagulogram);
- conducting an ECG and measuring blood pressure;
- MRI or CT scan of the vessels of the brain and neck (to accurately determine the location and size of the affected area and the condition of nearby vessels);
- examination of the patient by a neurologist, collecting anamnesis, identifying concomitant diseases that affect the development of cerebral infarction and the effectiveness of treatment.
In a hospital setting, differential diagnosis of ischemic stroke and other diseases with similar symptoms is carried out, primarily transient ischemic attacks, as well as epilepsy, brain tumors and other diseases.
Main symptoms
Some people may not realize at first that they are having a stroke. They may either be in an inadequate state or try to justify the symptoms by external factors. It is extremely important for the people around you to understand what exactly is happening. Because as soon as in this case it will be possible to help the person and start treatment in a timely manner.
The main symptom is headache, which occurs in the occipital area. It appears suddenly, and may have no obvious cause. At the same time, the painful sensations are very strong, they do not subside in a supine position. Often a stroke can occur in a dream, and in such a situation a person awakens abruptly . At the same time, if you change your position even slightly, the symptom will worsen significantly.
Moreover, during this disease a person will not only have a headache, but also experience other symptoms. It is also extremely important to pay attention to them, because they all talk about what exactly you have to deal with. The person begins to suffer from excessive drowsiness and may lose consciousness or fall into a coma.
Hearing is significantly impaired, and taste is also lost. In this case, this can happen either partially or completely. The sensitivity of the skin is also significantly reduced, which is why in some places a person does not feel touch or even pain.
Confusion and memory impairment are often observed during a stroke. A person may experience dizziness, problems with balance, and spatial orientation. There is significant muscle weakness in the arms and legs. Moreover, it is predominantly noted only in one direction.
In most cases, a person's speech is severely impaired. He cannot pronounce words correctly, connect them with each other, or is generally unable to speak. Sometimes a person doesn’t even understand what they are talking about . With a stroke, there is a sharp change in mood, which makes a person inadequate. He can be aggressive, whiny and overly nervous. In general, he behaves in a way that is uncharacteristic of his personality.
The patient often experiences facial asymmetry, with drooping of the corner of the mouth on one side. The ability to express emotions is significantly impaired, because facial expressions seem unnatural. If others notice the symptoms described above, then you should definitely call an ambulance. The sooner a person gets help, the better. If it’s too late to see a doctor, then complications after a stroke will not keep you waiting.
Consequences of ischemic stroke
Cerebral infarction causes a variety of adverse effects and complications, which depend on the location and size of the affected area and vary in severity, duration and ability to recover. The larger the lesion, the less chance of complete restoration of lost functions.
The most common consequences of ischemic cerebral stroke can be divided into several groups:
- speech disorders - observed quite often, especially in patients who have suffered a left-sided stroke; may manifest itself in the inability to pronounce words and general unintelligibility of speech, difficulty naming objects, problems with reading and writing;
- motor impairments - can be either partial or complete, up to paralysis; localized in a specific area (or even half) of the body; manifest themselves in impaired mobility, weakness; this type of complication complicates a person’s self-care skills and makes him dependent on the help of other people;
- impaired sensitivity in certain parts of the body - sometimes can remain for a long time, even when motor functions are restored (this is due to the fact that the nerve fibers responsible for conducting nerve impulses are restored very slowly);
- disorders in the cognitive and emotional-volitional spheres - weakening of intellectual abilities, problems with memory and attention, frequent mood swings, decreased communication skills;
- mental disorders - decreased emotional background, sleep problems, decreased appetite, depressive states, even thoughts of suicide.
In addition to the listed complications, patients may experience symptoms such as impaired coordination and unsteady gait, difficulty swallowing food, especially hard food, epileptic seizures, blurred vision, the risk of developing pneumonia, thrombosis of the extremities and other consequences that negatively affect the quality of life.
Separately, it is worth noting the risk of recurrent stroke. Unfortunately, about a third of patients who have suffered a stroke are subject to a second attack, which inevitably entails a serious threat to life and health.
Drowsiness after a stroke: an accident or a pattern
Stroke is an acute cerebrovascular accident (CVA), which is characterized by the appearance of focal neurological signs, and in the absence of adequate treatment leads to death.
There are ischemic stroke (as a result of blocking the lumen of the vessel), hemorrhagic stroke (bleeding in the brain) or subarachnoid bleeding. The consequences of this pathology are varied, multifaceted, and require serious comprehensive treatment and long-term rehabilitation.
For a speedy recovery, the body itself uses its internal reserves, which is why after a stroke they sleep a lot.
Two main types of stroke: ischemic and hemorrhagic
Causes of increased sleepiness after a stroke
Before turning to the factors that cause severe sleepiness after a cerebrovascular accident, it is important to note that patients can equally suffer from any sleep disorder.
According to the observations of neurologists, insomnia occurs after stroke in 35-45% of cases.
More often there is severe weakness, daytime drowsiness, and sound sleep at night. The causes of pathological hypersomnia can be various conditions.
- Impaired brain function after a stroke, associated with damage to certain areas of nervous tissue. Prolonged artery spasm deprives nerve cells of nutrition and oxygen. Hypoxia leads to the death of some neurons, swelling of the intercellular space, disruption of blood flow and impulse transmission. A lot of effort is spent on restoring existing neurological and cerebral symptoms, so the only way to replenish energy is healthy sleep. This process is a kind of compensatory reaction of the body to damage.
- Increased sleepiness during the day is the result of sleepless nights. The resulting disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system (paresis, paralysis of the limbs, pain, dizziness, swallowing disorders, incontinence of physiological functions) interfere with a good rest at night. In the morning, patients feel overwhelmed, exhausted, and tired. The only way to regain strength is to fall asleep during the day.
People who have had a stroke often wake up at night, so they sleep a lot during the day
- Depression. As psychotherapists note, after suffering a stroke, patients often complain of tearfulness, increased irritability, mood swings, and depression. Restricted mobility and a sharp deterioration in the quality of life directly affect the human psyche. First of all, sleep is disturbed: sleepless nights alternate with periods of severe drowsiness, fatigue, and apathy. Prescribed antidepressants can significantly improve the patient’s condition and regulate circadian rhythms.
- Elderly patients suffer from increased sleepiness much more than younger people. This is due to a whole bunch of existing chronic diseases, deviations in health, and a decrease in the ability to quickly and fully restore body functions. This is why people over 65 tend to sleep often and for a long time after a stroke.
Methods to combat sleep disorders
To cope with the changes that have arisen after a cerebrovascular accident, it is necessary to strictly follow all the recommendations of the attending neurologist, as well as a psychotherapist. The main goals of rehabilitation of post-stroke patients:
- elimination of the consequences of focal neurological disorders (disorders of movement, sensitivity, vision, etc.);
- restoration of important functions (breathing, heartbeat, blood circulation, excretion);
- rehabilitation of everyday, social, and labor skills.
Sleep disturbance depends on the location of the brain damage, its extent, depth, duration, severity, as well as the body’s response to circulatory disorders. The more severe the stroke, the deeper the sleep disturbances will be, the more difficult it is to eliminate them.
In addition to drug therapy in the form of vascular drugs, anticoagulants, sedatives, it is necessary to adjust the lifestyle, daily routine, and establish proper nutrition. Physiotherapeutic treatment, physical therapy, and massage also give good results.
Class on restoring movements in the hand after a stroke
All these measures help restore damaged functions, and with them eliminate drowsiness, increased fatigue, and fatigue. In addition, psychotherapeutic medications may be prescribed.
To improve the quality of night sleep and eliminate daytime sleepiness, you need to follow several general recommendations.
- Make a correct daily schedule: getting up, going to bed at the same time, extending daytime wakefulness for a better night's rest, short afternoon nap.
- Provide the patient with a comfortable location: a comfortable bed with orthopedic devices, room ventilation, optimal humidity and temperature in the room.
- Healthy eating: reducing carbohydrates, fatty or very hot foods.
Rehabilitation of post-stroke patients is a complex task, requiring a lot of effort, money, and time, which is why it is so important for the patient and his loved ones to be patient.
If a person sleeps a lot and often after a stroke, this is not so bad, but when pathological drowsiness or other sleep disorders occur, it is better to consult a doctor rather than try to fix the problem yourself.
Have you ever experienced insomnia?! Of course, you know firsthand what it is: frequent sleepless nights, fatigue, decreased ability to work, decreased mood, daytime sleepiness, a feeling of constant lack of sleep...
- Now answer the question: are you satisfied with this?
- Can this be tolerated?
- Are you ready to continue living like this?
- How much money have you already spent on ineffective treatment?
That's right - it's time to end this! Do you agree? That is why we decided to publish an exclusive interview with Elena Malysheva, in which she revealed the secret of getting rid of insomnia.
Read the interview further >>
Source: https://SonoLogia.ru/interesnoe/pochemu-posle-insulta-mnogo-spyat.html
Prognosis for life with ischemic stroke
When making a prognosis after a stroke, the main factors that medical workers rely on are:
- Size and localization of brain tissue lesions. Recovery after a cerebral infarction can proceed much faster if the affected area is relatively small and the lesion does not affect vital brain centers.
- A type of stroke. High mortality rates accompany atherothrombotic and cardioembolic forms of cerebral infarction, and the lowest – lacunar.
- Patient's age. The older the patient, the more unfavorable the prognosis for him.
- Accompanying illnesses. If the patient has diseases that caused the development of a stroke (for example, atherosclerosis and arterial hypertension), then the risk of recurrent blood clot rupture and blockage of the vessel is very high. Accordingly, the prognosis for such patients is not very favorable.
- Time factor. The outcome of an ischemic stroke will also largely depend on the speed of medical care provided and the duration of rehabilitation.
Osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine: symptoms and treatment
The main percentage of deaths occurs in the first two days from the onset of the disease; in the next 30 days, about a quarter of patients die (mainly from developed complications). Surviving patients acquire various forms of disability, which, however, may disappear with timely rehabilitation.
The survival rate of patients after a cerebral infarction gradually decreases with each passing year: if at the end of the first year of the disease about 70% of patients survive, then after 10 years - no more than 25%.
Consequences of a stroke: how to return to normal life, prevention
Additional education:
"Emergency Cardiology"
1990 – Ryazan Medical Institute named after Academician I.P. Pavlova
Contacts
The consequences of a stroke are presented in the form of respiratory and cardiac arrest, painful cough and other conditions. In this case, problems arise with the functioning of various internal organs. Hiccups during a stroke are a common symptom of the disease. This disease is dangerous due to its consequences and complications.
Medical indications
What is a stroke? This is a severe disruption of blood flow in the brain. The main consequences of the disease include:
- stunning or complete loss of consciousness;
- involuntary bowel movement;
- respiratory arrest;
- urinary incontinence after stroke;
- violation of the frequency, rhythm and depth of breathing;
- tachycardia, hypotension;
- heart failure;
- painful cough after a stroke.
It has been proven that the frequency of episodes of the disease increases with age. Persons with a sedentary, sedentary lifestyle are prone to strokes. They rapidly develop global or focal disorders of the brain.
The pathology is accompanied by vivid symptoms:
- pronounced facial asymmetry;
- slurred speech or its complete absence;
- misunderstanding of spoken speech;
- severe visual impairment;
- an epileptic attack may develop;
- paresis or paralysis of the limbs (often unilateral);
- increased tone of striated muscles.
Doctors distinguish 2 subtypes of the disease: hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes. Ischemia is caused by blockage of a cerebral artery by a thrombus. Persons with atherosclerosis and hypertension are more susceptible to developing the disease. The attack leaves a significant impact on the patient: the physical and emotional state changes radically, and behavioral characteristics appear.
Another reason for the development of the disease is a violation of blood flow to certain areas due to a ruptured blood vessel. This occurs due to sudden fluctuations in pressure. For the body, even a moderate stroke is severe stress, a crushing blow to the nervous system.
A person loses control over his body. This provokes strong anger, irritation, tearfulness, and aggression. Therefore, the care of loved ones often causes strong indignation. Their help is met with hostility. Increased excitability impairs the body's recovery process.
Pathogenesis of the disease
For the brain to function properly, a constant supply of oxygen is required. For comparison: the mass of the organ is 2% of the total weight of the body.
For the functioning of the organ, more than 20% of oxygen and 17% of glucose from the total intake are required. The brain is not designed to reserve oxygen.
Therefore, even minor ischemia lasting more than 5 minutes provokes irreversible damage to neurons. Restoring such structures is impossible.
In the acute period of the disease, large areas of damage appear. In this case, extensive swelling occurs, which aggravates the course of the disease, prolonging the recovery process. After a few weeks, the process subsides. The damage area is reduced. After a stroke, there is significant loss and impairment of many body functions.
This is due to damage to brain cells - neurons. They lose conductivity, the ability to function properly. The person stops coordinating his movements, thoughts, and begins to speak poorly.
Serious disruptions make it difficult for the body to recover after an attack. The death of neurons is triggered by a lack of blood and oxygen.
Scientists have proven that the basis of ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke is damage to blood vessels and disruption of blood flow in them.
Apoplexy significantly impairs a person's cognitive functions. Initially, memory is affected, resulting in complete or partial loss. The patient cannot remember his name and loved ones. Memory is similar to fragments of a vessel; the patient is unable to assemble them into a single picture.
Stroke causes significant functional impairment and structural changes in the brain. Therefore, the disease is accompanied by a decrease or complete absence of vision.
A sharp, sudden deterioration in vision is a harbinger of apoplexy. This symptom occurs if blood flow is interrupted for at least a minute.
Therefore, vision problems and pain in the head are the earliest manifestations of an attack.
Disease clinic
Moderate pathology with concomitant embolism or thrombosis causes complete loss of vision. Recurrent mild ischemia causes short-term problems. Therefore, restoration of vision depends on the severity and extent of the lesion.
The most common consequences of a stroke include paralysis and paresis. They can occur in any part of the body. It all depends on the location of the damage zone.
If the left lobe is affected, paralysis of the entire right side of the body or part of it is noted. Someone becomes deaf, goes blind, stops moving and speaking. Some patients retain communicative functions, but do not move.
The rest have all the negative consequences of the disease at the same time.
According to statistics, more than half of people with a stroke do not survive it. Patients who undergo it remain disabled. A fatal condition is hemorrhage in the right hemisphere. Damage to the left lobe is considered more favorable and has an easy, quick recovery.
Right-sided disturbance of blood flow in the brain
With a stroke, complications do not always appear. It all depends on the magnitude of the disorder and the type of lesion itself. With extensive right-sided lesions, problems with movement arise: persistent paresis, paralysis, disturbances of sensitivity and muscle tone.
Hemorrhage into the right hemisphere causes left-sided hemiparesis. In this case, a persistent violation of muscle tone of the spastic type occurs. As a result, contractures are formed, sensitivity and eye movement are impaired (the head and eyes are turned to the left).
During an attack of asphyxia, a tracheostomy is used.
Hemorrhagic intracerebral stroke, or subarachnoid hemorrhage, is characterized by a general cerebral clinical picture. Meningeal signs with episodes of loss of consciousness and cerebral coma are pronounced. Often there is severe pain in the head, attacks of dizziness, unsteadiness of gait, and falls.
Consequences of right-sided hemorrhagic stroke:
- left-sided hemiparesis;
- muscle spasms;
- sensory disturbance;
- significant dizziness in the head;
- vestibular disorders;
- blindness;
- marked decrease in visual acuity;
- ignoring the left half-space;
- left-sided diplopia;
- central pain syndrome;
- neuropsychiatric disorders;
- persistent sleep disturbances;
- problems with swallowing, sometimes the tongue sinks.
Recovery after a hemorrhagic stroke is somewhat difficult. Such patients are paralyzed, have bedsores, and septic ailments (pneumonia, damage to the genitourinary tract).
Complex arthropathy, spastic contractures, and sometimes hydrocephalus are observed. Such conditions prolong the patient’s healing and provoke depression and chronic stress.
This may cause relapses of the disease.
What does ischemia lead to?
Ischemic stroke develops more slowly, with a slight increase and subsequent regression of symptoms. With this type of stroke without paralysis, rapid healing and return to a full life are possible.
More severe cases of the disease leave behind formidable complications:
- paresis, paralysis of the left half of the body (the tongue may sink);
- urinary disorders after stroke;
- disturbance of perception and sensation;
- loss of memory for current events;
- ignoring the left half of the space;
- cognitive disorders;
- violations of the emotional-volitional plan.
After an ischemic stroke of the right hemisphere, pathological syndromes occur with the appearance of depressive states and behavioral disorders. Patients become untied, disinhibited, and do not feel tact and moderation.
They are characterized by a certain foolishness, a penchant for flat jokes. The presence of such disorders of the emotional-volitional sphere significantly lengthens and complicates healing.
Patients do not perceive reality objectively, therefore they require consultation with a psychiatrist.
Perinatal conditions
Cerebrovascular pathology, including hemorrhage, affects children of perinatal age. In older children and adolescents, the disease is diagnosed less frequently. Cerebral strokes develop with vascular malformations and cerebral aneurysms. Vasculitis, various angiopathy, severe damage to the heart and blood vessels (defects, arrhythmias, blockades, endocarditis) can provoke hemorrhage.
It has been proven that perinatal hemorrhage occurs due to traumatic injury to the skull. It develops against the background of the following phenomena:
- discrepancy between the size of the fetus and the birth canal;
- rapid labor activity;
- severe cervical rigidity;
- use of a vacuum extractor.
Prematurity is considered an important predisposing factor in the development of the disease. An unformed skull is too flexible and soft, and therefore increases the risk of stroke. What are the consequences of perinatal right hemisphere strokes?
The clinic of intraventricular strokes has several variants of the course.
Complications and consequences of cerebral stroke depend on the massiveness of the hemorrhage, the degree of hydrocephalus, the severity of focal disorders and the severity of concomitant pathology.
Often after perinatal strokes, cerebral palsy of varying severity, visual impairment (strabismus, amblyopia) and cognitive function occur.
Complications after a stroke of ischemic origin are caused by the “hypoxia-ischemia” syndrome. Movement disorders, some brain dysfunction, and mental retardation develop. Increasingly, after ischemia, a single epileptic seizure is observed in children.
Consequences of senile illness
Old age complicates the course and consequences of stroke, aggravated by severe cerebrovascular pathology and progression of encephalopathy. Therefore, after a stroke, the brain is not able to function fully: memory is impaired and intelligence declines.
The ischemic form of the disease leads to cognitive impairment. Epilepsy often develops after a stroke. Primary signs of an attack are observed within a week after the stroke. The difference in neurological manifestation is the absence of a visible catalyst factor. Epilepsy occurs unexpectedly.
During the rehabilitation period, epilepsy occurs due to cortical atrophy or a cyst, which has an irritating effect on the damaged tissues and the patient’s health. Late epilepsy after an attack can occur several months later (against the background of the appearance of a tissue scar).
This significantly complicates the rehabilitation of elderly patients. Major stroke and its consequences in old age are associated with neurological deficits and movement disorders. In this case, organs may fail.
Occasionally, a form of “thalamic” syndrome develops and visual impairment develops. The condition is dangerous, as there is a risk of urinary failure, cerebral edema with the development of dislocation-trunk syndrome or hydrocephalus. Dropsy occurs.
A stroke has characteristic signs by which the zone and extent of damage can be determined: lacunar, brainstem or spinal process. Problems with motor skills and spatial coordination indicate damage to the cerebellum. But often the spinal variant of the disease has a similar clinical picture.
Usually the side opposite the cerebral zone of the disorder is affected: the limbs and facial muscles fail, and dysarthria appears. In a spinal stroke, parts of the spinal cord are damaged. In this case, the patient is completely paralyzed. Peripheral neuropathy often occurs: there is no temperature sensitivity, taste is distorted.
Paresthesia often appears - an attack of tingling or numbness of the limbs. Problems with urodynamics are a clear manifestation of the consequences of lacunar infarction. The patient does not regulate renal and intestinal rhythm: does not control urination and defecation.
Aphasia is the loss of the ability to speak and adequately perceive speech. The intensity of the symptom directly depends on the severity of the condition. Deaths are the saddest consequences of cerebral hemorrhage. They occur in severe forms or in the absence of timely medical care.
Doctors' recommendations
Stroke is a disease that requires complex treatment. But this is only the first stage of therapy. At the second stage, it is important to carry out correct and adequate rehabilitation. This is a rather complex program involving various specialists. The participation of the patient himself in the process is mandatory.
It is important to convince the patient of the effectiveness of therapy and a speedy recovery from the disease. Physiotherapy methods improve the flow of medications into the brain, and manual therapy restores muscle sensitivity and performance.
Official therapy advises, against the background of drug treatment, to resort to the services of a competent psychologist. Many patients, hoping to heal quickly and easily, turn to unconventional treatment methods. Stroke is a serious disease that cannot be treated on your own. Otherwise, you can complicate its course (kidney failure) or provoke death.
Source: https://CardioPlanet.ru/zabolevaniya/insult/posledstviya-insulta
Rehabilitation after ischemic stroke
Rehabilitation measures after a stroke are designed for a long period.
The basic principle is a gradual complication and increase in the load on the patient’s body, using gentle treatment regimens :
- strict bed rest - at the very beginning of the development of the pathological condition, sudden movements and movements are contraindicated for the patient, but in caring for him, medical personnel use means aimed at preventing bedsores, wiping, turning over, elements of breathing exercises;
- moderately extended bed rest - the patient is allowed minimal physical activity (turning over independently, taking a sitting position, eating independently);
- ward mode - independent or with the help of medical personnel movement within the ward, use of special rehabilitation equipment (walkers), gradual transition to self-care;
- free mode.
The rehabilitation that people go through after a stroke consists of several stages and begins in the department where the patient was hospitalized (usually the neurology department).
At the end of the acute period, transfer to the rehabilitation department of a hospital or specialized sanatorium. Next, outpatient observation is connected to the clinic at the place of residence.
Rehabilitation measures after a cerebral infarction include:
- therapeutic exercises (physical therapy) and massage;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- taking medications prescribed by a doctor;
- dietary nutrition;
- compliance with the daily routine.
Many rehabilitation activities can be carried out at home.
What to do to get rid of weakness
For drug therapy of asthenic syndrome, patients who have suffered a stroke are prescribed vitamin complexes (Neurorubin, Neurobex), drugs to improve metabolic processes in brain neurons (Phenotropil, Glycine, Bilobil) and psychostimulants (Enerion, Cognifen, Entrop).
It is also important to ensure a normal amount of sleep at night. For this:
- the room in which the patient is located should be well ventilated and darkened;
- the patient’s position in bed – on the healthy side or on the back;
- the doctor may prescribe melatonin in order to restore normal biorhythm;
- take natural sleeping pills (valerian, motherwort, peony), prescription medications (Donormil, Sonovan);
- before going to bed you can drink warm milk with honey;
- relaxing breathing exercises are used, in which the exhalation should be longer than the inhalation (the optimal ratio is 1:2), you need to breathe only through the nose, without the participation of the pectoral muscles (stomach).
During the day, you need to make an effort to activate the patient:
- therapeutic exercises, massage;
- classes to restore speech and memory;
- washing with cool water, hygiene procedures;
- listening to music or audio books;
- frequent meals in fractional portions, food should not be hot;
- awakening breathing - smooth inhalation and sharp exhalation.
Watch the video about breathing exercises:
Treatment of ischemic stroke
In the treatment of stroke, the most important for the possibility of restoring lost brain abilities are the first 3 hours from the onset of symptoms.
In a hospital setting, after diagnosing the patient’s condition, it is possible to carry out thrombolytic therapy , the essence of which is the intravenous administration of special drugs that can dissolve blood clots.
However, after 4.5 hours from the onset of the pathological condition, this method of treatment loses its effectiveness and is not prescribed.
Even before hospitalization, emergency physicians provide the patient with so-called basic therapy aimed at stabilizing the patient’s condition (normalizing the cardiovascular and respiratory systems).
Basic therapy includes:
- maintaining water and electrolyte balance,
- normalization of tissue metabolism,
- control of body temperature and blood pressure,
- monitoring heart contractions.
In the presence of concomitant diseases of the cardiovascular system, the following may be prescribed:
- angioprotectors,
- anticoagulants,
- cardiac glycosides,
- antioxidants,
- and other means.
Specific treatment for a stroke consists of restoring impaired blood circulation in the affected area ( thrombolytic therapy ) and preventing new thrombus formation ( anticoagulant therapy ).
The therapeutic effect is achieved by taking medications and surgical treatment methods (according to health indications).
Treatment
After making a diagnosis and determining the type of mental disorder, the doctor must first prescribe medications that improve cerebral circulation. These include Vinpocetine, Sermion, Phenilin.
If there is a risk of developing blood clots, it is necessary to use anticoagulants, for example, aspirin with constant monitoring of the INR. Nootropics such as Piracetam, Aminalon, and Pantogam are recommended for treatment.
In the case of explosive psychopathy, therapy with sleeping pills, anti-anxiety drugs, and sedative medications is necessary: Valocordin, bromides, tablets based on motherwort, St. John's wort and valerian.
For asthenia and apathy, adaptogens have a good effect: ginseng, eleutherococcus, radiola rosea, lemongrass. In some countries, loading doses of B vitamins are used.
Treatment for dementia includes not only the use of medications, but also psychotherapy. You need to talk to the patient, listen to his personal experiences, reassure, encourage, explain what’s what. Psychotherapeutic methods are used, including autogenic training, hypnosis, and psychoanalysis.
Nutrition for patients after a stroke
A special diet after a stroke requires: limiting the consumption of salt and sugar, avoiding spicy, fatty and fried foods, various smoked foods, pickles and marinades. The main goal is to promote the recovery of the body and prevent new attacks of the disease.
Meals should be frequent ( at least 5-6 times a day ), but in small portions. It is recommended to include fresh vegetables and fruits rich in fiber, cereals, dairy products and lean meats and fish in your diet.
First courses are best made vegetarian and not too thick . Foods with a high potassium content (dried apricots, bananas, citrus fruits) and those that can remove free radicals from the body (blueberries, cranberries) can be of great benefit.
for patients after a stroke to drink a lot of fluids to avoid the formation of edema. As a rule, doctors recommend drinking no more than one liter of fluid per day.
First aid
It is the provision of first aid that allows you to avoid dangerous complications of a stroke. For this reason, it is extremely important to help the person so that his well-being can be brought back to normal. If the patient is conscious, then it will be necessary to ensure that his head is slightly higher than his body. This will reduce pressure on the brain. If possible, you should not move the person until the doctors arrive, so as not to worsen the situation.
You should not give the patient any food or food, especially if he does not want it himself. The fact is that the swallowing function could be impaired, causing food or water to enter the respiratory tract. This can lead to death, so you should not take such measures. Stroke and its consequences should only be treated by medical professionals.
The person should not be given any medications until the ambulance arrives. They can only harm a person more, so you should definitely refrain from using medications. The only way to provide direct access to fresh air is to remove excess clothing that interferes with normal breathing. You should also open a window if the patient is indoors.
If there are secretions or objects in the oral cavity, they must be removed. We are talking about chewing gum, food, mucus, blood and other things. If this is not done, then the person may suffocate.
When a person is unconscious, but is choking, he will definitely need to be turned on his side. It is important that your head rests on your hand and is slightly tilted forward. The leg should be bent at the knee so that the person cannot roll over. If vomit appears, then, being on the side, the person will not choke on it.
In a situation where a person is unconscious and there is no breathing, he should be turned onto his back. After this, you need to breathe and massage the heart if there is no pulse. Manipulations must be carried out until the person begins to breathe .
Or you need to perform actions before the ambulance arrives. At the same time, it is important to perform these actions only in a situation if a person knows how to do them.